(Press-News.org) Prof. Zuankai WANG, Associate Vice President (Research and Innovation) and Chair Professor of Nature-Inspired Engineering at The Hong Kong Polytechnic University (PolyU) has been bestowed one of the 10 winners of the Falling Walls Science Breakthroughs of the Year 2023 in Engineering and Technology category for his groundbreaking work on resolving the Leidenfrost effect.
The Award aims to foster research and innovation across all disciplines by celebrating cutting-edge discoveries. The Falling Walls Foundation, based in Berlin, established the Award to acknowledge the most recent breakthroughs in science and society worldwide.
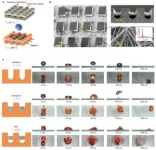
Prof. WANG’s innovation on structured thermal amour (STA) is recognised with the accolade of “Breaking the Wall to the Leidenfrost Effect.” His research “Inhibiting the Leidenfrost effect above 1,000°C for sustained thermal cooling,” published in Nature in 2022 tackles the longstanding challenges posed by the Leidenfrost effect since 1756.
When the temperature surpasses the Leidenfrost point, a continuous vapour layer forms between the solid and the liquid, leading to a reduction in heat transfer due to increased thermal resistance. Finding an efficient method for cooling hot surface has been a persistent challenge within thermal engineering and materials science.
Prof. WANG’s innovated STA strategy holds the potential to implement efficient liquid cooling at extremely high temperature, particularly in fields like aero-engines, space-engines and next generation nuclear reactors. This breakthrough also applies to electronics cooling which suffers from increased heat flux as a result of device miniaturization.
Prof. WANG said, “Solving this classical scientific problem at the heart of this award demands diverse and broad knowledge which I drew upon insights from surface science, materials, fluid mechanics, thermodynamics as well as advanced manufacturing.”
The invention pushes the boundaries of liquid cooling up to over 1,000°C, resulting in significant technological advancements that enhance thermal cooling in nuclear power plants, engines, microelectronic chips and electronics devices.
The impact of this work is far-reaching. Breaking the Leidenfrost effect at high temperatures also extends the temperature range of superwettablity, one of the Top 10 Emerging Technologies by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) in 2021. The current manifestation of superwettability is confined to a highly restricted temperature range. Prof. WANG’s ground breaking discovery dramatically extends the temperature range of superwettability above 1,000°C, unleashing limitless applications in chemistry and beyond.
Prof. WANG said, “The driving force on research is the curiosity to see if conventional perception and theory established centuries ago can be broken. I always encourage my research team and students to be proactive, passionate and persistent. Sometimes, a small idea and experiment can be a turning point of our life and bring us to a big world. We persist in making remarkable advancements in research by answering critical scientific questions or tackling long-standing technological challenges.”
END
PolyU scholar’s transformative work on the Leidenfrost effect wins the Falling Walls Science Breakthroughs of the Year 2023
2023-08-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Half as many AF patients dying of heart attacks and strokes in the UK
2023-08-25
University of Leeds news
Embargo: 25 August 2023, 12.30pm CEST
Patients living with one of the UK’s most common heart rhythm conditions are 50% less likely to die from a heart attack or stroke than they were at the start of the millennium, new research has found.
Analysis of the health records of more than 70,000 patients newly diagnosed with atrial fibrillation (AF) showed that mortality from related cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases more than halved over the 16-year study period.
AF is associated with an increased risk of stroke.
The research showed that dementia ...
The corona lockdowns changed the behavior of wild animals around the world
2023-08-25
In the spring of 2020, one country after another went into lockdown as Covid-19 spread across the globe. In some places, e.g. China, the civilian population was kept inside by the authorities. Other countries, like Spain, had a curfew in place for weeks, during which only short trips to the supermarket were allowed.
The lockdowns meant there were suddenly much fewer cars on the roads and people in forests and parks. While we were sitting at home watching Netflix, wild animals emerged from the bushes and edges of the forest. They ventured closer to the roads and cities that had suddenly emptied.
We know this thanks to data from GPS trackers attached to a large number of terrestrial ...
Starch discovery reaps benefits for brewing, baking and milling industries
2023-08-25
Research has brought clarity to the longstanding question of how starch granules form in the seeds of Triticeae crops – wheat, barley, and rye - unlocking diverse potential benefits for numerous industries and for human health.
Starch in wheat, maize, rice and potatoes is a vital energy-giving part of our diet and a key ingredient in many industrial applications from brewing and baking to the production of paper, glue, textiles, and construction materials.
