(Press-News.org) Kyoto, Japan -- From the early stages of cell mutations starting in puberty to their manifestations as breast cancer in later years, the entire process has remained shrouded in mystery.
Now, a team of researchers at Kyoto University has revealed the mechanism by which breast cancer is formed in the cells of the mammalian epithelium, whose main function is to secrete milk.
According to the team's first analysis, approximately 20 mutations accumulate annually in each epithelial cell until menopause. After menopause, however, the mutation rate significantlydecreases.
"Additionally, our results suggest that estrogen influences mutation accumulation in mammary epithelium, which correlates with our discovery of decreased accumulation after childbirth," says corresponding author Seishi Ogawa of KyotoU's Graduate School of Medicine.
As 70% of breast cancers are understood to be estrogen-sensitive, Ogawa's team may shed light on estrogen's role in the initiation of breast cancer.
Further investigation of the genetic relationship between breast cancer, its surrounding lesions, and normal epithelial cells led to mapping breast cancer's translocation-positive expansion. During this expansion process, cells of multiple origins that would subsequently develop breast cancer manifested themselves at the average age of 30. Previous studies have focused on driver mutations -- the genetic changes in cells that are already cancerous -- leading to abnormal growth. But these findings only paint a partial picture of the process and do not reveal the timing and order of driver mutations or cancer formation.
"Normal-looking tissues may already contain numerous populations of non-cancer cells -- or clones -- that have acquired mutations in cancer-related genes," says co-author author Tomomi Nishimuraof KyotoU's Graduate School of Medicine.
After examining the similarities and differences in the mutations of both cancer and non-cancer lesions originating from the clones, the team reconstructed an evolutionary tree to visualize the unique pattern of cancer evolution.
"Our study brings us closer to exposing the clinical profile of estrogen-sensitive breast cancer, particularly in pre-menopausal women, potentially aiding cancer risk monitoring and prevention," adds Ogawa.
###
The paper "Evolutionary histories of breast cancer and related clones" appeared on 26 July 2023 in Nature, with doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06333-9
About Kyoto University
Kyoto University is one of Japan and Asia's premier research institutions, founded in 1897 and responsible for producing numerous Nobel laureates and winners of other prestigious international prizes. A broad curriculum across the arts and sciences at undergraduate and graduate levels complements several research centers, facilities, and offices around Japan and the world. For more information, please see: http://www.kyoto-u.ac.jp/en
END
Tracking the ol' mutation trail
Unraveling the long history of breast cancer formation
2023-08-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
When the gig is up; gig workers don’t always trust their boss and that might be a good thing
2023-08-31
DURHAM, N.H. — As the so-called ‘gig economy’ continues to grow, so do questions about how this type of non-traditional work compares to full time work arrangements and how these new relationships differ and impact performance and commitment. Researchers from the University of New Hampshire took a closer look at gig workers – which include freelancers, independent contractors and temporary workers – and examined relationships between workers and their managers and found that one trait, trust, could be a double-edged sword.
“Millions of workers are now considered gig workers, offering them more flexibility ...
Tracking drivers’ eyes can determine ability to take back control from ‘auto-pilot’ mode
2023-08-31
A team of UCL-led researchers has developed a new method to determine the attention levels of drivers and their readiness to respond to warning signals when using auto-pilot mode.
The research, published in Cognitive Research: Principles and Implications, found that people’s attention levels and how engrossed they are in on-screen activities can be detected from their eye movements.
The findings suggest a new way to determine the readiness of drivers using auto-pilot mode to respond to real world signals, such as takeover requests from the car.
Although fully autonomous driverless cars are not yet available for personal use, cars with a “driverless” auto-pilot ...
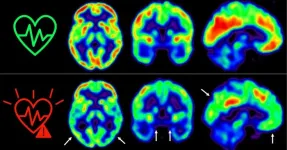
Early action to control cardiovascular risk factors preserves brain metabolism
2023-08-31
Cardiovascular disease and dementia frequently occur together in elderly people. Nevertheless, few longitudinal studies have examined how atherosclerosis and its associated risk factors affect brain health from middle age. Now, a new study by scientists at the Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares (CNIC) in Madrid provides new data on this relationship; the results confirm the importance of controlling traditional cardiovascular risk factors, such as hypertension, cholesterol, diabetes, smoking, ...
Avoid cannabis during adolescence, pregnancy and while driving, say experts
2023-08-31
Experts recommend avoiding cannabis during adolescence and early adulthood, in people prone to or with mental health disorders, in pregnancy, and before and while driving, based on an in-depth evidence review published by The BMJ today.
However, they say cannabidiol (one active compound in cannabis) is effective in people with epilepsy, and cannabis based medicines can help people with multiple sclerosis, chronic pain, inflammatory bowel disease, and in palliative care.
Their recommendations are based on an “umbrella review” of 101 meta-analyses on cannabis ...
Call for action over unreliable private online hormone tests
2023-08-31
A large private laboratory is still processing finger prick tests for oestrogen levels, which are sold by private retailers online, despite warnings they are unreliable, reveals an investigation published by The BMJ today.
