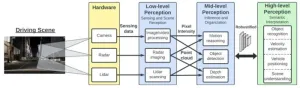
As part of an innovative prison reform program, the Oregon State Penitentiary created a healing garden on its grounds to provide some respite from the concrete and resemble the outside world. One incarcerated man who had spent most of the past two decades in solitary confinement described going to the garden as, “the first time I walked on grass in 20 years.”
“Many of us have found beauty in weeds and flowers growing through the cracks in the pavement,” he told UC San Francisco researchers, who helped institute and then evaluated the reforms. “There is both beauty and inspiration in knowing that we, who have fallen through the proverbial cracks in the system, can, if properly motivated and cultivated, grow through those very cracks.”
Oregon is one of a handful of states testing a Norwegian-inspired approach to prison reform that’s designed to bring greater humanity to corrections and improve conditions for staff as well as those who live behind walls. This includes reducing the use of solitary confinement. In the first evaluation of this method in a United States' prison, the UCSF researchers found the Norwegian techniques dramatically increased the time people spent outside their cells and, in turn, reduced disciplinary actions and violence.
The reforms increased the time residents spent outside their cells and engaged in social activities, particularly for those with serious mental health and behavioral problems, according to an analysis by the Amend team published in July in the online journal PLOS ONE.
From 2016 to 2021, the rate of assaults dropped almost 74% among residents who interacted with teams that had been trained in the techniques. And staff use-of-force incidents dropped nearly 86% in the Behavioral Health Unit, which houses individuals with mental health disorders who tend to have the most disruptive behaviors.
“The paper shows a promising model for transitioning people out of solitary confinement,” said Cyrus Ahalt, a UCSF public health researcher. “This model decreased violence, increased time out of the cell and accelerated movement out of these restricted units into general or more populated units.”
An approach that stresses dignity and respect
The pilot program builds upon efforts started in Norway in the 1990s to humanize its prisons and minimize its use of solitary confinement. By using techniques that focus on building relationships and trust, they have profoundly changed living conditions for imprisoned people with serious mental illnesses and histories of trauma and violence.
To begin with, incarcerated individuals are referred to as residents or patients, rather than inmates, convicts or prisoners. Correctional officers learn effective ways to listen, empathize and de-escalate conflicts through communication rather than resorting to giving orders or using force. The staff and residents are encouraged to create positive connections, talk with one another and socialize together. Sometimes the difference can be as basic as asking how someone’s day is going.
“This approach, called ‘The Resource Team,’ provides prison staff the training and inspiration they need to help incarcerated people in these units change their behavior – rather than locking them up and making them worse – so that they return to our communities as the best versions of themselves, as better family members and neighbors,” said Brie Williams, MD, MS, a geriatrician and professor of medicine at UCSF.
In 2015, Williams founded Amend at UCSF, which works to improve the health of both prison residents and staff. The Amend team leads immersion programs in the Norwegian Correctional Service for delegations of U.S. prison officials, policy makers and prison staff to learn about their approach to prisons. Norwegian teams also come to American prisons to help with officer training.
“We have this hidden public health crisis – not just among the people who live in the prisons, but the people who work there,” said David Cloud, JD, PhD, who is the research director of Amend. “If we’re going to end the human rights abuses in our prisons, then we’re going to have to really work on finding a way to show the people who work there a fundamentally different approach.”
More prisons adopt reforms
Aspects of the Norwegian-inspired approach are being introduced in Oregon, North Dakota, Washington and California, but Oregon was the first to start. They focused on changing the experience of people in isolation. Following a damning report from disability rights leaders in 2015, Oregon prison officials started trying to improve conditions but fell short of goals laid out in a signed memorandum. They learned about the Norwegian approach and began using it in 2019.
Solitary confinement, which increased during the COVID-19 pandemic, has long been shown to have detrimental physical and emotional effects, and most states have introduced or passed legislation to limit or ban its use. But policies to end it have faced resistance from inside correctional systems, making the achievement in Oregon even more notable.
Advocates of the reforms say there’s nothing intrinsically Norwegian about the approach, and it can be adapted for the United States. Before that can happen, however, correctional officers need to buy into the concept.
Toby Tooley was a captain at the Oregon State Penitentiary system in 2018 when he participated in an immersion program in Norway and brought the concepts home. He encountered some resistance from his fellow officers, but said they started to see the value both for the residents and for themselves. As incidents of violence began to drop, officers in the program saw their health and personal lives improve as their stress diminished.
“I was impacted both professionally and personally, and that motivated me to try to get this message out to as many people as I can,” said Tooley, who quit his job in 2021 to work as a program manager for Amend so he could promote the benefits of the model more broadly. “This absolutely has to go nationwide.”
About UCSF: The University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) is exclusively focused on the health sciences and is dedicated to promoting health worldwide through advanced biomedical research, graduate-level education in the life sciences and health professions, and excellence in patient care. UCSF Health, which serves as UCSF's primary academic medical center, includes top-ranked specialty hospitalsand other clinical programs, and has affiliations throughout the Bay Area. UCSF School of Medicine also has a regional campus in Fresno. Learn more at https://ucsf.edu, or see our Fact Sheet.
###
Follow UCSF
ucsf.edu | Facebook.com/ucsf | YouTube.com/ucsf
END