(Press-News.org) ARLINGTON, Va. (August 25, 2023) — Avoiding the unnecessary use of indwelling catheters and promptly removing catheters that are no longer needed are the first steps in preventing catheter-associated urinary tract infections in acute care hospitals, according to new recommendations developed by five medical societies and published today in the journal Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology.
“Urinary catheters can be associated with infection and also with non-infectious harms like trauma and obstruction,” said Payal Patel, M.D., an infectious disease physician at Intermountain Health and lead author of Strategies to Prevent Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infections in Acute Care Hospitals: 2022 Update. “Prevention of infection related to use of typical indwelling urinary catheters is multidisciplinary. Many members of the healthcare team, including doctors and nurses, have a role.”
Urinary tract infections are one of the most common healthcare-associated infections, and up to three-quarters of urinary tract infections are caused by an indwelling urinary catheter. Catheter-related infections have been associated with higher hospital mortality and increased length of stay at a cost of nearly $2,000 per hospitalized patient.
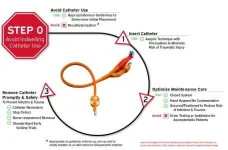
The updated recommendations include a model, “Disrupting the Lifecycle of the Urinary Catheter,” which identifies alternatives to indwelling catheters, shows how to follow guidance for safely inserting and maintaining catheters, and prompts healthcare personnel to initiate timely removal. Non-catheter strategies include prompt toileting, urinals, bedside commodes, incontinence garments, and/or the use of non-indwelling catheter strategies such as intermittent straight catheterization or external urinary catheters.
Since duration of catheterization is the most important risk factor for developing infection, the authors recommend at least daily review of continued catheterization, which can include automated reminders of the presence of a catheter or review during rounds of all patients with urinary catheters. Other essential practices include ensuring supplies are readily available for non-catheter and catheter management of patients’ urinary issues, and ensuring when catheters are used, they are positioned to beds and wheelchairs in ways that avoid kinking of tubing, which increases the risk of infection. Educating healthcare professionals about urine culture stewardship while providing indications for urine cultures is another new essential practice.
The document updates Strategies to Prevent Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infections in Acute Care Hospitals published in 2014. The Compendium, first published in 2008, is sponsored by the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology (SHEA) and is the product of a collaborative effort led by SHEA, with the Infectious Diseases Society of America, the Association for Professionals in Infection Control and Epidemiology, the American Hospital Association, and The Joint Commission, with major contributions from representatives of several organizations and societies with content expertise. It is a multiyear, highly collaborative guidance-writing effort by over 100 experts from around the world.
The urinary catheter paper is the final installment in the latest Compendium update, which began with publication of strategies to prevent ventilator and non-ventilator associated pneumonia in May of 2022. The societies also recently published a new Compendium section on implementation of infection prevention strategies and updated a section on hand hygiene, which can be each applied to condition-specific infection prevention strategies. Other updates describe strategies for preventing methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections, Clostridioides difficile infections, surgical site infections, and central line-associated bloodstream infections.
Each Compendium article contains infection prevention strategies, performance measures, and approaches to implementation. Compendium recommendations are derived from a synthesis of systematic literature review, evaluation of the evidence, practical and implementation-based considerations, and expert consensus.
###
About Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology
Published through a partnership between the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America and Cambridge University Press, Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology provides original, peer-reviewed scientific articles for anyone involved with an infection control or epidemiology program in a hospital or healthcare facility. ICHE is ranked 24th out of 94 Infectious Disease Journals in the latest Web of Knowledge Journal Citation Reports from Thomson Reuters.
About the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA)
The Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA) is a professional society representing more than 2,000 physicians and other healthcare professionals around the world who possess expertise and passion for healthcare epidemiology, infection prevention, and antimicrobial stewardship. The society’s work improves public health by establishing infection-prevention measures and supporting antibiotic stewardship among healthcare providers, hospitals, and health systems. This is accomplished by leading research studies, translating research into clinical practice, developing evidence-based policies, optimizing antibiotic stewardship, and advancing the field of healthcare epidemiology. SHEA and its members strive to improve patient outcomes and create a safer, healthier future for all. Visit SHEA online at shea-online.org, facebook.com/SHEApreventingHAIs and twitter.com/SHEA_Epi.
