(Press-News.org) About The Study: In a study of children ages 16 to 30 months assessed for autism in six specialty clinics, eye-tracking–based measurement of social visual engagement was predictive of autism diagnoses by clinical experts. Further evaluation of this test’s role in early diagnosis and assessment of autism in routine specialty clinic practice is warranted.
Authors: Warren Jones, Ph.D., of Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2023.13295)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/10.1001/jama.2023.13295?guestAccessKey=6082eb9c-4502-43de-aca9-e5d85de85263&utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=090523
END
Eye-tracking–based measurement of social visual engagement compared with expert clinical diagnosis of autism
JAMA
2023-09-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Measurements of social visual engagement to aid early diagnosis and assessment of autism
2023-09-05
About The Study: In two diagnostic studies of 1,089 children younger than age 3, objective eye-tracking–based measurements of social visual engagement quantified diagnostic status as well as individual levels of social disability, verbal ability, and nonverbal ability in autism. These findings suggest that objective measurements of social visual engagement can be used to aid in autism diagnosis and assessment.
Authors: Warren Jones, Ph.D., of Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link ...
Measuring children’s looking behavior yields new tool to help diagnose autism earlier, research shows
2023-09-05
ATLANTA (September 5, 2023) – Results of clinical studies published simultaneously today in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) and in JAMA Network Open demonstrate that measuring children’s looking behavior predicts expert clinical diagnosis of autism in children between ages 16 to 30 months tested with a high degree of accuracy. According to researchers from Marcus Autism Center, a subsidiary of Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta, this new tool can help clinicians diagnose autism earlier while also providing objective measurements of each child’s strengths and vulnerabilities, to help jumpstart effective support for child ...
Linking two solar technologies is a win-win for efficiency and stability
2023-09-05
While conventional silicon-based solar cells have had an unmistakable impact on the buildout of renewable energy resources around the world, additional performance improvements have become increasingly difficult to make as the devices approach their practical efficiency limits. This constraint has prompted scientists to seek out new technologies that can be combined with silicon cells to unlock higher efficiencies.
Solar cells made with crystals called perovskites are one such technology that have rapidly emerged as an appealing low-cost add-on, but perovskite cells are notoriously susceptible to voltage-induced ...
Why are male kidneys more vulnerable to disease than female kidneys? USC Stem Cell-led mouse study points to testosterone
2023-09-05
Female kidneys are known to be more resilient to disease and injury, but males need not despair. A new USC Stem Cell-led study published in Developmental Cell describes not only how sex hormones drive differences in male and female mouse kidneys, but also how lowering testosterone can “feminize” this organ and improve its resilience.
“By exploring how differences emerge in male and female kidneys during development, we can better understand how to address sex-related health disparities for patients with kidney ...
Racial and socioeconomic differences still determine survival rates of premature babies in the US
2023-09-05
The US continues to face stark inequalities in preterm birth and mortality rates between mothers of differing socioeconomic status and race, finds a new report led by UCL researchers.
The study, published in JAMA Paediatrics, examined data from the US National Centre for Health Statistics Birth Infant/Death Dataset, of over 12 million preterm infant births over the course of 25 years, between 1995 and 2020.
Preterm birth is defined as any infant born before 37 weeks and is the leading cause of infant death ...
3D-printed ‘living material’ could clean up contaminated water
2023-09-05
Researchers at the University of California San Diego have developed a new type of material that could offer a sustainable and eco-friendly solution to clean pollutants from water.
Dubbed an “engineered living material,” it is a 3D-printed structure made of a seaweed-based polymer combined with bacteria that have been genetically engineered to produce an enzyme that transforms various organic pollutants into benign molecules. The bacteria were also engineered to self-destruct in the presence ...
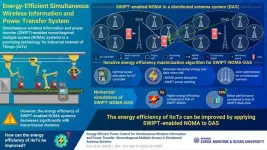
KMOU scientists develop an energy-efficient wireless power and information transfer system
2023-09-05
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoTs) refers to a technology that combines wireless sensors, controllers, and mobile communication technologies to make every aspect of industrial production processes intelligent and efficient. Since IIoTs can involve several small battery-driven devices and sensors, there is a growing need to develop a robust network for data transmission and power transfer to monitor the IIoT environment.
In this regard, wireless power transfer is a promising technology. It utilizes radio frequency signals to power small devices that consume minimal power. Recently, simultaneous wireless information ...
ERC starting grants: 400 bright minds awarded over €628 million
2023-09-05
This funding, part of the EU’s Horizon Europe programme, will be invested in scientific projects spanning all disciplines of research. For example, a geochemist in the Netherlands will study Venus’ atmosphere to better understand habitability beyond Earth; a computer scientist in Germany seeks to make virtual reality more inclusive to physically disabled people; a geneticist in the UK aims to analyse parasites that cause malaria; and a researcher in Israel is set to investigate how algorithms are used at work to supervise employees.
ERC President Professor Maria Leptin said: “It is part of our mission to give early-career talent the independence to pursue ambitious ...
Dr. Niels Schröter wins ERC Starting Grant
2023-09-05
This is the first ERC Starting Grant to be hosted at the Max Planck Institute of Microstructure Physics. ChiralTopMat aims to provide the direct experimental observation of chiral spin-hedgehogs in structurally chiral crystals and to explore ways to control their properties for applications in magnetic memory devices. Moreover, another focus will be to test the stability of topological Berry curvature monopoles against strong electronic interactions that Schröter’s group recently discovered in a chiral topological semimetal, a material that combines structural ...
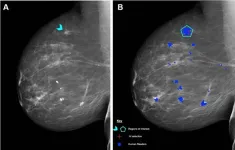
AI performs comparably to human readers of mammograms
2023-09-05
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Using a standardized assessment, researchers in the UK compared the performance of a commercially available artificial intelligence (AI) algorithm with human readers of screening mammograms. Results of their findings were published in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Mammographic screening does not detect every breast cancer. False-positive interpretations can result in women without cancer undergoing unnecessary imaging and biopsy. To improve the sensitivity and specificity of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] Eye-tracking–based measurement of social visual engagement compared with expert clinical diagnosis of autismJAMA