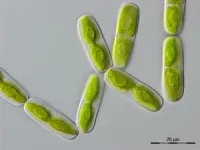
(Press-News.org) The Earth's surface is covered by plants. They make up the majority of biomass on land and exhibit a wide range of diversity, from mosses to trees. This astounding biodiversity came into existence due to a fateful evolutionary event that happened just once: plant terrestrialization. This describes the point where one group of algae, whose modern descendants can still be studied in the lab, evolved into plants and invaded land around the world. An international group of researchers, spearheaded by a team from the University of Göttingen, generated large scale gene expression data to investigate the molecular networks that operate in one of the closest algal relatives of land plants, a humble single-celled alga called Mesotaenium endlicherianum. Their results were published in Nature Plants.
Using a strain of Mesotaenium endlicherianum that has been kept safe in the Algal Culture Collection at Göttingen University (SAG) for over 25 years and the unique experimental set-up there, the researchers exposed Mesotaenium endlicherianum to a continuous range of different light intensities and temperatures. Janine Fürst-Jansen, researcher at the University of Göttingen, states: “Our study began by examining the limits of the alga's resilience – to both light and temperature. We subjected it to a wide temperature range from 8 °C to 29 °C. We were intrigued when we observed the interplay between a broad temperature and light tolerance based on our in-depth physiological analysis.” How the algae respond was not only investigated on a morphological and physiological level, but also by reading the information of about 10 billion RNA snippets. The study used network analysis to investigate the shared behaviour of almost 20,000 genes simultaneously. In these shared patterns, “hub genes” that play a central role in coordinating gene expression in response to various environmental signals were identified. This approach not only offered valuable insights into how algal gene expression is regulated in response to different conditions but, combined with evolutionary analyses, how these mechanisms are common to both land plants and their algal relatives.
Professor Jan de Vries, University of Göttingen, says: “What is so unique about the study is that our network analysis can point to entire toolboxes of genetic mechanisms that were not known to operate in these algae. And when we look at these genetic toolboxes, we find that they are shared across more than 600 million years of plant and algal evolution!” As Armin Dadras, PhD student at the University of Göttingen, explains: "Our analysis allows us to identify which genes collaborate in various plants and algae. It's like discovering which musical notes consistently harmonize in different songs. This insight helps us uncover long-term evolutionary patterns and reveals how certain essential genetic 'notes' have remained consistent across a wide range of plant species, much like timeless melodies that resonate across different music genres.”
Original publication: Dadras A, Fürst-Jansen JMR et al. “Environmental gradients reveal stress hubs predating plant terrestrialization”, Nature Plants 2023 DOI: 10.1038/s41477-023-01491-0
Contact:
Professor Jan de Vries
University of Göttingen
Faculty of Biology and Psychology
Institute of Microbiology and Genetics
Department of Applied Bioinformatics
Goldschmidtstraße 1, 37077 Göttingen, Germany
Tel: +49 (0)551 39-23755
Email: devries.jan@uni-goettingen.de
www.uni-goettingen.de/en/613776.html
END
Algae provide clues about 600 million years of plant evolution
Research team led by Göttingen University investigates 10 billion RNA snippets to identify “hub genes”
2023-08-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Editorial: Epigenetic aging in oocytes
2023-08-30
“In summary, our group demonstrates basic principles in the early aging of mammalian oocytes.”
BUFFALO, NY- August 30, 2023 – A new editorial paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 15, entitled, “Epigenetic aging in oocytes.”
Aging-related phenotypes span many different tissues and cell types, and start to occur at different ages - a different typical age for every cell type. In their new editorial, researchers Peera Wasserzug-Pash and Michael ...
Can taking statins after a bleeding stroke lower risk of another stroke?
2023-08-30
MINNEAPOLIS – People who have had a stroke called an intracerebral hemorrhage who take cholesterol-lowering drugs called statins may have a lower risk of having another stroke, especially ischemic stroke, compared to people who also had an intracerebral hemorrhage but were not taking statins, according to a new study published in the August 30, 2023, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
Intracerebral hemorrhage is caused by bleeding in the brain. Ischemic stroke is caused by a blockage of blood flow to the brain and is the most common type of stroke.
“Previous research has had mixed results on the risk of ...
Stanford-led study reveals way to help prevent childhood stunting
2023-08-30
A relatively small intervention could have a huge impact on a damaging condition that stalks children in the developing world. A new Stanford-led study shows that adding zinc to farmland soil can help prevent childhood stunting, a condition due to chronic undernutrition that is associated with poor brain development and long-lasting harmful consequences, such as reduced school performance and increased disease risks. The paper, published Aug. 21 in Scientific Reports is the first large-scale study to examine the association between children’s nutritional status or health outcomes and soil mineral availability in India, ...
Validation of a comprehensive genomic profiling assay: NeXT Dx™
2023-08-30
“NeXT Dx incorporates a range of features and comprehensive genome variant detection methods that lead to improved disease management and possible enhanced clinical utility.”
BUFFALO, NY- August 30, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on August 30, 2023, entitled, “Analytic validation of NeXT Dx™, a comprehensive genomic profiling assay.”
In this new research paper, researchers Juan-Sebastian Saldivar, Jason Harris, Erin Ayash, Manqing Hong, Prateek Tandon, Saloni Sinha, Patricia Miranda Hebron, Erin E. Houghton, ...