END
FINDINGS
UCLA researchers find that they can electronically recruit patients for biomedical research at rates up to 40 times higher than the traditional method of patient portal messages by embedding study recruitment into the pre-appointment preCheck-in page.
BACKGROUND
While patient portal messages are increasingly used to recruit patients for research studies, this method typically results in study enrollment rates of 1-8%. In addition, this method of study recruitment has historically led to ...
A new fund to fast-track patient access to potentially valuable new medicines may incentivise the pharmaceutical industry to develop high priced drugs for rare diseases with weak evidence on clinical benefits.
Health economics and policy academics from the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine (LSHTM), writing in the Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine, warn that if the NHS England Innovative Medicines Fund (IMF) is not implemented appropriately, it risks disincentivising the generation of essential evidence and could shift the financial burden from the pharmaceutical industry to the public finances.
The IMF operates on similar terms to ...
Certain gut problems, such as constipation, difficulty swallowing, and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), may be early warning signs of the neurological condition Parkinson’s disease, suggests research published online in the journal Gut.
Gastrointestinal symptoms are thought to precede the development of cerebrovascular disease, such as stroke or a brain aneurysm, or Alzheimer’s disease, and it has been suggested (Braak’s hypothesis) that gut conditions may precede the development of Parkinson’s disease too.
To ...
Over 60s with the unhealthiest lifestyles are significantly more likely to require admission to a nursing home than their peers with the healthiest lifestyles, suggest the findings of a large population study published online in the Journal of Epidemiology & Community Health.
Physical inactivity, smoking, poor diet and sleep disorders between the ages of 60 and 64 seemed to be particularly influential: they were associated with a more than doubling in the risk of admission, the findings show.
Modifiable lifestyle risk factors are associated with the development and progression of several long term conditions, ...
We are delighted to announce that the Beverage Plant Research articles are now indexed in CABI specialized databases. This important milestone ensures that articles published in Beverage Plant Research are easily found when searching for beverage plant literature and it enables this journal authors to keep track of how often their article has been cited by others. According to the correspondence made by CABI, the Beverage Plant Research will be indexed from Volume 1, 2021.
About Beverage Plant Research
Beverage Plant Research (e-ISSN: ...
“Eco-friendly” paper drinking straws contain long-lasting and potentially toxic chemicals, a new study has concluded.
In the first analysis of its kind in Europe, and only the second in the world, Belgian researchers tested 39 brands of straws for the group of synthetic chemicals known as poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS).
PFAS were found in the majority of the straws tested and were most common in those made from paper and bamboo, the study, published ...
Enormous amounts of sediment, or sand and mud, flowed through Houston waterways during Hurricane Harvey in 2017, due in part to modifications made by humans to bayous, rivers and streams over the past century, that could seriously impact future flooding events and be costly to the City of Houston.
New analysis by geology researchers at the University of Houston found 27 million cubic meters of sediment, or 16 Astrodomes, moved through 12 Houston waterways and Addicks and Barker reservoirs during Harvey, the largest rainfall event in U.S. history. After the storm, up to five feet ...
A stem cell patch developed by USC researchers for patients with macular degeneration will soon be tested in a phase 2b clinical trial.
This latest milestone in the patch’s development was made possible by a combined $21 million in support from a state organization, a nonprofit foundation and the university. Last month, the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine (CIRM) awarded an estimated $12.4 million to the USC-supported startup Regenerative Patch Technologies (RPT) to test the safety and efficacy ...
For the first time, researchers have used a surface normal nonlinear photodetector (SNPD) to improve the speed and energy efficiency of a diffractive optical neural network (ONN). The new device lays the groundwork for large-scale ONNs, which can perform high-speed processing at the speed of light in an extremely energy efficient manner.
Farshid Ashtiani from Nokia Bell Labs will present this research at Frontiers in Optics + Laser Science (FiO LS), which will be held 9 – 12 October 2023 at the Greater Tacoma Convention ...
Smoothies can be a tasty and convenient way to get the important fruits and vegetables you need for a healthy diet. But is a banana and blueberry smoothie the best combo? Researchers at the University of California, Davis, suggest that blending certain ingredients in smoothies can influence whether your body is getting a nutritional boost.
The study, published today in the Royal Society of Chemistry’s journal Food and Function, used smoothies to test how various levels of polyphenol oxidase, an enzyme in many fruits and vegetables, affects the levels of flavanols in food to be absorbed by the body. Flavanols ...