(Press-News.org) UNDER EMBARGO UNTIL 11:00 A.M. EDT ON TUESDAY, AUGUST 29, 2023
Social media’s effects on propagating misinformation among the lay public are widely debated, but a new paper from JAMA suggests physicians using social media are revolutionizing medical education.
La Jolla, Calif. (August 29, 2023) — Ever wonder what your doctor is doing on social media? A new study published in JAMA led by John W. Ayers, Ph.D., from the Qualcomm Institute within the University of California San Diego, finds some physicians are harnessing the reach of social media to share and debate medical advancements.
The research team obtained all posts containing #MedEd made to X, formerly Twitter, from January 2012 through December 2022. There were 4,397,691 original posts with the hashtag #MedEd on X during this time. The number of posts increased each year, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic, most recently from 692,095 during 2021 to 1,178,647 during 2022.
“To put our findings into context, social media is the largest publisher of medical knowledge,” said Ayers, who is vice chief of innovation in the Division of Infectious Disease and Global Public Health at UC San Diego School of Medicine in addition to his Qualcomm Institute affiliation. “Unlike traditional knowledge resources that are kept in medical schools or paywalled, social media harnesses the collective wisdom and insights of millions of doctors transparently.”
Harnessing #MedEd to Accelerate Medical Science and Improve Practice
“Social media has been the subject of intense scrutiny, particularly concerns over misinformation; however, for health professionals like myself, social media is incredibly valuable for staying up to date on the latest medical advancements,” said Aaron Goodman, M.D., an associate clinical professor at UC San Diego School of Medicine and study coauthor, who goes by the moniker Papa Heme on X, where he shares content on oncology and hematology to his 127,000+ mostly physician followers.
“New medical knowledge is often nuanced, and well-informed people can have valid, differing opinions on the same data,” added physician-scientist and study co-author Davey Smith, M.D., chief of the Division of Infectious Disease and Global Public Health at UC San Diego School of Medicine and co-director of the university’s Altman Clinical and Translational Research Institute. “Social media is a way to rapidly disseminate such information and provide a platform to robustly debate the veracity of such new knowledge.”
“The potential for #MedEd to improve medical education is considerable, but the risks of dismissing #MedEd is potentially greater,” continued Smith. “Our study suggests now is time to invest more resources into #MedEd to unite the tens of millions of health professionals across the globe in continuous learning and teaching.”
The piece “#MedEd: Medical Education and Knowledge Translation on Social Media” (doi:10.1001/jama.2023.12465) was published by JAMA on August 29, 2023.
###
END
New research led by the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology & Neuroscience (IoPPN) at King’s College London has found that selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) treatment for postnatal depression is associated with improvements in child behaviour up to five years after childbirth.
Up to 15% of women experience postnatal depression which has been shown to be associated with poor outcomes for mothers’ and their children. Researchers at King’s IoPPN, in collaboration with the University of Oslo, analysed data from ...
CORVALLIS, Ore. – In northern Yellowstone National Park, saplings of quaking aspen, an ecologically important tree in the American West, are being broken by a historically large bison herd, affecting the comeback of aspen from decades of over-browsing by elk.
Findings of the research led by Luke Painter of Oregon State University were published today in Ecology and Evolution.
The study comes five years after Painter, who teaches ecology and conservation in the OSU College of Agricultural Sciences, published a paper in Ecosphere showing that wolf reintroduction in Yellowstone had been a catalyst for aspen recovery both outside and ...
INDIANAPOLIS -- LOINC® from Regenstrief Institute is issuing its semiannual content update with 1,945 new concepts to help health systems, laboratories and other health organizations exchange medical data. The release contains newly created content based on requests submitted by stakeholders from more than 100 countries.
LOINC version 2.75 is available for download from the LOINC website and via the LOINC Terminology Service using HL7® FHIR®. The updated version includes new, edited and newly mapped concepts ...
Jason Yang has been awarded nearly $400,000 from the National Institute on Aging to explore the role of lifestyle physical activity (light movements, walking) in cognition among insufficiently active older adults with higher risks for Alzheimer’s or related dementias. The exercise science assistant professor will use the two-year R21 grant to help determine if frequent and regular engagement in lifestyle physical activity over time may benefit cognitive function for this population.
A ...
Sleep is a critical part of a child’s overall health, but it can also be an important factor in the way they behave.
According to a new study from the Youth Development Institute at University of Georgia, getting enough sleep can help children combat the effects of stressful environments.
“Stressful environments are shown to make adolescents seek immediate rewards rather than delayed rewards, but there are also adolescents who are in stressful environments who are not impulsive,” said lead author Linhao Zhang, a fourth-year doctoral student in UGA’s College of Family and Consumer Sciences. “We looked at what explains that link and what makes some people ...
Abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA), a common degenerative vascular disease, particularly afflicts men over the age of 60, with up to 8% affected. Characterized by the abnormal dilation of the abdominal aorta, AAA risks a potentially fatal rupture. Despite increasing research efforts, effective pharmaceutical strategies to curb aneurysm growth remain elusive.
In a study published in the journal of Genes & Diseases, researchers from Sant Pau Hospital Research Institute and Biomedical Research Institute Sant Pau scrutinized the Wnt signaling pathway's deregulation in human abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA). This ...
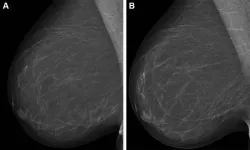
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Combining artificial intelligence (AI) systems for short- and long-term breast cancer risk results in an improved cancer risk assessment, according to a study published in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Most breast cancer screening programs take a one-size-fits-all approach and follow the same protocols when it comes to determining a woman’s lifetime risk of developing breast cancer. Using mammography-based deep learning models may improve the accuracy of breast cancer risk assessment and can also lead to earlier ...
An anti-obesity drug can be delivered selectively to the liver using a nanogel-based carrier, according to a study. Synthetic thyroid hormone mimics are promising treatments for metabolic diseases including metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH), high cholesterol, type 2 diabetes, and inflammatory liver disease; however, the molecules are not highly bioavailable or potent, which are necessary to see significant weight loss. S. Thayumanavan and colleagues designed a nanogel-based carrier with anionic moieties on the surface ...
Digital Science, a technology company serving stakeholders across the research ecosystem, is pleased to announce that Australia’s Nuclear Science and Technology Organisation (ANSTO) has chosen Symplectic Elements from Digital Science’s flagship products to advance awareness of its world-class research.
ANSTO is the home to some of Australia’s most significant national infrastructure for research. Thousands of scientists from industry and academia benefit from gaining access to ANSTO’s ...
Though drug developers have achieved some progress in treating Alzheimer’s disease with medicines that reduce amyloid-beta protein, other problems of the disease including inflammation, continue unchecked. In a new study, scientists at The Picower Institute for Learning and Memory at MIT describe a candidate drug that in human cell cultures and Alzheimer’s mouse models reduced inflammation and improved memory.
The target of the new “A11” molecule is a genetic transcription factor called PU.1. Prior research has shown that amid Alzheimer’s disease, PU.1 ...