(Press-News.org) UMC Utrecht will lead an international consortium that will try to answer a key question that’s in the mind of many pediatricians, infectiologists, pulmonologists and other health professionals: “Why are children that had an RSV infection in early childhood at increased risk of developing asthma later in life?” The project - which will run for five years - is funded by a HORIZON HLTH 2023 grant from the European Commission of € 7 million.
Chronic respiratory tract diseases such as asthma and COPD are non-communicable diseases for which infections by several respiratory viruses and genetics constitute major risk factors. The molecular and physiological mechanisms of how these viral infections cause and contribute to non-communicable disease development are unknown. The Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) is a virus that infects nearly all infants before the age of 2 years and is linked to asthma development. However, it is not clear what changes in the immature lungs of susceptible infants that causes later asthma development. It’s also not yet clear how to revert possible damage done by RSV infection to immature lungs.
Interdisciplinary approach
In the CLARITY (Causative Link between respirAtory syncytial viRus and chronic lung diseases: Identifying Targets for therapY) research consortium, the investigators will use an integrative approach to identify genetic risk factors and mechanisms underlying virus-induced asthma. Specifically, using two national cohorts (Estonian and Spanish), they will try to identify human genetic risk factors and RSV strains that contribute to severe bronchiolitis. They will also analyze how RSV perturbs intracellular networks to change cellular properties that trigger asthma development. In addition, researchers will use artificial intelligence-based techniques to integrate generated data with the current biological knowledge, to generate RSV-induced perturbation signatures and to identify druglike compounds that are able to revert the effects of the RSV-induced perturbations. Finally they will validate both mechanisms and candidate compounds in patient derived airway organoid models and, if promising, in a controlled human infection model trial.
Virus-triggered asthma
Immunologist Marianne Boes PhD (Center for Translational Immunology and Department of Pediatrics, UMC Utrecht) is CLARITY project coordinator and principal investigator. She explains: “CLARITY is expected to impact the understanding, prevention and possibly treatment of virus-triggered asthma. The results will enable the development of a genetic risk score for long-term asthma development that enables personalized prevention campaigns, which will be developed jointly with patient groups. The molecular mechanisms discovered, and the drug-like compounds that revert the perturbation signatures, will enable development of mechanism-targeted drugs. Fundamentally, the mechanisms identified in this specific model for a strong viral contribution to non-communicable disease will likely represent general mechanisms of how viral infections cause onset and development of other non-communicable diseases.”
Impact
The expected outcomes of the project are of considerable socio-economic value, since they ultimately aim at reducing disease burden and promoting well-being and empowering patients, their caregivers and the public. The impact of the outcomes will be delivered at multiple levels and may contribute to advancing the management of respiratory diseases, providing to a certain extent real clinical utility, and improving public awareness of RSV and its link with chronic respiratory tract diseases such as asthma and COPD.
CLARITY consortium
In the CLARITY consortium – which will be coordinated by UMC Utrecht – nine partners from four EU countries will collaborate: one university, three clinical centers, one public health organization, three research institutions and one patient organization. The project – which will run for 5 years - is funded by a HORIZON HEALTH 2023 grant of € 7 million from the European Commission, of which close to € 2 million has been allocated to UMC Utrecht.
END
UMC Utrecht investigates the link between RSV infection and chronic respiratory tract disease
2023-09-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study shows making cities greener doesn’t just capture carbon – it reduces it
2023-09-01
Dozens of European cities could reach net zero carbon emissions over the next 10 years by incorporating nature into their infrastructure, according to a new study.
Published recently in the journal, Nature Climate Change, the analysis shows the ways cities can orchestrate a wide range of green solutions like parks, streetscaping and roof gardens to not only capture carbon emissions, but help reduce them.
The study was undertaken by researchers from Sweden, the U.S. and China. It recommends the most effective approaches for natural carbon sequestration in 54 cities in the EU. And it shows how blending these steps with other climate ...
Researchers find Antarctic ice shelves thinner than previously thought
2023-09-01
COLUMBUS, Ohio – As global ice dams begin to weaken due to warming temperatures, a new study suggests that prior attempts to evaluate the mass of the huge floating ice shelves that line the Antarctic ice sheet may have overestimated their thickness.
The research, recently published in the Journal of Glaciology, is the first large-scale study of its kind to compare ice shelf thickness data from ice-penetrating radar measurements to thickness data estimated from contemporary surface elevation measurements.
By juxtaposing vast datasets of 20 of the 300 ...
