(Press-News.org) Smoothies can be a tasty and convenient way to get the important fruits and vegetables you need for a healthy diet. But is a banana and blueberry smoothie the best combo? Researchers at the University of California, Davis, suggest that blending certain ingredients in smoothies can influence whether your body is getting a nutritional boost.
The study, published today in the Royal Society of Chemistry’s journal Food and Function, used smoothies to test how various levels of polyphenol oxidase, an enzyme in many fruits and vegetables, affects the levels of flavanols in food to be absorbed by the body. Flavanols are a group of bioactive compounds that are good for your heart and cognitive health and are naturally found in apples, pears, blueberries, blackberries, grapes and cocoa — common smoothie ingredients.
“We sought to understand, on a very practical level, how a common food and food preparation like a banana-based smoothie could affect the availability of flavanols to be absorbed after intake,” said lead author Javier Ottaviani, director of the Core Laboratory of Mars Edge, which is part of Mars, Inc., and an adjunct researcher with the UC Davis Department of Nutrition.
Slice an apple or peel a banana and the fruit will quickly turn brown. That happens because of polyphenol oxidase, or PPO, an enzyme naturally present in those foods. The browning occurs when the food containing that enzyme is exposed to air, cut or bruised. The researchers wanted to know whether consuming freshly prepared smoothies made with different PPO-containing fruits impacted the amount of flavanols available to the body.
Bananas versus berries
The researchers had participants drink a smoothie made with banana, which has naturally high PPO activity, and a smoothie made with mixed berries, which have naturally low PPO activity. Participants also took a flavanol capsule as a control. Blood and urine samples were analyzed to measure how much flavanols were present in the body after ingesting the smoothie samples and capsule. The researchers found that those who drank the banana smoothie had 84% lower levels of flavanols in their body compared to the control.
“We were really surprised to see how quickly adding a single banana decreased the level of flavanols in the smoothie and the levels of flavanol absorbed in the body,” Ottaviani said. “This highlights how food preparation and combinations can affect the absorption of dietary compounds in foods.”
Last year, the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics issued a dietary recommendation, advising people to consume 400 to 600 milligrams of flavanols daily for cardiometabolic health. Ottaviani said for people who are trying to consume those flavanols, they should consider preparing smoothies by combining flavanol-rich fruits like berries with other ingredients that also have a low PPO activity like pineapple, oranges, mango or yogurt.
He also said bananas remain a great fruit to be eaten or consumed in smoothies. For those who want to consume smoothies with bananas, or other high PPO activity fruits and vegetables such as beet greens, the suggestion is to not combine them with flavanol-rich fruits such as berries, grapes and cocoa.
The findings of this study could spur future research into how other foods are prepared and the effects on flavanols, for example, Ottaviani said tea is a major dietary source of flavanols and depending on how it is prepared, a different amount of flavanols would be available for absorption.
“This is certainly an area that deserves more attention in the field of polyphenols and bioactive compounds in general,” said Ottaviani.
Jodi Ensunsa, Reedmond Fong, Jennifer Kimball and Alan Crozier, all affiliated with the UC Davis Department of Nutrition and researchers affiliated with the UC Davis Department of Internal Medicine, University of Reading, King Saud University and Mars, Inc. contributed to the research.
The study was funded by a research grant from Mars, Inc., which collaborates with researchers to study potential benefits of cocoa flavanols for human health.
END
The right combo: Getting the most health benefits from fruit smoothies
Researchers find adding a banana decreased the level of flavanols in smoothies
2023-08-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
$12 million grant funds foundational research on early liver transplantation
2023-08-24
Alcohol-associated liver disease accounts for 50% of liver-related deaths, and its rates are rising worldwide. But one of the best treatment options, early liver transplantation (ELT)—transplants done with no mandatory period of abstinence from alcohol—is also one of the most controversial, partly because of concerns that patients will relapse to alcohol after transplantation.
Part of the problem is that livers for transplants are in short supply, and researchers lack data to determine who will benefit most from ELT. Studies show that decisions about who gets a transplant can, at times, be influenced by bias or unsystematic. ...
Study shows technology boosts public health programs
2023-08-24
An examination of the SCALE-UP Counts program was recently published in the journal Pediatrics. This analysis, led by Yelena Wu, PhD, investigator at Huntsman Cancer Institute and associate professor in the department of dermatology at the University of Utah (the U), and David Wetter, PhD, MS, investigator at Huntsman Cancer Institute and professor in the department of population health sciences at the U, received support from RADx-Underserved Populations (RADx-UP) and funding from the National Institute of Health (NIH).
