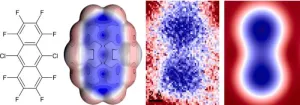
(Press-News.org) Scientists from the IOCB Prague, the Institute of Physics of the Czech Academy of Sciences, and Palacký University Olomouc, have once again successfully uncovered the mysteries of the world of molecules and atoms. They have experimentally confirmed the correctness of a decades-old theory that assumed a non-uniform distribution of electron density in aromatic molecules. This phenomenon significantly affects the physicochemical properties of molecules and their interactions. This research expands the possibilities for designing new nanomaterials and is the theme of a paper that has just been published in Nature Communications.
The same team of authors in its previous groundbreaking study published in Science described the non-uniform distribution of electrons in an atom, the so-called σ-hole. Now the researchers have confirmed the existence of the so-called π-hole. In aromatic hydrocarbons, we find electrons in clouds above and below the plane of carbon atoms. If we replace the peripheral hydrogens with more electronegative atoms or groups of atoms that pull electrons away, the originally negatively charged clouds turn into positively charged electron holes.
Scientists have taken the advanced method of scanning electron microscopy and pushed its capabilities further. The method works at subatomic resolution and can therefore image not only atoms in molecules but also the structure of the electron shell of an atom. As one of the researchers involved, Bruno de la Torre from the Czech Advanced Technology and Research Institute (CATRIN) of Palacký University Olomouc, points out, the success of the experiment described here is mainly due to the excellent facilities at his home institution and the participation of excellent Ph.D. students.
"Thanks to our previous experience with the Kelvin Probe Force Microscopy (KPFM) technique, we have been able to refine our measurements and acquire very complete data sets that have helped us to deepen our understanding not only of how the charge is distributed in the molecules but also of what observables are obtained with the technique," says Bruno de la Torre.
Modern force microscopy has long been the domain of researchers at the Institute of Physics. Not only in the case of molecular structures have they used the unprecedented spatial resolution to the full. Some time ago they confirmed the existence of a non-uniform distribution of electron density around halogen atoms, the so-called σ-holes. This achievement was published in 2021 by Science. The former as well as current research was significantly contributed to by one of the most cited Czech scientists of today, Prof. Pavel Hobza from the Institute of Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry of the Czech Academy of Sciences (IOCB Prague).
"The confirmation of the existence of the π-hole, as well as the σ-hole before it, fully demonstrates the quality of the theoretical predictions of quantum chemistry, which have accounted for both phenomena for decades. It shows that they can be relied upon even in the absence of available experiments," says Pavel Hobza.
The results of Czech scientists’ research at the subatomic and submolecular levels can be compared to the discovery of cosmic black holes. They had also been theorized for decades before their existence was confirmed by experiments.
A better knowledge of the distribution of the electron charge will help the scientific community to understand many chemical and biological processes in the first place. On a practical level, it will translate into the ability to build new supramolecules and subsequently into the development of advanced nanomaterials with improved properties.
Original article: B. Mallada, M. Ondráček, M. Lamanec, A. Gallardo, A. Jiménez-Martin, B. de la Torre, P. Hobza, P. Jelínek, Visualization of π-hole in molecules by means of Kelvin probe force microscopy. Nat Commun 14, 4954 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-40593-3
---
The Institute of Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry of the Czech Academy of Sciences / IOCB Prague is a leading internationally recognized scientific institution whose primary mission is the pursuit of basic research in chemical biology and medicinal chemistry, organic and materials chemistry, chemistry of natural substances, biochemistry and molecular biology, physical chemistry, theoretical chemistry, and analytical chemistry. An integral part of the IOCB Prague’s mission is the implementation of the results of basic research in practice. Emphasis on interdisciplinary research gives rise to a wide range of applications in medicine, pharmacy, and other fields.
END
Scientists continue to push the boundaries of imaging techniques and reveal the mysterious world of molecules
They have experimentally confirmed the correctness of a decades-old theory that assumed a non-uniform distribution of electron density in aromatic molecules
2023-08-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Prescription for fruits, vegetables linked to better heart health, food security
2023-08-29
Research Highlights:
Adults at risk for heart disease who participated in produce prescription programs for an average of six months increased their consumption of fruits and vegetables and had reduced blood pressure, body mass index and blood sugar levels.
Among adults and children, produce prescription programs also appeared to decrease food insecurity — the lack of equitable and stable availability, access, affordability and consumption of healthy foods and drinks — and improve self-reported health status.
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT/5 a.m. ET Tuesday, August 29, 2023
DALLAS, August 29, 2023 — ...
Wildfire, soil emissions increasing air pollution in remote forests
2023-08-29
Satellite data from across California’s landscapes reveal an increase in nitrogen dioxide levels in remote forest areas, and wildfire and soil emissions are likely the reasons why, according to a paper from University of California, Davis, published today in the journal Environmental Research Letters.
Nitrogen dioxide is short-lived in the atmosphere but plays a central role in the formation of the pollutants ozone and particulate matter, which can lead to respiratory issues and asthma in humans, as well as harm plants and crop yields.
