(Press-News.org) OAK BROOK, Ill. – Using a standardized assessment, researchers in the UK compared the performance of a commercially available artificial intelligence (AI) algorithm with human readers of screening mammograms. Results of their findings were published in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Mammographic screening does not detect every breast cancer. False-positive interpretations can result in women without cancer undergoing unnecessary imaging and biopsy. To improve the sensitivity and specificity of screening mammography, one solution is to have two readers interpret every mammogram.
According to the researchers, double reading increases cancer detection rates by 6 to 15% and keeps recall rates low. However, this strategy is labor-intensive and difficult to achieve during reader shortages.
“There is a lot of pressure to deploy AI quickly to solve these problems, but we need to get it right to protect women’s health,” said Yan Chen, Ph.D., professor of digital screening at the University of Nottingham, United Kingdom.
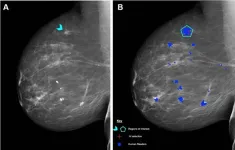
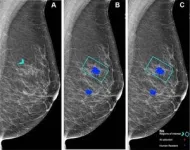
Prof. Chen and her research team used test sets from the Personal Performance in Mammographic Screening, or PERFORMS, quality assurance assessment utilized by the UK’s National Health Service Breast Screening Program (NHSBSP), to compare the performance of human readers with AI. A single PERFORMS test consists of 60 challenging exams from the NHSBSP with abnormal, benign and normal findings. For each test mammogram, the reader’s score is compared to the ground truth of the AI results.
“It’s really important that human readers working in breast cancer screening demonstrate satisfactory performance,” she said. “The same will be true for AI once it enters clinical practice.”
The research team used data from two consecutive PERFORMS test sets, or 120 screening mammograms, and the same two sets to evaluate the performance of the AI algorithm. The researchers compared the AI test scores with the scores of the 552 human readers, including 315 (57%) board-certified radiologists and 237 non-radiologist readers consisting of 206 radiographers and 31 breast clinicians.
“The 552 readers in our study represent 68% of readers in the NHSBSP, so this provides a robust performance comparison between human readers and AI,” Prof. Chen said.
Treating each breast separately, there were 161/240 (67%) normal breasts, 70/240 (29%) breasts with malignancies, and 9/240 (4%) benign breasts. Masses were the most common malignant mammographic feature (45/70 or 64.3%), followed by calcifications (9/70 or 12.9%), asymmetries (8/70 or 11.4%), and architectural distortions (8/70 or 11.4%). The mean size of malignant lesions was 15.5 mm.
No difference in performance was observed between AI and human readers in the detection of breast cancer in 120 exams. Human reader performance demonstrated mean 90% sensitivity and 76% specificity. AI was comparable in sensitivity (91%) and specificity (77%) compared to human readers.
“The results of this study provide strong supporting evidence that AI for breast cancer screening can perform as well as human readers,” Prof. Chen said.
Prof. Chen said more research is needed before AI can be used as a second reader in clinical practice.
“I think it is too early to say precisely how we will ultimately use AI in breast screening,” she said. “The large prospective clinical trials that are ongoing will tell us more. But no matter how we use AI, the ability to provide ongoing performance monitoring will be crucial to its success.”
Prof. Chen said it’s important to recognize that AI performance can drift over time, and algorithms can be affected by changes in the operating environment.
“It’s vital that imaging centers have a process in place to provide ongoing monitoring of AI once it becomes part of clinical practice,” she said. “There are no other studies to date that have compared such a large number of human reader performance in routine quality assurance test sets to AI, so this study may provide a model for assessing AI performance in a real-world setting.”
###
“Performance of a Breast Cancer Detection AI Algorithm Using the Personal Performance in Mammographic Screening Scheme.” Collaborating with Dr. Chen were Adnan G. Taib, B.M.B.S., Iain T. Darker, Ph.D., and Jonathan J. James, FRCR.
In 2023, Radiology is celebrating its 100th anniversary with 12 centennial issues, highlighting Radiology’s legacy of publishing exceptional and practical science to improve patient care.
Radiology is edited by Linda Moy, M.D., New York University, New York, N.Y., and owned and published by the Radiological Society of North America, Inc. (https://pubs.rsna.org/journal/radiology)
RSNA is an association of radiologists, radiation oncologists, medical physicists and related scientists promoting excellence in patient care and health care delivery through education, research and technologic innovation. The Society is based in Oak Brook, Illinois. (RSNA.org)
For patient-friendly information on breast cancer screening, visit RadiologyInfo.org.
