(Press-News.org) A recent study by the University of Eastern Finland and Balettakademien Stockholm found that performing in a dance company and being involved in its activities play a significant role in the identity and disease-related identity negotiation in people with Parkinson’s disease. Performing in the dance company and sharing the process of performing with others created a strong group identity for the dancers with Parkinson’s disease. The dancers’ experiences of watching and being watched provided them with novel ways of expressing themselves and being seen without their identity being associated with Parkinson’s disease.
Earlier studies have focused on dance interventions in group settings, i.e., dance classes, aimed at rehabilitation and social participation. They have shown that dance is a promising form of adjunct therapy for patients with Parkinson’s disease. In people with mild to moderate Parkinson’s disease for example, dance has led to significant improvements in balance, gait and functional mobility. The new study, published in Nordic Journal of Dance, focused on the significance of dance as a performative art form in Parkinson’s disease. The study involved eight dancers from the Swedish Kompani Parkinson dance company, which performs both in Sweden and abroad. The dancers completed an online questionnaire and most of them also participated in a focus group interview.
The dancers considered cohesion, division of responsibilities, peer support, acceptance and trust as essential aspects of functioning within the group. The study suggests that membership in the company and group identity also enabled the dancers to negotiate their personal identity.
“The group offered trust and social support in a way that was not based on cognitive or physical ability, but on embodied expression. For the participants, this was something new and significant,” says Senior Researcher Hanna Pohjola of the University of Eastern Finland.
For the dancers with Parkinson’s disease, the novel group identity provided an opportunity to negotiate an embodied identity that was tied to artistry – not to Parkinson’s disease. Although the disease sets its limits on what the body can do, the dancers were not limited or confined by art, allowing them to rediscover themselves.
“Being a part of the group and performing as a member of the company also allowed the dancers to change their perception of the self. Being a dancer and having expressive capacity were seen as something without limitations, allowing people to grow and develop despite possible functional limitations.”
The study was conducted as part of the Narrating through Dance in Life Fractures project, which is funded by the Kone Foundation. The project examines the experiential and psychosocial consequences of dance in different life transitions.
END
Dance as a performative art form enhanced identity negotiation and strengthened group identity in people with Parkinson’s disease
2023-08-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Myocardial infarction, the number one cause of sudden death, may be treated by modulating the immune response.
2023-08-25
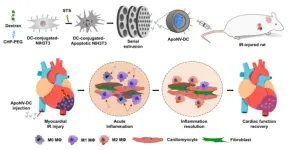
Myocardial infarction, the number one cause of sudden death in adults and the number two cause of death in Korea, is a deadly disease with an initial mortality rate of 30%, and about 5-10% of patients die even if they are transported to a medical center for treatment. The number of myocardial infarction patients in Korea has been increasing steeply, from 99,647 in 2017 to 126,342 in 2021, an increase of 26.8% in five years. Until now, drug administration, percutaneous angioplasty, and arterial bypass surgery have been known as treatments, but ...
Alternatives to indwelling urinary catheters help patients avoid infections and urethral trauma
2023-08-25
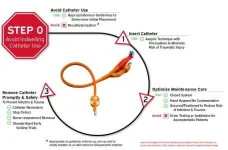
ARLINGTON, Va. (August 25, 2023) — Avoiding the unnecessary use of indwelling catheters and promptly removing catheters that are no longer needed are the first steps in preventing catheter-associated urinary tract infections in acute care hospitals, according to new recommendations developed by five medical societies and published today in the journal Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology.
“Urinary catheters can be associated with infection and also with non-infectious harms like trauma and obstruction,” said Payal Patel, M.D., an infectious disease physician at Intermountain Health and ...
UCLA researchers say embedding study recruitment in pre-appointment check-in may significantly boost participation
2023-08-25
FINDINGS
UCLA researchers find that they can electronically recruit patients for biomedical research at rates up to 40 times higher than the traditional method of patient portal messages by embedding study recruitment into the pre-appointment preCheck-in page.
