(Press-News.org) Halle/Saale, Fort Lauderdale. More than 100 years of observations in nature have revealed a universal pattern of species abundances: Most species are rare but not very rare, and only a few species are very common. These so-called global species abundance distributions have become fully unveiled for some well-monitored species groups, such as birds. For other species groups, such as insects, however, the veil remains partially unlifted. These are the findings of an international team of researchers led by the German Centre for Integrative Biodiversity Research (iDiv), the Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU) and the University of Florida (UF), published in the journal Nature Ecology and Evolution. The study demonstrates how important biodiversity monitoring is for detecting species abundances on planet Earth and for understanding how they change.
“Who can explain why one species ranges widely and is very numerous, and why another allied species has a narrow range and is rare?” This question was asked by Charles Darwin in his ground-breaking book “The Origin of Species”, published over 150 years ago. A related challenge has been to understand how many species are common (numerous) and how many are rare, the so-called global species abundance distribution (gSAD).
Two main gSAD models have been proposed in the last century: R. A. Fisher, a statistician and biologist, proposed that most species are very rare and that the number of species declines for more common species (so-called log-series model). On the other hand, F. W. Preston, an engineer and ecologist, argued that only few species are actually very rare and that most species have some intermediate level of commonness (so-called log-normal model). However, until now and despite decades of research, scientists did not know which model describes the planet’s true gSAD.
Solving this problem calls for vast amounts of data. The study authors used data from the Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF) and downloaded data representing over 1 billion species observations in nature from 1900 to 2019.
“The GBIF database is an amazing resource for all sorts of biodiversity related research, particularly because it brings together both data collected from professional and citizen scientists all over the world,” says first author Dr Corey Callaghan. He began the study while working at iDiv and MLU and is now working at the UF.
Callaghan and his fellow researchers divided the downloaded data into 39 species groups, for instance, birds, insects, or mammals. For each, they compiled the respective global species abundance distribution (gSAD).
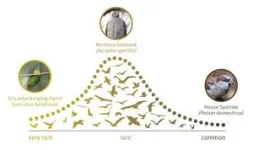
The researchers detected a potentially universal pattern, which emerges once the species abundance distribution is fully unveiled: Most species are rare but not very rare, and only a few species are very common, as predicted in the log-normal model. However, the researchers also found that the veil has been fully lifted only for a few species groups like cycads and birds. For all other species groups, the data are yet insufficient.
“If you don’t have enough data, it looks as though most species are very rare,” says senior author Prof Henrique Pereira, research group head at iDiv and the MLU. “But by adding more and more observations, the picture changes. You start seeing that there are, in fact, more rare species than very rare species. You can see this shift for cycads and birds when comparing the species observations from back in 1900, when less data was available, with the more comprehensive species observations we have today. It is fascinating: we can clearly see the phenomenon of unveiling the full species abundance distribution, as predicted by Preston several decades ago, but only now demonstrated at the scale of the entire planet.”
“Even though we have been recording observations for decades, we have only lifted the veil for a few species groups,” says Callaghan. “We still have a long way to go. But GBIF and the sharing of data really represents the future of biodiversity research and monitoring, to me.”
The new study's findings enable scientists to assess how far the gSADs have been unveiled for different species groups. This allows for answering another long-standing research question: How many species are out there? This study finds that while for some groups like birds, nearly all species have been identified, this is not the case for other taxa such as insects and cephalopods.
The researchers believe that their findings may help in answering Darwin’s question of why some species are rare, and others are common. The universal pattern they found may point to general ecological or evolutionary mechanisms that govern the commonness and rarity of species. While more research is being done, humans continue to alter the planet’s surface and the abundance of species, for instance, by making common species less common. This complicates the researchers’ task: They need not only to understand how species abundances evolve naturally but also how human impacts are altering these patterns simultaneously. There may still be a long way to go before Darwin’s question is finally answered.
END
Most species are rare. But not very rare
Over time, biodiversity observations around the world have unveiled a potential universal pattern of how many species are common, very rare or somewhere in-between
2023-09-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Extreme El Niño weather saw South America’s forest carbon sink switch off
2023-09-04
Extreme El Niño weather saw South America’s forest carbon sink switch off
Hot and dry conditions resulted in increased tree death
Evidence that most forest areas withstand periods of severe drought
Greatest impact in forests with drier climates
Tropical forests in South America lose their ability to absorb carbon from the atmosphere when conditions become exceptionally hot and dry, according to new research.