UC Davis names Blake Meyers as new Genome Center director
2023-08-30
Blake Meyers, a principal investigator at the Donald Danforth Plant Science Center and a professor of plant sciences from the University of Missouri - Columbia, has been named the new director and Novozymes Chair in Genomics at the UC Davis Genome Center. Meyers, who studies plant RNA biology, bioinformatics and functional genomics, will step into the role on March 1.
A member of the National Academy of Sciences, Meyers succeeds the center’s founding director Richard Michelmore, a distinguished professor in the departments of Plant Sciences, Molecular and Cellular Biology, and Medical Microbiology and Immunology.
Roots ...
NASA to demonstrate laser communications from space station
2023-08-30
NASA uses the International Space Station — a football field-sized spacecraft orbiting Earth — to learn more about living and working in space. For over 20 years, the space station has provided a unique platform for investigation and research in areas like biology, technology, agriculture, and more. It serves as a home for astronauts conducting experiments, including advancing NASA’s space communications capabilities.
In 2023, NASA is sending a technology demonstration known as the Integrated LCRD Low Earth Orbit User ...
Educational attainment protects against a genetic risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease
2023-08-30
A new study by researchers from Mass General Brigham further illustrates that when it comes to risk of Alzheimer’s disease, even genetically determined forms of the disease, genetics is only one piece of the puzzle. Researchers investigated the influence of genetics and educational attainment on cognitive decline by studying data from 675 people who carry a mutation that predisposes them to early onset Alzheimer’s disease. Carriers of this mutation—known as PSEN1 E280A—have a median age of 49 for onset of dementia. The team found that among ...
Virtual institute at the University of Kansas to combat cyber threats
2023-08-30
LAWRENCE, KANSAS — A new virtual institute established at the University of Kansas School of Engineering will train the next generation of military and civilian leaders to better combat the growing threat of cyberattacks and protect the electromagnetic spectrum (EMS).
KU received a two-year, $1.5 million grant from the Department of Defense to establish the program, known as the Virtual Institutes for Cyber and Electromagnetic Spectrum Research and Employ, or VICEROY, Virtual Institute. The grant is overseen by the Griffiss Institute, which is a nonprofit talent ...
How to write in water?
2023-08-30
Writing is an age-old cultural technique. Thousands of years ago, humans were already carving signs and symbols into stone slabs. Scripts have become far more sophisticated since then but one aspect remains the same: Whether the writer is using cuneiform or a modern alphabet, a solid substrate, such as clay or paper, is required to fix the written structures in place. However, researchers at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU), TU Darmstadt, and Wuhan University asked themselves how to write in a bulk fluid like water without fixing substrates. The concept would not be unlike the way aircraft leave three-dimensional vapor trails behind them when they ...
Stanford Medicine-led study finds genetic factor fends off Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s
2023-08-30
About one in every five people carries a version of a gene that, although largely unsung, appears to confer protection against both Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease, Stanford Medicine investigators and their colleagues have learned. These lucky people may someday benefit all the more from a vaccine that could slow or stall the progression of these two most common neurodegenerative conditions.
An analysis of medical and genetic data from hundreds of thousands of people of diverse ancestries from several continents has revealed ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Breaking through water treatment limits with defect-free, high-efficiency next-generation ceramic filters!
Researchers determine structural motifs of water undecamer cluster
Researchers enhance photocatalytic hydrogen evolution performance of covalent organic frameworks by constitutional isomer strategy
Molecular target drives immunogenicity in cancer immunotherapy
Plant cell structure could hold key to cancer therapies and improved crops
Sustainable hydrogen peroxide production: Breakthroughs in electrocatalyst design for on-site synthesis
Cash rewards for behavior change: A review of financial incentives science in one health contexts and implications
One Health antimicrobial resistance modelling: from science to policy
Artificial feeding platform transforms study of ticks and their diseases
Researchers uncover microscopic mechanism of alkali species dissolution in water clusters
Methionine restriction for cancer therapy: A comprehensive review of mechanisms and clinical applications
White House autism briefing linked to swift shifts in prescribing patterns, study finds
Specialist palliative care can save the NHS up to £8,000 per person and improves quality of life
New research warns charities against ‘AI shortcut’ to empathy
Cannabis compounds show promise in fighting fatty liver disease
Study in mice reveals the brain circuits behind why we help others
Online forum to explore how organic carbon amendments can improve soil health while storing carbon
Turning agricultural plastic waste into valuable chemicals with biochar catalysts
Hidden viral networks in soil microplastics may shape the future of sustainable agriculture
Americans don’t just fear driverless cars will crash — they fear mass job losses
Mayo Clinic researchers find combination therapy reduces effects of ‘zombie cells’ in diabetic kidney disease
Preventing breast cancer resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors using genomic findings
Carbon nanotube fiber ‘textile’ heaters could help industry electrify high-temperature gas heating
Improving your biological age gap is associated with better brain health
Learning makes brain cells work together, not apart
Engineers improve infrared devices using century-old materials
Physicists mathematically create the first ‘ideal glass’
Microbe exposure may not protect against developing allergic disease
Forest damage in Europe to rise by around 20% by 2100 even if warming is limited to 2°C
Rapid population growth helped koala’s recovery from severe genetic bottleneck
[Press-News.org] Algae provide clues about 600 million years of plant evolutionResearch team led by Göttingen University investigates 10 billion RNA snippets to identify “hub genes”