(Press-News.org) CHICAGO, Aug. 25, 2023 – Acetaminophen or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen are recommended as first-line treatments for managing short-term dental pain in children under age 12, according to a new clinical practice guideline developed by the American Dental Association Science & Research Institute (ADASRI), the University of Pittsburgh School of Dental Medicine and the Center for Integrative Global Oral Health at the University of Pennsylvania School of Dental Medicine. The guideline has been endorsed by the American Dental Association.
A guideline panel determined that, when used as directed, acetaminophen alone, NSAIDs (like ibuprofen) alone or acetaminophen in combination with NSAIDS can effectively manage a child’s pain after a tooth extraction or during a toothache when dental care is not immediately available. These and other recommendations are now available in the September issue of The Journal of the American Dental Association.
The guideline evaluated doses of acetaminophen and NSAIDs that may differ from the dosing printed on the over-the-counter packages of these medications. According to the guideline, when acetaminophen or NSAIDs are administered as directed by a dentist or other health care provider, the risk of harm to children from either medication is low.
Guideline senior author Paul Moore, D.M.D., Ph.D., M.P.H., is professor emeritus at the University of Pittsburgh’s School of Dental Medicine. He said the recommendations align with previous guidance from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), which contraindicated the use of codeine and tramadol in children under age 12 in 2017.
“While prescribing opioids to children has become less frequent overall, this guideline ensures that both dentists and parents have evidence-based recommendations to determine the most appropriate treatment for dental pain,” Dr. Moore said. “Parents and caregivers can take comfort that widely available medications that have no abuse potential, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, are safe and effective for helping their children find relief from short-term dental pain.”
In 2020, the FDA awarded the University of Pittsburgh and ADASRI a three-year $1.5 million grant to develop a clinical practice guideline for the management of acute pain in dentistry in children, adolescents and adults. A group of researchers and methodologists from ADASRI, the University of Pittsburgh School of Dental Medicine, the Center for Integrative Global Oral Health at the University of Pennsylvania School of Dental Medicine, McMaster University and the Art of Democracy worked together to develop the guideline.
“This clinical prescribing guideline is a critical step in supporting appropriate treatment of pediatric acute dental pain through the use of acetaminophen and NSAIDs," said Patrizia Cavazzoni, M.D., director of the FDA Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. “Not only will this advice allow for better treatment of this kind of pain, but it will help prevent unnecessary prescribing of medications with abuse potential, including opioids.”
This is the first of two guidelines on acute dental pain management. A second set of recommendations for adolescents and adults is in development. The new acute pediatric pain management guideline can be found at ada.org/painmanagement.
For more information on how the ADA is working to combat opioid misuse, while continuing to help patients manage dental pain, visit ada.org/opioids.
The contents of the guidelines are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily represent the official views of, nor an endorsement by, FDA, HHS or the U.S. government.
About the American Dental Association
The not-for-profit ADA is the nation's largest dental association, representing 159,000 dentist members. The premier source of oral health information, the ADA has advocated for the public's health and promoted the art and science of dentistry since 1859. The ADA's state-of-the-art research facilities develop and test dental products and materials that have advanced the practice of dentistry and made the patient experience more positive. The ADA Seal of Acceptance has long been a valuable and respected guide to consumer dental care products. The Journal of the American Dental Association (JADA), published monthly, is the ADA's flagship publication and the best-read scientific journal in dentistry. For more information about the ADA, visit ADA.org. For more information on oral health, including prevention, care and treatment of dental disease, visit the ADA's consumer website MouthHealthy.org.
END
New guideline details dental pain management strategies for pediatric patients
Experts recommend NSAIDs and/or acetaminophen to manage short-term dental pain in children
2023-08-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
In Type 1 diabetes, verapamil prevents decline of IGF-1 and promotes beta-cell IGF-1 signaling
2023-08-25
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. – In 2012, University of Alabama at Birmingham researcher Anath Shalev, M.D., reported that a decades-old blood pressure medication called verapamil completely reversed diabetes in animal models. In 2018, the team had translated these findings into a randomized, controlled, clinical trial, demonstrating significantly improved beta cell function for one year in human subjects with recent onset Type 1 diabetes. By last year, in a small follow-up study, Shalev and colleagues had found that adult Type 1 diabetes patients taking oral verapamil required less daily insulin ...
How being in space impairs astronauts’ immune system
2023-08-25
A new study led by researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden has examined how T cells of the immune system are affected by weightlessness. The results, which are published in the journal Science Advances, could explain why astronauts’ T cells become less active and less effective at fighting infection.
The next steps in the exploration of space are human missions to the moon and to Mars. Space is an extremely hostile environment that poses threats to human health. One such threat is changes to the immune system that occur in astronauts while in space and ...
