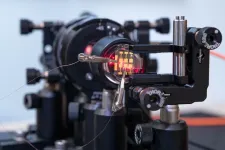
(Press-News.org) Digital information exchange can be safer, cheaper and more environmentally friendly with the help of a new type of random number generator for encryption developed at Linköping University, Sweden. The researchers behind the study believe that the new technology paves the way for a new type of quantum communication.
In an increasingly connected world, cybersecurity is becoming increasingly important to protect not just the individual, but also, for example, national infrastructure and banking systems. And there is an ongoing race between hackers and those trying to protect information. The most common way to protect information is through encryption. So when we send emails, pay bills and shop online, the information is digitally encrypted.
To encrypt information, a random number generator is used, which can either be a computer programme or the hardware itself. The random number generator provides keys that are used to both encrypt and unlock the information at the receiving end.
Different types of random number generators provide different levels of randomness and thus security. Hardware is the much safer option as randomness is controlled by physical processes. And the hardware method that provides the best randomness is based on quantum phenomena – what researchers call the Quantum Random Number Generator, QRNG.
“In cryptography, it’s not only important that the numbers are random, but that you’re the only one who knows about them. With QRNG’s, we can certify that a large amount of the generated bits is private and thus completely secure. And if the laws of quantum physics are true, it should be impossible to eavesdrop without the recipient finding out,” says Guilherme B Xavier, researcher at the Department of Electrical Engineering at Linköping University.
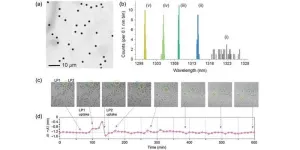
His research group, together with researchers at the Department of Physics, Chemistry and Biology (IFM), has developed a new type of QRNG, that can be used for encryption, but also for betting and computer simulations. The new feature of the Linköping researchers’ QRNG is the use of light emitting diodes made from the crystal-like material perovskite.
Their random number generator is among the best produced and compares well with similar products. Thanks to the properties of perovskites, it has the potential to be cheaper and more environmentally friendly.
Feng Gao is a professor at IFM and has been researching perovskites for over a decade. He believes that the recent development of perovskite light emitting diodes (PeLEDs) means that there is an opportunity to revolutionise, for example, optical instruments.
“It’s possible to use, for example, a traditional laser for QRNG, but it’s expensive. If the technology is eventually to find its way into consumer electronics, it’s important that the cost is kept down and that the production is as environmentally friendly as possible. In addition, PeLEDs don’t require as much energy to run,” says Feng Gao.
The next step is to develop the material further to make the perovskite lead-free and to extend its lifetime, which is currently 22 days. According to Guilherme B Xavier, their new QRNG could be available for use in cybersecurity within five years.
“It’s an advantage if electronic components that are to be used for sensitive data are manufactured in Sweden. If you buy a complete randomness generator kit from another country, you can’t be sure that it’s not being monitored.”
The study was funded by the Swedish Research Council, the Knut and Alice Wallenberg Foundation through the Wallenberg Centre for Quantum Technology and the European Research Council.
END
Better cybersecurity with new material
Quantum random number generation based on a perovskite light emitting diode
2023-09-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
People with lung conditions face extra risks from climate change
2023-09-04
People living with lung conditions, such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), face even greater risks from climate change, according to an expert report published today (Monday) in the European Respiratory Journal [1].
The report brings together evidence on how the effects of climate change, such as heatwaves, wildfires and flooding, will exacerbate breathing difficulties for millions of people around the world, particularly babies, young children and the elderly.
On behalf of the European Respiratory Society, which represents more than 30,000 lung specialists from 160 countries, the authors ...
ChatGPT is debunking myths on social media around vaccine safety, say experts
2023-09-04
ChatGPT could help to increase vaccine uptake by debunking myths around jab safety, say the authors of a study published in the peer-reviewed journal Human Vaccines and Immunotherapeutics.
The researchers asked the artificial intelligence (AI) chatbot the top 50 most frequently-asked Covid-19 vaccine questions. They included queries based on myths and fake stories such as the vaccine causing Long Covid.
Results show that ChatGPT scored nine out of 10 on average for accuracy. The rest of the time it was correct but left some gaps in the information provided, according to the study.
Based on these findings, experts who led the study from the GenPoB research group based ...
