(Press-News.org) When the COVID-19 pandemic swept into New Mexico in the spring of 2020, seriously ill patients from all over the state were brought to The University of New Mexico Hospital in Albuquerque, where many wound up in intensive care, breathing with the help of ventilators.
Early on, researchers from the UNM Center for Global Health launched a study of hospitalized patients to gauge the severity of symptoms from the infection, gathering data on 475 patients from April 2020 through December 2021.
In paper published this week in PNAS Nexus, they reported that patients who identified as American Indian/Alaska Native (AI/AN) were sicker and more likely to die in the hospital than Hispanic and non-Hispanic white patients, even though they had fewer pre-existing conditions.
The study was led by Center Director D.J. Perkins, PhD, Professor of Medicine, and Research Associate Professor Ivy Hurwitz, PhD, both of whom donned protective gear to visit the ICU and obtain consent from patients willing to participate in the study.
“There was never an original plan based on race and ethnicity,” Perkins said. “We literally didn’t know about whether there would be disproportionate levels of hospitalization or severe disease.”
Hurwitz added that as they began recruiting patients in the hospital, “We saw a lot of people who were really, really sick in the ICU, and a lot of those people unfortunately were American Indian. It was really sad. They were really suffering disproportionately.”
The researchers collected data on patient demographics, infection duration, blood test results, comorbidities (underlying health risks), treatments that the patients received, major clinical events and in-hospital deaths.
In the patient pool, 47% self-identified as Hispanic, 31% were AI/AN and 19% were non-Hispanic white (the remainder, including Black and Asian American, were excluded from analysis for statistical reasons).
The scientists also assessed comorbid conditions known to worsen outcomes for COVID-19. “COPD, sleep apnea, hyperlipidemia, hypothyroidism, and history of past smoking differed among the groups and was lowest in AI/AN patients,” they wrote. In fact, non-Hispanic whites scored highest overall in comorbidities.
The American Indian patients were also younger on average, but more likely to need ventilators and have blood results indicating more severe disease. They were also more prone to shock and brain injury from the infection and were hospitalized longer.
A similar pattern of relatively severe disease in Native Americans was seen during the 1918 influenza pandemic, historical tuberculosis outbreaks, and the 2009 H1N1 influenza pandemic, the authors noted.
The explanation for the disproportionate burden of severe disease and death in the AI/AN people likely involves multiple factors, the authors wrote, “and may include social determinants of health, as well as potential immunological responses to the virus, among many other non-medical and medical factors.”
An earlier phase of the research prior to emergence of the Delta variant showed that AI/AN patients had significantly higher and protracted SARS-CoV-2 viral loads in their blood.
“In a large group of people, be it pre-Delta or Delta, the strongest predictor of severe disease is virus in the blood and, what travels along with that, because they’re intertwined with their co-variants, is being self-identified American Indian,” Perkins said.
END
Native American patients were sicker and more likely to die during the COVID-19 pandemic, UNM researchers find
2023-09-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New research explains “Atlantification” of the Arctic Ocean
2023-09-01
New research by an international team of scientists explains what’s behind a stalled trend in Arctic Ocean sea ice loss since 2007. The findings indicate that stronger declines in sea ice will occur when an atmospheric feature known as the Arctic dipole reverses itself in its recurring cycle.
The many environmental responses to the Arctic dipole are described in a paper published online today in the journal Science. This analysis helps explain how North Atlantic water influences Arctic Ocean climate. Scientists call it Atlantification.
The research is led by professor Igor Polyakov of the University of Alaska Fairbanks College of ...
Landscape-based methodology reveals ecological stability in the Qingzang plateau
2023-09-01
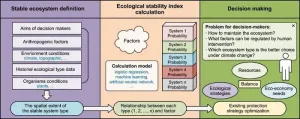
In a groundbreaking study published in Volume 17 of the journal Environmental Science and Ecotechnology, researchers from the Chinese Academy of Sciences introduced a landscape-oriented framework to assess ecological stability in China's Qingzang Plateau (QP). The QP demonstrated a medium-high stability level with minimal changes in recent years. Ecological stability involves understanding changes in ecosystem components over time, with two major concepts explored: systems close to equilibrium and non-equilibrium behavior. Despite lacking a consensus on the definition of "ecological stability", stability indices ...