For a long time, tropical forests have acted as a carbon sink, taking more ...
Blowing snow contributes to Arctic warming
2023-09-04
When it comes to global warming trends, the Arctic is a troubling outlier. The Arctic warms nearly four times faster than the global average, and aerosols play an important role in that warming. Scientists have long known that pollutants from other regions can accumulate in the Arctic atmosphere where they alter atmospheric chemistry, absorb sunlight, and affect local weather patterns, leading to localized warming that melts ice and snow. Sea salt particles dominate aerosol mass concentration, but their production mechanisms and impact on Arctic climate have remained unclear.
Atmospheric scientists led by Jian Wang, director of the Center for Aerosol ...
Innovative solutions for chemical challenges: Harnessing the potential of machine learning
2023-09-04
In a review published in Engineering, scientists explore the burgeoning field of machine learning (ML) and its applications in chemistry. Titled “Machine Learning for Chemistry: Basics and Applications,” this comprehensive review aims to bridge the gap between chemists and modern ML algorithms, providing insights into the potential of ML in revolutionizing chemical research.
Over the past decade, ML and artificial intelligence (AI) have made remarkable strides, bringing us closer to the realization of intelligent machines. The advent of deep learning methods and enhanced data storage capabilities has played a pivotal role in this progress. ML has already demonstrated success ...
Uncovering thalassemia diversity in southern china through next-generation sequencing
2023-09-04
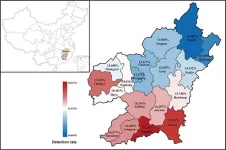
Around 5.2% of the global population carries abnormal hemoglobin genes [1]. Each year, 300,000 to 500,000 children are born with severe hemoglobinopathies worldwide, with approximately 80% of these cases occurring in developing countries [2]. Thalassemia is the most common hereditary hemoglobinopathy and occurs in 4.4 out of every 10,000 live births [3]. It is prevalent in Mediterranean coastal areas, Africa, the Middle East, Southeast Asia, and southern China.
A previous study indicated that Ganzhou, the southernmost city in Jiangxi province, had a thalassemia prevalence ...
NYU Abu Dhabi researchers develop novel tumor-targeting nanospheres with the potential to dramatically improve light-based cancer diagnosis and treatment
2023-09-04
Abu Dhabi, UAE (September 4, 2023) – In a breakthrough in cancer therapeutics, a team of researchers at the Magzoub Biophysics Lab at NYU Abu Dhabi (NYUAD) has made a significant advance in light-based therapies – biocompatible and biodegradable tumor-targeting nanospheres that combine tumor detection and monitoring with potent, light-triggered cancer therapy to dramatically increase the efficacy of existing light-based approaches.
Non-invasive, light-based therapies, photodynamic therapy (PDT) and photothermal therapy (PTT) have the potential to be safe and effective alternatives to conventional cancer treatments, which are beset by a ...
Ecosystem footprint concept and its potential applications in environmental management
2023-09-04
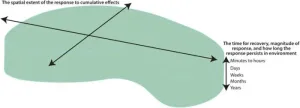
Traditionally, the impact of human activity on an ecosystem has lacked context when planning restorative ecosystem mitigation and management strategies. Multiple human activities over time and space, the resilience of a particular ecosystem, and the stress caused by many individual or related, overlapping activities that generate cumulative effects may affect the overall "ecosystem response footprint," or ability of an ecosystem to adapt and change to human activity.
A team of marine scientists reviewed the most recent perspectives on ecological footprints to rigorously define the term "ecosystem response footprint" as the ...
First-in-class targeted microRNA therapy slows cancer tumor growth
2023-09-04
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. – A new cancer therapy developed by Purdue University researchers attacks tumors by tricking cancer cells into absorbing a snippet of RNA that naturally blocks cell division. As reported today in Oncogene, tumors treated with the new therapy did not increase in size over the course of a 21-day study, while untreated tumors tripled in size over the same time period.
