(Press-News.org)
AURORA, Colo. (Aug. 30, 2023) – Scientists at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus have made a `paradigm shifting’ discovery on the mechanisms required for learning and memory that could lead to new therapies for Alzheimer’s disease and potentially Down syndrome.
The study was published Wednesday in the journal Nature.
For over 30 years, researchers believed that LTP or long-term potentiation, which is crucial for learning and memory, required enzymatic actions by an enzyme known as CaMKII.
But a team of researchers led by Ulli Bayer, PhD, professor of pharmacology at the University of Colorado School of Medicine, found that LTP requires structural not enzymatic functions of CaMKII.
That’s significant, Bayer said, because it opens the door to the therapeutic use of a new class of inhibitors that target only the enzymatic activity of CaMKII, but not the structural functions required for memory and learning.
Previous studies by Bayer’s laboratory showed that inhibiting enzymatic CaMKII activity protects against some of the effects of amyloid-beta (Abeta) plaques in the brain, a hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease (AD).
The researchers found one group of inhibitors that protected from the Abeta effects without impairing LTP, making it potentially useful in treating a number of brain diseases without debilitating side effects.
“The implications are that a certain class of CaMKII activity inhibitors actually could be used chronically to treat brain conditions including Alzheimer’s disease,” said Bayer, senior author of the study. “This is super novel, as it has previously been thought that any CaMKII activity inhibitor would block synaptic plasticity that underlies learning and memory so their chronic use would be counter-indicated.”
Bayer said if the inhibitors work in humans, they could provide additional benefit in conjunction with any current AD treatment strategies.
“That’s because different mechanisms are targeted,” he said. “We are targeting the downstream effects of Abeta. While we are not even pretending that this would be curative, it has the potential to dramatically alleviate some of the most devastating symptoms of memory loss and learning.”
The Bayer lab is now testing whether the predictions made by their ground-breaking paper can be harnessed for human therapy.
About the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus
The University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus is a world-class medical destination at the forefront of transformative science, medicine, education and patient care. The campus encompasses the University of Colorado health professional schools, more than 60 centers and institutes, and two nationally ranked independent hospitals - UCHealth University of Colorado Hospital and Children's Hospital Colorado - that treat more than two million adult and pediatric patients each year. Innovative, interconnected and highly collaborative, the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus delivers life-changing treatments, patient care and professional training and conducts world-renowned research fueled by over $690 million in research grants. For more information, visit www.cuanschutz.edu.
###
Find the latest University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus news here.
END
Modern medicine depends on antibiotics to treat infections by disabling targets inside bacterial cells. Once inside these cells, antibiotics bind to certain sites on specific enzyme targets to stop bacterial growth. Randomly occurring changes (mutations) in the genes for these targets occur naturally, in some cases making the target harder for the antibiotic to attach to, and that bacterial version resistant to treatment.
For this reason, the more antibiotics have been used over time, the greater the chances that bacterial populations will evolve to have mutants resistant to existing antibiotics, and the more urgent the call for new approaches ...
Coastal wetlands and coral reef islands will struggle to grow fast enough to keep pace with rising sea levels driven by climate change, according to a new study published in Nature. The study was conducted by an international team that includes a Tulane University researcher. The findings show that the future of marshes and other low-lying coastal areas depend heavily on whether global warming can be limited to less than 2 degrees Celsius (3.6 degrees Fahrenheit) as formulated by the Paris Agreement.
A key finding of the paper is that coastal marshes, mangroves, ...
Researchers have a new way to connect quantum devices over long distances, a necessary step toward allowing the technology to play a role in future communications systems.
While today’s classical data signals can get amplified across a city or an ocean, quantum signals cannot. They must be repeated in intervals — that is, stopped, copied and passed on by specialized machines called quantum repeaters. Many experts believe these quantum repeaters will play a key role in future communication networks, allowing enhanced security and enabling connections between remote quantum computers.
The Princeton study, published Aug. ...
Cardiovascular disease remains the leading cause of racial disparities in mortality between Black and white people in the United States. New research from the University of Chicago Medicine suggests that parental incarceration may be contributing to these health gaps.
According to the new study, people who experienced a parent or parental figure’s incarceration anytime before the age of 18 had higher levels of hypertension and coronary disease biomarkers than people whose parents were not incarcerated. These results indicate that mass incarceration may have transgenerational health consequences.
Adverse childhood experiences (ACEs) are difficult ...
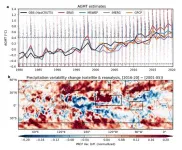
A collaborative international research team led by Professor Yoo-Geun Ham from Chonnam National University and Professor Seung-Ki Min from Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) has made a discovery on the impact of global warming on global daily precipitation. Using a deep learning approach, they have unveiled a significant change in the characteristics of global daily precipitation for the first time. Their research findings were published on August 30 in the online version of Nature, the ...
Remember when IBM’s Deep Blue won against Gary Kasparov at chess in 1996, or Google’s AlphaGo crushed the top champion Lee Sedol at Go, a much more complex game, in 2016? These competitions where machines prevailed over human champions are key milestones in the history of artificial intelligence. Now a group of researchers from the University of Zurich and Intel has set a new milestone with the first autonomous system capable of beating human champions at a physical sport: drone racing.
The AI system, called Swift, won multiple races against three world-class champions in first-person view (FPV) ...
An existing blood cancer drug has shown promise in killing ‘silent’ HIV cells and delaying reinfections – a significant pre-clinical discovery that could lead to a future cure for the disease.
Hidden HIV cells, known as latent infection, are responsible for the virus permanently remaining in the body and cannot be treated by current therapy options. These hibernating, infected cells are the reason why people living with HIV require life-long treatment to suppress the virus.
Led by WEHI and The Peter Doherty Institute for Infection ...
The safety of tall buildings in the world's cities, in the face of extreme external traumas like vehicle impacts, blasts or fires, has been tested using a model developed by structural engineers at the University of Surrey – with reassuring results.
Surrey's structural engineers partnered with industry experts to check and enhance the robustness of skyscrapers. Surrey's researchers collaborated with experts at the respected collective of architects, designers, engineers and planners, Skidmore, Owings & Merrill (SOM), famous for buildings like the Burj Khalifa, the world's tallest skyscraper, and the Sears ...
Toronto, ON, August 30, 2023 – Higher stroke risk among females with atrial fibrillation may be related to sex-based disparities in cardiovascular care, according to a new study from Women’s College Hospital, the Peter Munk Cardiac Centre (PMCC) at University Health Network (UHN) and ICES.
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is a common type of irregular heart rhythm that is associated with a higher risk of stroke—after the age of 40, one in four strokes are caused by AF. Previous studies have found that female sex (assigned at birth) is a risk factor for AF-associated stroke. Recent research suggested that ...
In the case of boredom, we think of many situations in life but intuitively not of exams. However, an international team of academics led by Thomas Götz from the University of Vienna has now studied exactly this phenomenon of test boredom for the first time and found remarkable results. According to the study, school students are actually very bored during exams. The study also showed that utter boredom has a negative effect on exam results. The research results have been published recently in the Journal of Educational Psychology.
Although boredom is currently a very intensively studied phenomenon, test boredom has so far been completely ignored ...