BACKGROUND
While patient portal messages are increasingly used to recruit patients for research studies, this method typically results in study enrollment rates of 1-8%. In addition, this method of study recruitment has historically led to ...
New ‘promising medicines’ fund may incentivise commercialisation of high price drugs with weak evidence on clinical benefits
2023-08-25
A new fund to fast-track patient access to potentially valuable new medicines may incentivise the pharmaceutical industry to develop high priced drugs for rare diseases with weak evidence on clinical benefits.
Health economics and policy academics from the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine (LSHTM), writing in the Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine, warn that if the NHS England Innovative Medicines Fund (IMF) is not implemented appropriately, it risks disincentivising the generation of essential evidence and could shift the financial burden from the pharmaceutical industry to the public finances.
The IMF operates on similar terms to ...
Certain gut conditions may be early warning signs of Parkinson’s disease
2023-08-25
Certain gut problems, such as constipation, difficulty swallowing, and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), may be early warning signs of the neurological condition Parkinson’s disease, suggests research published online in the journal Gut.
Gastrointestinal symptoms are thought to precede the development of cerebrovascular disease, such as stroke or a brain aneurysm, or Alzheimer’s disease, and it has been suggested (Braak’s hypothesis) that gut conditions may precede the development of Parkinson’s disease too.
To ...
Poor lifestyle of over 60s linked to heightened risk of nursing home care
2023-08-25
Over 60s with the unhealthiest lifestyles are significantly more likely to require admission to a nursing home than their peers with the healthiest lifestyles, suggest the findings of a large population study published online in the Journal of Epidemiology & Community Health.
Physical inactivity, smoking, poor diet and sleep disorders between the ages of 60 and 64 seemed to be particularly influential: they were associated with a more than doubling in the risk of admission, the findings show.
Modifiable lifestyle risk factors are associated with the development and progression of several long term conditions, ...
Beverage Plant Research indexed in CABI
2023-08-25
We are delighted to announce that the Beverage Plant Research articles are now indexed in CABI specialized databases. This important milestone ensures that articles published in Beverage Plant Research are easily found when searching for beverage plant literature and it enables this journal authors to keep track of how often their article has been cited by others. According to the correspondence made by CABI, the Beverage Plant Research will be indexed from Volume 1, 2021.
About Beverage Plant Research
Beverage Plant Research (e-ISSN: ...
Paper drinking straws may be harmful and may not be better for the environment than plastic versions, researchers warn
2023-08-25
“Eco-friendly” paper drinking straws contain long-lasting and potentially toxic chemicals, a new study has concluded.
In the first analysis of its kind in Europe, and only the second in the world, Belgian researchers tested 39 brands of straws for the group of synthetic chemicals known as poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS).
PFAS were found in the majority of the straws tested and were most common in those made from paper and bamboo, the study, published ...
Sediment movement during Hurricane Harvey could negatively impact future flooding, prove costly to Houston, UH study finds
2023-08-25
Enormous amounts of sediment, or sand and mud, flowed through Houston waterways during Hurricane Harvey in 2017, due in part to modifications made by humans to bayous, rivers and streams over the past century, that could seriously impact future flooding events and be costly to the City of Houston.
New analysis by geology researchers at the University of Houston found 27 million cubic meters of sediment, or 16 Astrodomes, moved through 12 Houston waterways and Addicks and Barker reservoirs during Harvey, the largest rainfall event in U.S. history. After the storm, up to five feet ...
USC-supported startup receives major grant for clinical trial of a promising eye treatment
2023-08-24
A stem cell patch developed by USC researchers for patients with macular degeneration will soon be tested in a phase 2b clinical trial.
This latest milestone in the patch’s development was made possible by a combined $21 million in support from a state organization, a nonprofit foundation and the university. Last month, the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine (CIRM) awarded an estimated $12.4 million to the USC-supported startup Regenerative Patch Technologies (RPT) to test the safety and efficacy ...