Research explores why daughters in Chinese families of son preference fail to break from sustained exploitation
2023-09-01
New research from Lancaster University Management School (LUMS) unveils the extent of sustained exploitation within many Chinese families that have a clear preference for sons over daughters – and why daughters can stay ‘trapped’ in this situation throughout their lives.
The new study explores Chinese families that have a strong preference for sons, where daughters are expected to make substantial financial or labour contributions to their parents before and after marriage– often to subsidise the schooling and living ...
Adding immune modulator to targeted therapy does not improve survival in difficult-to-treat thyroid cancer
2023-09-01
Results of a multicenter phase II clinical trial led by the University of Chicago Medicine Comprehensive Cancer Center show that adding an immunomodulatory agent to treatment with the targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) cediranib did not make a difference in outcomes for treating patients with an advanced form of thyroid cancer that develops from thyroid follicular cells called differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC).
The findings were published in Annals of Oncology on May 13, 2023.
Most patients with DTC receive successful treatment. But a small group develops cancer that recurs or spreads to other parts of the body, making it hard to treat with traditional methods like ...
Linking infectious and narcology care is effective in suppressing HIV in people who inject drugs in Russia
2023-09-01
BOSTON – New research from Boston Medical Center found that providing pragmatic support, specifically rapid access to antiretroviral therapy, pharmacotherapy for opioid use disorder, and strengths-based case management, improved treatment outcomes for people with HIV who inject drugs in St. Petersburg, Russia. Published in The Lancet HIV, researchers from the Linking Infectious and Narcology Care – Part II (LINC-II) trial highlight that the odds of achieving viral load suppression at 12 months are 3 times higher for participants randomized to the intervention group.
Russia ...
Study could help explain why certain brain tumors don’t respond well to immunotherapy
2023-09-01
A study led by researchers at the UCLA Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center sheds new light on why tumors that have spread to the brain from other parts of the body respond to immunotherapy while glioblastoma, an aggressive cancer that originates in the brain, does not.
In people with tumors that originated in other parts of the body but spread to the brain, treatment with a type of immunotherapy called immune checkpoint blockade appears to elicit a significant increase in both active and exhausted T cells — signs that the T cells have been triggered to fight the cancer. The ...
Red blood cells exposed to oxygen deficiency protect against myocardial infarction
2023-09-01
Red blood cells exposed to oxygen deficiency protect against myocardial infarction, according to a new KI study published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation. The study also shows that the protective effect is enhanced by a nitrate-rich vegetable diet.
Red blood cells carry oxygen from the lungs to all of the body’s cells and carbon dioxide back to the lungs. A new study, conducted at Karolinska Institutet in collaboration with Karolinska University Hospital, now shows that red blood cells have an intrinsic function of protecting against ...
UMC Utrecht investigates the link between RSV infection and chronic respiratory tract disease
2023-09-01
UMC Utrecht will lead an international consortium that will try to answer a key question that’s in the mind of many pediatricians, infectiologists, pulmonologists and other health professionals: “Why are children that had an RSV infection in early childhood at increased risk of developing asthma later in life?” The project - which will run for five years - is funded by a HORIZON HLTH 2023 grant from the European Commission of € 7 million.
Chronic respiratory tract diseases such as asthma and COPD ...
Study shows making cities greener doesn’t just capture carbon – it reduces it
2023-09-01
Dozens of European cities could reach net zero carbon emissions over the next 10 years by incorporating nature into their infrastructure, according to a new study.
Published recently in the journal, Nature Climate Change, the analysis shows the ways cities can orchestrate a wide range of green solutions like parks, streetscaping and roof gardens to not only capture carbon emissions, but help reduce them.
The study was undertaken by researchers from Sweden, the U.S. and China. It recommends the most effective approaches for natural carbon sequestration in 54 cities in the EU. And it shows how blending these steps with other climate ...
Researchers find Antarctic ice shelves thinner than previously thought
2023-09-01
COLUMBUS, Ohio – As global ice dams begin to weaken due to warming temperatures, a new study suggests that prior attempts to evaluate the mass of the huge floating ice shelves that line the Antarctic ice sheet may have overestimated their thickness.
The research, recently published in the Journal of Glaciology, is the first large-scale study of its kind to compare ice shelf thickness data from ice-penetrating radar measurements to thickness data estimated from contemporary surface elevation measurements.
By juxtaposing vast datasets of 20 of the 300 ...