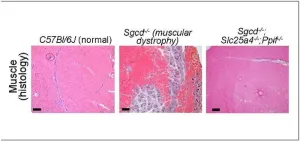
Mitochondria pore emerges as potential key to managing muscular dystrophies
2023-08-25
Ever since the Jerry Lewis telethons began in the 1960s, millions of people have become familiar with an otherwise rare disease called muscular dystrophy (MD).
The medical world has learned much over the ensuing years, including that more than 30 closely related disorders exist that can produce the gradual muscle degeneration that steals a child’s ability to walk and eventually disrupts other organ functions. An estimated 250,000 people in the U.S. are living with a muscular dystrophy. While many are living longer lives thanks to improved treatments, no cure has been found.
Now an eye-opening study ...
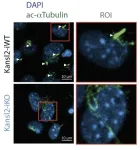
Unlocking the secrets of cell antennas
2023-08-25
Cilia are thin, eyelash-like extensions on the surface of cells. They perform a wide variety of functions, acting as mechanosensors or chemosensors, and play a crucial role in many signaling pathways. In the last few decades, the organelle has undergone a remarkable, but at the same time sinister, career transformation. It evolved from an organelle whose relevance was unclear to becoming a central player in the pathogenesis of a large group of diseases. These so-called ciliopathies are associated with a wide range of symptoms, including hearing loss, visual impairment, obesity, kidney disease, and mental disability. Different gene mutations impair cilia formation, ...
How origami might inform disease diagnoses
2023-08-25
Researchers at the USC Viterbi School of Engineering looked to origami to create new sensors that could someday be employed to detect deformations in organs and also for use in wearables and soft robotics.
Their paper, “High-Stretchability and Low-Hysteresis Strain Sensors Using Origami-Inspired 3D Mesostructures,” featured in Science Advances explains how USC researchers Hangbo Zhao, Xinghao Huang, Liangshu Liu, Yung Hsin Lin, Rui Feng, Yiyang Shen, and Yuanning Chang developed “stretchable strain sensors,” ...
Weight loss medication benefits patients with heart failure and obesity
2023-08-25
Amsterdam, Netherlands – 25 Aug 2023: Semaglutide improves heart failure-related symptoms and physical function and results in greater weight loss compared with placebo in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) and obesity, according to late breaking research presented in a Hot Line session today at ESC Congress 2023.1
Approximately half of patients with heart failure in the community have HFpEF.2 Most patients with HFpEF are overweight or obese, and growing evidence suggests that obesity and excess adiposity are not simply comorbidities, ...
Oral anticoagulation is not effective in patients with atrial high-rate episodes
2023-08-25
Amsterdam, Netherlands – 25 Aug 2023: Blood thinners (anticoagulants) cause bleeding without preventing stroke in patients with atrial high rate episodes (AHRE), but without electrocardiogram (ECG)-diagnosed atrial fibrillation, according to late breaking research presented in a Hot Line session today at ESC Congress 2023 and simultaneously published in the New England Journal of Medicine.1
Anticoagulants prevent strokes in patients with atrial fibrillation but are not effective in those without atrial fibrillation, for example in patients with ...
Colchicine fails to reduce primary outcomes in COP-AF trial but encouraging signals found
2023-08-25
Amsterdam, Netherlands – 25 Aug 2023: Colchicine does not significantly reduce perioperative atrial fibrillation (AF) or myocardial injury after non-cardiac surgery (MINS) in patients undergoing major non-cardiac thoracic surgery, according to late breaking research presented in a Hot Line session today at ESC Congress 2023.1
Perioperative AF occurs in approximately 10% of patients after major thoracic surgery, while MINS has an incidence of about 20% in the same patient population.2 Patients with perioperative AF and MINS have a poor prognosis.3,4 High levels ...
First ESC Guidelines covering all acute coronary syndromes published today
2023-08-25
Amsterdam, Netherlands – 25 Aug 2023: The European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Guidelines on acute coronary syndromes are published online today in European Heart Journal.1 The document covers the management of unstable angina and all types of acute myocardial infarction.
“Time is critical in acute coronary syndromes. When an artery supplying the heart with blood becomes blocked, the quicker we open the artery and restore flow, the less damage occurs to the heart muscle,” said Guidelines task force ...
First international guidelines on heart muscle diseases published today
2023-08-25
Amsterdam, Netherlands – 25 Aug 2023: The European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Guidelines on cardiomyopathies are published online today in European Heart Journal.1 This is the first international guideline document to include all cardiomyopathy subtypes, and the first time that specific recommendations are made for cardiomyopathies other than hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
“This pioneering document reflects the advances in genetics and cardiac imaging and the advent of new treatments that target specific causes of disease,” said Guidelines task force chairperson Dr. Elena Arbelo of the Hospital Clinic, University of Barcelona, Spain.
“At the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
[Press-News.org] New guideline details dental pain management strategies for pediatric patientsExperts recommend NSAIDs and/or acetaminophen to manage short-term dental pain in children