Di-isononyl phthalate disrupts pregnancy in mice, study finds
2023-09-01
We are constantly exposed to phthalates in our environment through plastic products such as storage containers, medical devices, packages, fabrics, and toys. Specifically, di-isononyl phthalate is inevitably becoming a part of our lives. Unfortunately, the impact of DiNP on the establishment and maintenance of pregnancy is largely unknown. In a new study, researchers used mice to understand how DiNP affects pregnancy.
“Although we finally recognize that environmental chemicals impact women's health, most studies have focused on men’s reproductive health and very few studies have looked at how these chemicals affect women,” said Jodi Flaws (EIRH co-leader/MME), ...
Health System Program Improved Equity in Allocation of Scarce Medication
2023-09-01
A program designed to ensure fairness and that people living in the most disadvantaged U.S. neighborhoods would be offered a scarce, potentially life-saving medication proved feasible in a large health system. The approach can improve equity in receipt of the drug by people disproportionately affected by disease, according to a new analysis published today in JAMA Health Forum by University of Pittsburgh and UPMC scientist-clinicians.
However, the study revealed that more work needs to be done in building trust with and improving the ability to contact Black patients to ensure they ultimately receive scarce medications and other health care resources ...
Weighted lottery to equitably allocate scarce supply of COVID-19 monoclonal antibody
2023-09-01
About The Study: The results of this study suggest that a weighted lottery to allocate scarce resources is feasible and may result in more drug allocation to individuals who reside in disadvantaged neighborhoods and who identify as Black; however, Black individuals allocated the drug may be less likely to accept allocation and receive it.
Authors: Erin K. McCreary, Pharm.D., of the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit ...
Telehealth vs in-clinic medication abortion services
2023-09-01
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest that telehealth medication abortion services (tele-MAB) facilitates abortion care access for those further from brick-and mortar abortion facilities and, thus, may mitigate the impacts of travel logistics and costs. Additionally, tele-MAB may better meet the needs of those with prior abortion experience, perhaps due to greater familiarity with the abortion process.
Authors: Anna E. Fiastro, M.P.H., M.E.M., Ph.D., of the University of Washington in Seattle, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.31900)
Editor’s ...
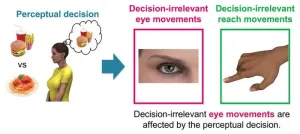
The eyes are a window into the deciding mind
2023-09-01
Researchers worldwide are seeking visible indicators of what is going on inside our minds as we think about issues and take decisions. They are searching for the ability to probe the invisible workings of the mind by monitoring subtle signals from the body. New insights from experiments at Tohoku University have revealed a link between eye movements and certain types of decision-making. Kazumichi Matsumiya and Shota Furukawa at the university's Graduate School of Information Sciences reported their findings in the journal Communications Biology.
"Our work has revealed that eye movements that are not ...
Three types of boreal summer intraseasonal oscillation influence precipitation over the Yangtze river valley in various ways
2023-09-01
The Yangtze River Valley (YRV) is one of the most densely populated and economically developed regions in China. Summer precipitation over this region shows considerable intraseasonal variability with a period of 10–90 days, which can induce extreme precipitation events and lead to massive economic losses and human casualties.
The Boreal Summer Intraseasonal Oscillation (BSISO) is the intraseasonal variability active in the tropical Indian Ocean and western Pacific region. Over the last three decades, scientists have studied the influence of the BSISO, because it is an essential predictability source in extended-range forecasts.
A new study published in Atmospheric ...
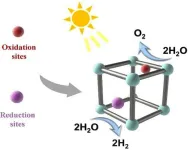
Roadmap drafted for research into metallic ‘sponges’ for clean hydrogen
2023-09-01
Metal organic frameworks (MOFs) could deliver a major efficiency boost to the photocatalytic production of clean hydrogen. Chemical engineers have drafted a comprehensive overview of the state of their field and a plan for where it needs to focus.
Clean hydrogen production remains an energy-intensive and therefore costly proposition, inhibiting the battle against global warming. Metal organic frameworks—in effect tiny molecular ‘sponges’—look set to radically improve the efficiency of photocatalytic production of hydrogen due to their unique structural ...
Radical new approach to managing type 2 diabetes receives $3.5 million from NIH
2023-09-01
The National Institutes of Health has provided $3.5 million for a large-scale clinical trial testing a radical new approach to managing type 2 diabetes that, in an earlier study, put almost 70% of participants in remission without weight loss or medication.
The approach was developed by UVA Health’s Daniel J. Cox, PhD. It is built on the notion that educating people about how to make wise dietary and exercise choices can allow them to control their blood sugar and possibly even alter the course of the disease.
“Instead of focusing on reducing weight with diets ...