The SCALE-UP Counts program was designed to promote COVID-19 testing through collaboration ...
A global observatory to monitor Earth's biodiversity
2023-08-24
At a time of nature crisis driven by unparalleled rates of biodiversity loss, a new interconnected system to monitor biodiversity around the world is urgently needed to direct and focus conservation action.
"The lethal combination of habitat loss, the exploitation of natural populations, pollution, and climate change is causing species extinction rates not seen since the last mass extinction 65 million years ago," said Prof. Andrew Gonzalez, Liber Ero Chair in Conservation Biology at McGill University, and co-Chair of GEO BON. "We lack the means to monitor these impacts ...
High drug price associated with decreased treatment retention for patients with chronic liver disease
2023-08-24
MINNEAPOLIS/ST. PAUL (08/24/2023) — Researchers from the University of Minnesota Medical School and College of Pharmacy have found that high costs for hepatic encephalopathy treatment in patients with end-stage liver disease were associated with decreased treatment retention for patients. The study results were recently published in Hepatology Communications.
Hepatic encephalopathy is the loss of brain function that occurs in people with severe liver disease. The condition is associated with high morbidity and mortality. ...
Optimizing tobacco cessation treatment with lung cancer screening
2023-08-24
MINNEAPOLIS/ST. PAUL (08/24/2023) —Lung cancer is the deadliest cancer in the United States, and 80% of lung cancer deaths are linked to one risk factor: smoking. While lung cancer screenings are a critical part of prevention and treatment for the disease and 15 million Americans qualify for yearly screenings, over half those eligible for screenings are still actively smoking. Without standard smoking cessation measures in place, the benefits of the screenings have not been fully realized.
New ...
New quantum device generates single photons and encodes information
2023-08-24
A new approach to quantum light emitters generates a stream of circularly polarized single photons, or particles of light, that may be useful for a range of quantum information and communication applications. A Los Alamos National Laboratory team stacked two different, atomically thin materials to realize this chiral quantum light source.
“Our research shows that it is possible for a monolayer semiconductor to emit circularly polarized light without the help of an external magnetic field,” ...
Making materials more durable through science
2023-08-24
ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. — A team at Sandia National Laboratories developed a molecule that helps change the way some materials react to temperature fluctuations, which makes them more durable. It’s an application that could be used in everything from plastic phone cases to missiles.
Polymers, which include various forms of plastics, are made up of many smaller molecules, bonded together. This bond makes them especially strong and an ideal product to be used to protect delicate components in a wide variety of items. But with time, use and exposure to different environments, all materials begin to deteriorate.
Hot ...
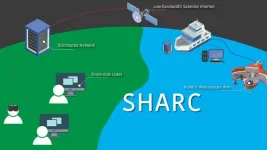
New framework for oceanographic research provides potential for broader access to deep sea scientific exploration
2023-08-24
Woods Hole, Mass. (August 23, 2023) -- Scientific exploration of the deep ocean has largely remained inaccessible to most people because of barriers to access due to infrastructure, training, and physical ability requirements for at-sea oceanographic research.
Now, a new and innovative framework for oceanographic research provides a way for shore-based scientists, citizen scientists, and the general public to seamlessly observe and control robotic sampling processes.
The Shared Autonomy for Remote Collaboration (SHARC) framework “enables remote participants to conduct shipboard operations and control ...
How pre-eclampsia accelerates aging in women
2023-08-24
ROCHESTER, Minnesota — Pre-eclampsia, a life-threatening surge in blood pressure, is an enigmatic condition. Each year, it causes the deaths of more than 70,000 women worldwide. Because scientists do not know what causes it, they lack targeted strategies to treat it.
Delivery, the only available therapy, is not the cure it is often made out to be, according to Vesna D. Garovic, M.D., Ph.D., a nephrologist at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota, who has devoted her career to studying this common pregnancy complication.
"Even after delivery, women ...
Sweet corn yield at the mercy of the environment, except for one key factor
2023-08-24
URBANA, Ill. — A new analysis from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign and the USDA-Agricultural Research Service (ARS) has identified the top factors accounting for yield variability in processing sweet corn (used for canned and frozen products), including one within the control of processors.
“We used a very robust approach to account for sweet corn yield with field-level data across some 16,000 fields and 27 years. Year and production region were the two most important variables, which makes ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
[Press-News.org] The right combo: Getting the most health benefits from fruit smoothiesResearchers find adding a banana decreased the level of flavanols in smoothies