Starch granules of different crops vary greatly in size and shape. Wheat starch (and those of other Triticeae) uniquely have two distinct types of granules: large A-type granules and smaller B-type granules.
The ratio ...
Insights from past warming: Enhanced temperature seasonality in China during the mid-Holocene
2023-08-25
Against the background of global warming, the temperature seasonality has changed obviously at global and regional scales, which has exerted significant ecological and societal impacts. As a populous country highly sensitive to climate change, China experienced an overall decreasing trend of the amplitude of the annual temperature cycle during 1961–2007. This national-scale average downward trend is likely to continue throughout the rest of the 21st century according to future projections, with a spatially robust decrease in most regions but increases at more local scales. ...
A new analytical framework assesses the risk of invasive golden mussels in water diversion projects
2023-08-25
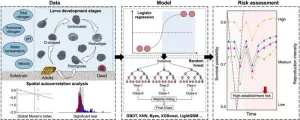
Water diversion projects, though meant to correct unequal water distribution, unintentionally promote the growth of invasive aquatic species like the golden mussel. This fast-reproducing, substrate-clinging mussel causes biofouling, damaging structures and water quality, and leading to socio-economic and ecological issues. Yet, how environmental factors aid this colonization remains largely unclear, necessitating further research.
In a ground-breaking study published on 24 July 2023 in the journal Environmental Science and Ecotechnology, researchers from Tsinghua University, utilized logistic ...
Kessler Foundation team examines influence of processing speed on treatment benefits of cognitive rehabilitation for individuals with traumatic brain injury
2023-08-25
East Hanover, NJ. August 25, 2023. Scientists at Kessler Foundation reported results from a randomized controlled trial examining the influence of processing speed on treatment benefits of the Kessler Foundation modified Story Memory Technique (KF-mSMT®) in individuals with moderate to severe traumatic brain injury (TBI). They found that processing speed played a role in benefit from the KF-mSMT on a list learning task, but not on a prose memory task.
Their article, “The influence of information processing speed on benefit from learning and memory rehabilitation in TBI: a sub-analysis of the TBI-MEM trial,” (do: 10.1080/02699052.2023.2216024) ...
Drexel develops new innovative model for cell and gene therapy education with grants from Bristol Myers Squibb
2023-08-25
Drexel University’s School of Biomedical Engineering, Science and Health Systems, in collaboration with Drexel’s College of Medicine, has received grants from the pharmaceutical company Bristol Myers Squibb, to support the education and training of diverse and talented students looking to pursue careers in cell and gene therapy.
The funding provided close to $1 million to support the creation of a new Cell and Gene Therapy Technology, Engineering, Analytics, Manufacturing, & Science academic program, known as CGT-TEAMS, that launched this summer ...
Waking up to Asian economic miracles
2023-08-25
By Alistair Jones
SMU Office of Research – American economist Milton Friedman cast a long shadow with his 1970 article, 'A Friedman Doctrine: The Social Responsibility of Business is to Increase its Profits'. For decades, it became a touchstone for free-market economies, interpreted as the sole purpose of a firm was to make money for its shareholders.
But there's an alternative dynamic, an awareness that companies also have a responsibility to stakeholders – such as employees, customers, suppliers, communities and government. This stakeholder capitalism has a corporate purpose beyond profit maximisation, aiming ...
Food recognition and logging: New research focuses on local Singaporean food
2023-08-25
By Stuart Pallister
SMU Office of Research – Two Singapore Management University researchers have embarked on a three-year project, funded by Singapore’s Ministry of Education, to ‘de-bias’ digital food recognition and develop a more robust machine learning system capable of correctly identifying Singapore’s multiracial food.
The two researchers from SMU’s School of Computing and Information Sciences, Professor Ngo Chong Wah and Associate Professor Rajesh Balan, already have extensive ...
Augusta University researcher calls for modernizing the UN's traditional approach to population replacement measurement
2023-08-25
AUGUSTA, Ga. (August 24, 2023) – In 2021, Arni S.R. Srinivasa Rao, PhD, presented a critique on the formula of net population replacement levels at the International Population Conference 2021 in Hyderabad, India. It was one of the first times he had publicly shared his latest research on population replacement commonly calculated through net reproduction rate (NRR). A blog on the same topic written by him also appeared in Population Association of America’s PAA Affairs.
Rao, the director at the Laboratory for Theory and Mathematical Modeling in the Division of Infectious Diseases at the Medical College of Georgia at Augusta University, has published ...