Cancer can begin almost anywhere in the human body. It is characterized by cells that divide uncontrollably and that may be able to ignore signals to ...
Invasive Alien Species Pose Major Global Threats to Nature, Economies, Food Security and Human Health: IPBES report
2023-09-04
The severe global threat posed by invasive alien species is underappreciated, underestimated, and often unacknowledged. According to a major new report by the Intergovernmental Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES), more than 37,000 alien species have been introduced by many human activities to regions and biomes around the world. This conservative estimate is now rising at unprecedented rates. More than 3,500 of these are harmful invasive alien species – seriously threatening nature, nature’s contributions to people and good quality of life. Too often ignored until it is too late, invasive alien species are a ...
Korean Scientific payload for observing the lunar space environment begins its transfer to the US for the scheduled 2024 launch
2023-09-04
The Ministry of Science and ICT (Minister Jong-Ho Lee, hereinafter referred to as 'MSIT') and the Korea Astronomy and Space Science Institute (Director Young-Deuk Park, hereinafter referred to as 'KASI') announced the beginning of the transfer of the lunar space environment monitor, 'LUSEM'(Lunar Space Environment Monitor) that will be aboard United States’ unmanned lunar lander in 2024, has began on September 4th.
LUSEM is a payload developed by the Korea Astronomy and Space Science Institute (KASI) in participation with the U.S. NASA's CLPS(Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative ...
IOP Publishing appoints Dr. David Gevaux as Chief Editor of Reports on Progress in Physics
2023-09-04
IOP Publishing (IOPP) has appointed Dr. David Gevaux as the first Chief Editor of Reports on Progress in Physics. Taking up the post from the 4th of September, Dr. Gevaux will lead on ambitious plans for the journal, as its scope expands to include groundbreaking new research content alongside the authoritative reviews for which it is well known across all areas of physics.
Working closely with Professor Subir Sachdev, the Editor in Chief of Reports on Progress in Physics, Dr. Gevaux will champion the editorial ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
This ancient plant-eater had a twisted jaw and sideways-facing teeth
Jackdaw chicks listen to adults to learn about predators
Toxic algal bloom has taken a heavy toll on mental health
Beyond silicon: SKKU team presents Indium Selenide roadmap for ultra-low-power AI and quantum computing
Sugar comforts newborn babies during painful procedures
Pollen exposure linked to poorer exam results taken at the end of secondary school
7 hours 18 mins may be optimal sleep length for avoiding type 2 diabetes precursor
Around 6 deaths a year linked to clubbing in the UK
Children’s development set back years by Covid lockdowns, study reveals
Four decades of data give unique insight into the Sun’s inner life
Urban trees can absorb more CO₂ than cars emit during summer
Fund for Science and Technology awards $15 million to Scripps Oceanography
New NIH grant advances Lupus protein research
New farm-scale biochar system could cut agricultural emissions by 75 percent while removing carbon from the atmosphere
From herbal waste to high performance clean water material: Turning traditional medicine residues into powerful biochar
New sulfur-iron biochar shows powerful ability to lock up arsenic and cadmium in contaminated soils
AI-driven chart review accurately identifies potential rare disease trial participants in new study
Paleontologist Stephen Chester and colleagues reveal new clues about early primate evolution
UF research finds a gentler way to treat aggressive gum disease
Strong alcohol policy could reduce cancer in Canada
Air pollution from wildfires linked to higher rate of stroke
Tiny flows, big insights: microfluidics system boosts super-resolution microscopy
Pennington Biomedical researcher publishes editorial in leading American Heart Association journal
New tool reveals the secrets of HIV-infected cells
HMH scientists calculate breathing-brain wave rhythms in deepest sleep
Electron microscopy shows ‘mouse bite’ defects in semiconductors
Ochsner Children's CEO joins Make-A-Wish Board
Research spotlight: Exploring the neural basis of visual imagination
Wildlife imaging shows that AI models aren’t as smart as we think
Prolonged drought linked to instability in key nitrogen-cycling microbes in Connecticut salt marsh
[Press-News.org] Most species are rare. But not very rareOver time, biodiversity observations around the world have unveiled a potential universal pattern of how many species are common, very rare or somewhere in-between