END
A Perspective sheds light on why megaprojects take so long and cost so much—and what can be done to prevent the problem. Why did Boston’s “Big Dig” building project go 19 billion dollars over budget and take 9 years longer than anticipated? Globally, between $6 trillion and $9 trillion is spent on megaprojects every year, including everything from space telescopes to wind farms. In the United States, the recently passed $1 trillion infrastructure bill means a new era of megaprojects is at hand. In a Perspective, Guru Madhavan and colleagues review the causes behind ballooning costs and extended timelines for such megaprojects. Problems include premature ...
Researchers have developed an energy-efficient computing-based chip with smell-sensing units that can detect food spoilage and provides real-time conditions continuously throughout the spoilage process. The system is described in a study published in Advanced Science.
Other electronic noses, or artificial olfactory systems (AOSs), have been developed in the past, but they have numerous limitations, including high energy consumption, time delays, and data loss.
The AOS developed in this study requires little energy and integrates sensing and computing units on the same chip. It detects food spoilage by employing thin zinc oxide ...
Sending an email with a forged address is easier than previously thought, due to flaws in the process that allows email forwarding, according to a research team led by computer scientists at the University of California San Diego.
The issues researchers uncovered have a broad impact, affecting the integrity of email sent from tens of thousands of domains, including those representing organizations in the U.S. government–such as the majority of U.S. cabinet email domains, including state.gov, ...
Sept. 5, 2023 – In a new report posted online in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, a global consensus conference of 32 critical care experts with broad international representation and from diverse backgrounds has proposed a new definition of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). In addition to the experts, critical care societies from around the world provided input, once they received feedback from their members. The report, which builds on the 2012 Berlin Definition of ARDS, will be published Jan. 1, 2024 in the American Thoracic Society’s AJRCCM.
ARDS is a life-threatening illness in which the lungs ...
AMES, IA – During Frito-Lay's first "Crash the Super Bowl" contest in 2006, thousands of participants submitted 30-second videos promoting Doritos. Entries were winnowed down to five finalists, and a public vote selected the winning commercial, which aired during the most watched American television broadcast of the year.
The ad boosted Doritos sales and pulled in awards, sparking other big brands, like Nestlé, BMW and Fisher-Price, to launch their own crowdsourcing contests.
"Crowdsourcing has become more prevalent over the last decade. It can generate innovative ideas and solutions and engage ...
A new opinion piece published in Health Affairs Forefront raises questions around current approaches to assess drug safety and effectiveness in people with obesity. The article sheds light on how increased body fat can modify the effects of drugs used to treat common conditions, in some cases rendering the drugs ineffective or unsafe for people with obesity.
The article, titled “Assessments Of Drug Safety And Effectiveness Continue To Fail People With Obesity,” argues that drug manufacturers should be required to show correct dosing instructions on their labels ...
Over the course of four weeks this summer, a motley crew of biologists, engineers, entrepreneurs and programmers gathered at predetermined sites within Windsor Nature Park, a 185-acre tropical rainforest located in the heart of Singapore. They’d traveled from all over the world to participate in a one-of-a-kind competition hosted by the XPRIZE Foundation, in which 13 teams would have three days to identify as many organisms within the forest as possible.
Up to 10 winning teams would equally split $2 million and advance to the 2024 finals, where they’d vie for the first-place prize of $5 million. But there was a catch: All observations and data collection ...
Approximately 95% of the world’s food supply is directly or indirectly produced on soil, according to the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Soil health is therefore critical to the health of all living organisms—especially plants. Equally as critical, resources that consider the overlap between soil’s mineral nutrition and plant diseases have been scarce, until members of the American Phytopathological Society (APS) recognized this gap.
APS PRESS has newly published an updated edition of the first book to successfully combine the two important plant science disciplines of nutrition and pathology. Mineral Nutrition and Plant Disease, ...
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Seven years after an initial $17.9 million award from the National Institutes of Health, the Illinois Kids Development Study at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign will receive approximately $13.7 million – awarded in two phases – to continue its work for another seven years. The money coming to Illinois is part of a national collaborative effort to explore how environmental exposures influence child development, cognition, growth and health.
IKIDS is part of Environmental Influences on Child Health Outcomes, a national initiative to study five ...
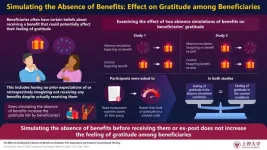
Gratitude is a strong emotion, usually felt by a person who benefits from an intentional good deed of another person. Receiving gifts or benefits can instill a feeling of gratitude in people who receive them, i.e., beneficiaries, encouraging them to be more prosocial, while also helping to create a bond with their benefactors. This has led several researchers to examine the determinants of gratitude. Interestingly, beneficiaries often have preconceived beliefs about receiving a benefit. For instance, they may have no prior expectations of receiving a ...