Journalist Emma Wilkinson reports that Eurofins, a large laboratory based in the UK, is still carrying out finger prick tests for oestradiol despite problems being identified in 2021 and two other laboratories and one online retailer withdrawing the tests over concerns that the results might not always be accurate.
Finger prick tests for oestradiol are sold by online retailers for between £50 and £180, depending on what is included in ...
Home-monitoring during IVF equally safe and successful
2023-08-31
Home monitoring of ovulation prior to placing frozen embryos during an IVF process works just as well as hospital checks to determine the best time. In addition, it is more pleasant for women to undergo this in their own environment, and it places less burden on the hospital facilities. "Monitoring ovulation at home means a hospital visit once for the placement of these embryos instead of 3 to 4 times for hospital monitoring. This is more sustainable and reduces the cost of treatment by up to 80%," says Tijtske Zaat, researcher at Amsterdam UMC. The study was published today in The Lancet.
To optimize fertility treatments, researchers ...
Treatment for problematic snoring can also reduce night-time heartburn and respiratory symptoms
2023-08-31
A treatment for obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA) can also reduce night-time heartburn, coughing and wheezing according to a study published today (Thursday) in ERJ Open Research [1].
People with OSA often snore loudly, their breathing starts and stops during the night, and they may wake up several times. Not only does this cause tiredness, but it can also increase the risk of high blood pressure, stroke, heart disease and type 2 diabetes.
Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machines work by blowing air through a face mask throughout the night to prevent the user’s airway from closing. CPAP is ...
Boys who smoke in their early teens risk passing on harmful epigenetic traits to future children
2023-08-31
EMBARGOED: NOT FOR RELEASE UNTIL 00.01 BST ON THURSDAY 31 AUGUST 2023.
Boys who smoke in their early teens risk passing on harmful epigenetic traits to future children
People whose fathers smoked in their early teens had epigenetic markers associated with asthma, obesity, and low lung function
Biomarkers associated with paternal preconception smoking were different from those associated with maternal or personal smoking
‘We must act now to stop teenage vaping’ say scientists
A new study suggests boys who smoke in their early teens risk damaging the genes of their future children, increasing their chances of developing ...
Emphasising the need for energy independence could change the views of climate deniers, study says
2023-08-30
Emphasising the need for energy independence and environmental stewardship could help to change people’s minds about the climate crisis, a new study says.
Climate change deniers focus on what they can see and have experienced personally, so solutions need to be framed in a way which makes sense to local communities.
But for this to work the political-media ecosystem also needs to shift to support climate action, and their corporate backers held accountable for the damage they have wrought, according to the research.
The study, published in Ethnos Journal of Anthropology, was carried out by Dr Susannah Crockford from the University of Exeter.
Dr Crockford ...
Study helps explain SARS-CoV-2 variants’ rapid spread
2023-08-30
The omicron variants of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, which have rapidly spread around the world over the past year, latch onto our cells more tightly, invade them more efficiently, and elude many of the antibodies induced by previous infections and vaccines. These are some of the key findings from a multinational team of researchers reporting today in the journal Nature.
The lead authors of the study were Amin Addetia, a graduate student, and Young-Jun Park, a research scientist, in the laboratory of David Veesler, professor of biochemistry at the University of Washington School of Medicine, and Luca Picolli, director ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Enzymes work as Maxwell's demon by using memory stored as motion
Methane’s missing emissions: The underestimated impact of small sources
Beating cancer by eating cancer
How sleep disruption impairs social memory: Oxytocin circuits reveal mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities
Natural compound from pomegranate leaves disrupts disease-causing amyloid
A depression treatment that once took eight weeks may work just as well in one
New study calls for personalized, tiered approach to postpartum care
The hidden breath of cities: Why we need to look closer at public fountains
Rewetting peatlands could unlock more effective carbon removal using biochar
Microplastics discovered in prostate tumors
ACES marks 150 years of the Morrow Plots, our nation's oldest research field
Physicists open door to future, hyper-efficient ‘orbitronic’ devices
$80 million supports research into exceptional longevity
Why the planet doesn’t dry out together: scientists solve a global climate puzzle
Global greening: The Earth’s green wave is shifting
You don't need to be very altruistic to stop an epidemic
Signs on Stone Age objects: Precursor to written language dates back 40,000 years
MIT study reveals climatic fingerprints of wildfires and volcanic eruptions
A shift from the sandlot to the travel team for youth sports
Hair-width LEDs could replace lasers
The hidden infections that refuse to go away: how household practices can stop deadly diseases
Ochsner MD Anderson uses groundbreaking TIL therapy to treat advanced melanoma in adults
A heatshield for ‘never-wet’ surfaces: Rice engineering team repels even near-boiling water with low-cost, scalable coating
Skills from being a birder may change—and benefit—your brain
Waterloo researchers turning plastic waste into vinegar
Measuring the expansion of the universe with cosmic fireworks
How horses whinny: Whistling while singing
US newborn hepatitis B virus vaccination rates
When influencers raise a glass, young viewers want to join them
Exposure to alcohol-related social media content and desire to drink among young adults
[Press-News.org] Tracking the ol' mutation trailUnraveling the long history of breast cancer formation