(Press-News.org) As climate change continues to pose severe challenges to ensuring sustainable food supplies around the world, scientists from McGill University are looking for ways to improve the resilience and nutritional quality of potatoes. Professor Martina Strömvik and her team have created a potato super pangenome to identify genetic traits that can help produce the next super spud.
“Our super pangenome sheds light on the potato’s genetic diversity and what kinds of genetic traits could potentially be bred into our modern-day crop to make it better,” says Professor Strömvik, who collaborated with researchers across Canada, the Unites States and Peru. “It represents 60 species and is the most extensive collection of genome sequence data for the potato and its relatives to date,” she adds.
A genome is an organism’s complete set of genetic instructions known as the DNA sequence, while a pangenome aims to capture the complete genetic diversity within a species, and a super pangenome also includes multiple species.
Imagining a disease-free and drought or frost-proof potato
The potato is a staple food source for many people around the world – and it’s one of the most important food crops globally, after rice and wheat in terms of human consumption. “Wild potato species can teach us a lot about what genetic traits are critical in adapting to climate change and extreme weather, enhancing nutritional quality, and improving food security,” says Professor Strömvik.
To build the potato pangenome, the researchers used supercomputers to crunch data from public databanks, including gene banks in Canada, the United States, and Peru.
According to the researchers, the pangenome can be used to answer many questions about the evolution of this important crop that was domesticated by Indigenous peoples in the mountains of southern Peru nearly 10,000 years ago. It could also be used to help identify specific genes to create a super spud using traditional breeding or gene editing technology.
“Scientists hope to develop something that can defend against various forms of diseases and better withstand extreme weather like lots of rain, frost, or a drought,” says Professor Strömvik.
About the study
“Pangenome analyses reveal impact of transposable elements and ploidy on the evolution of potato species” by Ilayda Bozan, Sai Reddy Achakkagari, Noelle L. Anglin, David Ellis, Helen H. Tai, and Martina V. Strömvik was published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
END
The search for the super potato
Scientists have assembled the genome sequences of nearly 300 varieties of potatoes and its wild relatives to develop more nutritious, disease-free, and weather-proof crop
2023-08-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Better paths yield better AI
2023-08-31
Deep Learning (DL) performs classification tasks using a series of layers. To effectively execute these tasks, local decisions are performed progressively along the layers. But can we perform an all-encompassing decision by choosing the most influential path to the output rather than performing these decisions locally?
In an article published today in Scientific Reports, researchers from Bar-Ilan University in Israel answer this question with a resounding "yes". Pre-existing deep architectures have been improved by updating the most influential paths to the output.
"One can ...
Children’s books are still Whiter, and more male, than US society
2023-08-31
A new paper in the Quarterly Journal of Economics, published by Oxford University Press, finds that children’s books in the United States continue to underrepresent ethnic minorities. In addition, it finds that male characters are overrepresented in such stories and children are often presented with lighter skin tones for no apparent editorial reason.
Education teaches children about the world, its people, and their place in it. Much of this happens through the books society presents to children ...
New insight for stabilizing halide perovskite via thiocyanate substitution
2023-08-31
α-FAPbI3, a promising solar cell material with a cubic perovskite structure that is metastable at room temperature, can be stabilized by introducing a pseudo-halide ion like thiocyanate (SCN–) into its structure, demonstrated by Tokyo Tech researchers in a new study. Their finding provides new insights into the stabilization of the α-phase via grain boundary and pseudo-halide engineering.
The light we receive every day from the Sun, if harnessed efficiently, can help us tackle the ongoing global energy crisis as well as our concern with climate change. Materials with good photophysical properties, i.e., light absorption, ...
Scientists develop finger sweat test to detect antipsychotic drugs in patients
2023-08-31
Antipsychotic drugs treat incredibly vulnerable patients. Maintaining a treatment regimen is difficult for many patients, but not taking the medication is associated with a higher risk of poor health outcomes. These drugs are also very powerful with strong side-effects, and blood tests are often used to calibrate a patient’s dosage and confirm that they are taking the recommended dose.