The researchers looked at summertime surface and satellite concentrations of nitrogen dioxide between 2009 ...
Can an artificial kidney finally free patients from dialysis?
2023-08-29
Scientists at UC San Francisco are working on a new approach to treating kidney failure that could one day free people from needing dialysis or having to take harsh drugs to suppress their immune system after a transplant.
They have shown for the first time that kidney cells, housed in an implantable device called a bioreactor, can survive inside the body of a pig and mimic several important kidney functions. The device can work quietly in the background, like a pacemaker, and does not trigger the recipient’s immune system to go on the attack.
The ...
Researchers discover common origin behind major childhood allergies
2023-08-29
Several major childhood allergies may all stem from the community of bacteria living in our gut, according to a new study led by researchers at the University of British Columbia and BC Children’s Hospital.
The research, published in Nature Communications, identifies gut microbiome features and early life influences that are associated with children developing any of four common allergies — eczema, asthma, food allergy and/or hay fever. The findings could lead to methods of predicting whether a child will develop allergies, and ways to prevent them from developing at all.
“We’re ...
Produce prescription programs yield positive health benefits for participants, study finds
2023-08-29
Around the country, non-profits and local governments are testing the idea of food as medicine through “produce prescription programs”—with promising results, according to researchers from the Friedman School of Nutrition Science and Policy at Tufts University.
By prescribing free, healthy foods similar to how doctors prescribe medications, clinicians and policy makers hope to remove financial barriers to accessing fruits and vegetables to individuals with diet-related illness. Specifically, produce prescriptions offer vouchers, debit cards, or loyalty cards to access free or discounted produce at grocery retail ...
Innovative therapy for anorexia nervosa shows promise
2023-08-29
**EMBARGOED UNTIL 3:00am CT TUESDAY, AUGUST 29, 2023**
Tulsa, Okla. – A trailblazing study conducted by researchers at the Laureate Institute for Brain Research (LIBR) in Tulsa, Okla., has made significant strides with a novel technique for treating anorexia nervosa (AN), an eating disorder characterized by low body weight, body image abnormalities, and anxiety. The study, “The impact of floatation therapy on body image and anxiety in anorexia nervosa: a randomized clinical efficacy ...
An investment in more research to benefit children and adolescents
2023-08-29
Launched in 2019, the Botnar Research Centre for Child Health (BRCCH) aims to drive innovative health research that benefits children and adolescents globally – especially those living in low- or middle-income countries. Within this centre, the University of Basel and ETH Zurich work in partnership with the University Children’s Hospital Basel (UKBB) and the Swiss Tropical and Public Health Institute (Swiss TPH).
Over the past four years, the BRCCH has supported around 80 researchers and 29 research projects worldwide. For example, researchers improved the treatment of cleft lip and palate and developed biotechnology to monitor paediatric gut ...
Maintaining stable weight increases longevity among older women
2023-08-29
Reaching the age of 90, 95 or 100, known as exceptional longevity, was more likely for women who maintained their body weight after age 60, according to a multi-institutional study led by University of California San Diego. Older women who sustained a stable weight were 1.2 to 2 times more likely to achieve longevity compared to those who experience a weigh loss of 5 percent or more.
Reporting in the Aug. 29, 2023 online issue of the Journal of Gerontology: Medical Sciences, researchers investigated the associations of weight changes later in life with exceptional longevity ...
Air pollution and its threat to health are unequally spread throughout the world, and so are the opportunities to combat it
2023-08-29
As global pollution edged upward in 2021, so did its burden on human health, according to new data from the Air Quality Life Index (AQLI). If the world were to permanently reduce fine particulate pollution (PM2.5) to meet the World Health Organization’s (WHO) guideline, the average person would add 2.3 years onto their life expectancy—or a combined 17.8 billion life-years saved worldwide.
This data makes clear that particulate pollution remains the world’s greatest external risk to human health, with the impact on life expectancy comparable to that of smoking, more than 3 times that of alcohol use and unsafe water, and more than ...
Overcoming the challenges to synthesising iron–sulfur proteins outside the glovebox
2023-08-29
Fe–S clusters, which are a part of Fe–S proteins, are found across all forms of life. They play a significant role as biological cofactors—helper molecules that assist these proteins in different biochemical transformations—that are involved in respiration and metabolism. These clusters are of keen research interest since they are considered to be a critical part of evolution. They serve as a link between pre-biotic chemistry (chemical processes that existed prior to the emergence of life forms) and the complex molecular and biological systems we know today. Put simply, they ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
Maternal acetaminophen use and child neurodevelopment
Digital microsteps as scalable adjuncts for adults using GLP-1 receptor agonists
Researchers develop a biomimetic platform to enhance CAR T cell therapy against leukemia
Heart and metabolic risk factors more strongly linked to liver fibrosis in women than men, study finds
[Press-News.org] Scientists continue to push the boundaries of imaging techniques and reveal the mysterious world of moleculesThey have experimentally confirmed the correctness of a decades-old theory that assumed a non-uniform distribution of electron density in aromatic molecules