Growing evidence supporting the protein leverage hypothesis
2023-09-04
Humans, like many other species, regulate protein intake more strongly than any other dietary component and so if protein is diluted there is a compensatory increase in food intake. The hypothesis proposes that the dilution of protein in modern-day diets by fat and carbohydrate-rich processed foods is driving increased energy intake as the body seeks to satisfy its natural protein drive - eating unnecessary calories until it does so.
This paper, resulting from the Royal Society Discussion Meeting held in London last October, shows that observational, experimental and mechanistic research increasingly supports ...
Why breast cancer survivors don't take their medication, and what can be done
2023-09-02
For roughly 80% of breast cancer survivors, treatment doesn’t end with surgery, radiation and chemotherapy. Instead, for the next five to 10 years, doctors recommend that they take medication to block sex hormones, which can fuel tumor growth and spark recurrence.
The drugs are life-saving: They’ve been shown to cut risk of cancer recurrence by as much as half in patients with hormone receptor-positive tumors (HR+)—the most common form of breast cancer. Yet despite their promised benefits, 40% of patients stop taking them early and a third ...
New scalable, etching-based technique for precise tuning of microdisk lasers
2023-09-02
Micro- and nanodisk lasers have recently emerged as promising optical sources and probes for various applications in the fields of nanophotonics and biomedicine. Their ability to achieve lasing at a deterministic wavelength and ultra-narrowband precision is critical for several applications in on-chip photonic communications, on-chip bioimaging, biochemical sensing, and quantum photonic information processing. However, the large-scale fabrication of such precise wavelength micro- and nanodisk lasers remains challenging. Current nanofabrication processes introduce randomness in ...
Seismologists use deep learning for improved earthquake forecasting
2023-09-02
For more than 30 years, the models that researchers and government agencies use to forecast earthquake aftershocks have remained largely unchanged. While these older models work well with limited data, they struggle with the huge seismology datasets that are now available.
To address this limitation, a team of researchers at the University of California, Santa Cruz and the Technical University of Munich created a new model that uses deep learning to forecast aftershocks: the Recurrent Earthquake foreCAST (RECAST). In a paper published today in Geophysical Research Letters, the scientists show how the deep learning model is more flexible ...
Software developed at UC Davis analyzes calcium ‘sparks’ that can contribute to arrhythmia
2023-09-01
(SACRAMENTO, Calif.) — A team of UC Davis and University of Oxford researchers have developed an innovative tool: SparkMaster 2. The open-source software allows scientists to analyze normal and abnormal calcium signals in cells automatically.
Calcium is a key signaling molecule in all cells, including muscles like the heart. The new software enables the automatic analysis of distinct patterns of calcium release in cells. This includes calcium "sparks," microscopic releases of calcium within cardiac cells associated ...
Could insights from ants help people build better transportation networks?
2023-09-01
Key takeaways
Ants can either forage for food as individuals or recruit other members of their colonies to help search for or carry food back to their nests.
UCLA biologists found that the strategies ants use to forage play a bigger role in how they build their nests than innate, evolutionary “blueprints” do.
When building nests, ants strike a balance between transportation efficiency and architectural constraints. Researchers say that observation could help humans design more efficient transportation systems tailored to specific needs.
Could ants’ nests hold the secret to reducing traffic congestion on the 405 Freeway?
In a new study, UCLA biologists ...
Invasive spotted lanternfly may not damage hardwood trees as previously thought
2023-09-01
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — In 2012, when the spotted lanternfly (Lycorma delicatula) arrived in the U.S. from its home in China, scientists, land managers, and growers were understandably concerned that the sap-feeding insect would damage native and commercial trees. New long-term research led by Penn State has discovered that hardwood trees, such as maple, willow and birch, may be less vulnerable than initially thought.
“Since the lanternfly was first introduced to the northeastern U.S., the question has been, ‘How at-risk are our forests?’ said Kelli Hoover, professor of entomology at Penn State. “So far, we haven't had a good answer. Our study is the first ...
$26M NIH grant addresses environmental influences on child health
2023-09-01
EAST LANSING, Mich. – Backed by a $26 million federal grant, researchers at three Michigan universities, a leading health care system, and a state agency will continue a long-term study of how exposure to environmental factors during pregnancy and early childhood can impact health for a lifetime.
The funding from the National Institutes of Health, or NIH, is for the second phase of a national research program called ECHO, which stands for the Environmental Influences on Child Health Outcomes, and includes a sample of mothers, infants and children from across the United States. The first phase began in 2016.
“This award shows the research ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] Better cybersecurity with new materialQuantum random number generation based on a perovskite light emitting diode