However, blood tests are invasive and potentially uncomfortable. Scientists have now discovered a way to test the levels of common antipsychotic drugs in the sweat ...
Acting fast when an epidemic hits
2023-08-31
A team of researchers at the University of Waterloo and Dalhousie University have developed a method for forecasting the short-term progression of an epidemic using extremely limited amounts of data.
Their model, the Sparsity and Delay Embedding-based Forecasting model, or SPADE4, uses machine learning to predict the progression of an epidemic using only limited infection data. SPADE4 was tested on both simulated epidemics and real data from the fifth wave of the Covid-19 pandemic in Canada and successfully predicted the epidemics’ progressions with 95 per cent confidence.
“Covid taught us that we really need to come up with methods ...
Tracking the ol' mutation trail
2023-08-31
Kyoto, Japan -- From the early stages of cell mutations starting in puberty to their manifestations as breast cancer in later years, the entire process has remained shrouded in mystery.
Now, a team of researchers at Kyoto University has revealed the mechanism by which breast cancer is formed in the cells of the mammalian epithelium, whose main function is to secrete milk.
According to the team's first analysis, approximately 20 mutations accumulate annually in each epithelial cell until menopause. After menopause, however, the mutation rate significantlydecreases.
"Additionally, our results suggest ...
When the gig is up; gig workers don’t always trust their boss and that might be a good thing
2023-08-31
DURHAM, N.H. — As the so-called ‘gig economy’ continues to grow, so do questions about how this type of non-traditional work compares to full time work arrangements and how these new relationships differ and impact performance and commitment. Researchers from the University of New Hampshire took a closer look at gig workers – which include freelancers, independent contractors and temporary workers – and examined relationships between workers and their managers and found that one trait, trust, could be a double-edged sword.
“Millions of workers are now considered gig workers, offering them more flexibility ...
Tracking drivers’ eyes can determine ability to take back control from ‘auto-pilot’ mode
2023-08-31
A team of UCL-led researchers has developed a new method to determine the attention levels of drivers and their readiness to respond to warning signals when using auto-pilot mode.
The research, published in Cognitive Research: Principles and Implications, found that people’s attention levels and how engrossed they are in on-screen activities can be detected from their eye movements.
The findings suggest a new way to determine the readiness of drivers using auto-pilot mode to respond to real world signals, such as takeover requests from the car.
Although fully autonomous driverless cars are not yet available for personal use, cars with a “driverless” auto-pilot ...
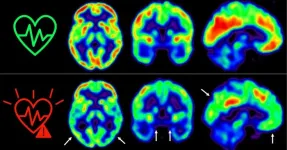
Early action to control cardiovascular risk factors preserves brain metabolism
2023-08-31
Cardiovascular disease and dementia frequently occur together in elderly people. Nevertheless, few longitudinal studies have examined how atherosclerosis and its associated risk factors affect brain health from middle age. Now, a new study by scientists at the Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares (CNIC) in Madrid provides new data on this relationship; the results confirm the importance of controlling traditional cardiovascular risk factors, such as hypertension, cholesterol, diabetes, smoking, ...
Avoid cannabis during adolescence, pregnancy and while driving, say experts
2023-08-31
Experts recommend avoiding cannabis during adolescence and early adulthood, in people prone to or with mental health disorders, in pregnancy, and before and while driving, based on an in-depth evidence review published by The BMJ today.
However, they say cannabidiol (one active compound in cannabis) is effective in people with epilepsy, and cannabis based medicines can help people with multiple sclerosis, chronic pain, inflammatory bowel disease, and in palliative care.
Their recommendations are based on an “umbrella review” of 101 meta-analyses on cannabis ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Does online sports gambling affect substance use behaviors?
How do rapid socio-environmental transitions reshape cancer risk?
Do abortion bans affect birth rates and food-assistance costs?
Can artificial intelligence help reduce the carbon footprint of weather forecasting models?
Mangrove forests are short of breath
Low testosterone, high fructose: A recipe for liver disaster
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
[Press-News.org] The search for the super potatoScientists have assembled the genome sequences of nearly 300 varieties of potatoes and its wild relatives to develop more nutritious, disease-free, and weather-proof crop