(Press-News.org) About The Study: In this study of 633,000 children treated in 586 emergency departments across 11 states, mortality of Black children was greater than that of white children at all quartile levels of readiness among those with acute medical emergencies but not traumatic injuries. Increased readiness was associated with decreased mortality overall, and it decreased most for Black children with acute medical emergencies.
Authors: Peter C. Jenkins, M.D., M.Sc., of the Indiana University School of Medicine in Indianapolis, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.32160)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.32160?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=090523
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is an online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
END
Emergency department pediatric readiness and disparities in mortality based on race and ethnicity
JAMA Network Open
2023-09-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Cardiac arrest survival at EMS agencies in catchment areas with primarily Black and Hispanic populations
2023-09-05
About The Study: Risk-standardized survival rates for out-of-hospital cardiac arrest were 1.9% lower at emergency medical service (EMS) agencies working in Black and Hispanic catchment areas than in white catchment areas in this study including 764 EMS agencies. This difference was not explained by EMS response times, rates of EMS termination of resuscitation, or first responder rates of initiating cardiopulmonary resuscitation or applying an automated external defibrillator. These findings suggest there is a need for further assessment of these discrepancies.
Authors: Paul S. Chan, M.D., M.Sc., Saint Luke’s Hospital ...
Eye-tracking–based measurement of social visual engagement compared with expert clinical diagnosis of autism
2023-09-05
About The Study: In a study of children ages 16 to 30 months assessed for autism in six specialty clinics, eye-tracking–based measurement of social visual engagement was predictive of autism diagnoses by clinical experts. Further evaluation of this test’s role in early diagnosis and assessment of autism in routine specialty clinic practice is warranted.
Authors: Warren Jones, Ph.D., of Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2023.13295)
Editor’s ...
Measurements of social visual engagement to aid early diagnosis and assessment of autism
2023-09-05
About The Study: In two diagnostic studies of 1,089 children younger than age 3, objective eye-tracking–based measurements of social visual engagement quantified diagnostic status as well as individual levels of social disability, verbal ability, and nonverbal ability in autism. These findings suggest that objective measurements of social visual engagement can be used to aid in autism diagnosis and assessment.
Authors: Warren Jones, Ph.D., of Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link ...
Measuring children’s looking behavior yields new tool to help diagnose autism earlier, research shows
2023-09-05
ATLANTA (September 5, 2023) – Results of clinical studies published simultaneously today in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) and in JAMA Network Open demonstrate that measuring children’s looking behavior predicts expert clinical diagnosis of autism in children between ages 16 to 30 months tested with a high degree of accuracy. According to researchers from Marcus Autism Center, a subsidiary of Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta, this new tool can help clinicians diagnose autism earlier while also providing objective measurements of each child’s strengths and vulnerabilities, to help jumpstart effective support for child ...
Linking two solar technologies is a win-win for efficiency and stability
2023-09-05
While conventional silicon-based solar cells have had an unmistakable impact on the buildout of renewable energy resources around the world, additional performance improvements have become increasingly difficult to make as the devices approach their practical efficiency limits. This constraint has prompted scientists to seek out new technologies that can be combined with silicon cells to unlock higher efficiencies.
Solar cells made with crystals called perovskites are one such technology that have rapidly emerged as an appealing low-cost add-on, but perovskite cells are notoriously susceptible to voltage-induced ...
Why are male kidneys more vulnerable to disease than female kidneys? USC Stem Cell-led mouse study points to testosterone
2023-09-05
Female kidneys are known to be more resilient to disease and injury, but males need not despair. A new USC Stem Cell-led study published in Developmental Cell describes not only how sex hormones drive differences in male and female mouse kidneys, but also how lowering testosterone can “feminize” this organ and improve its resilience.
“By exploring how differences emerge in male and female kidneys during development, we can better understand how to address sex-related health disparities for patients with kidney ...
Racial and socioeconomic differences still determine survival rates of premature babies in the US
2023-09-05
The US continues to face stark inequalities in preterm birth and mortality rates between mothers of differing socioeconomic status and race, finds a new report led by UCL researchers.
The study, published in JAMA Paediatrics, examined data from the US National Centre for Health Statistics Birth Infant/Death Dataset, of over 12 million preterm infant births over the course of 25 years, between 1995 and 2020.
Preterm birth is defined as any infant born before 37 weeks and is the leading cause of infant death ...
3D-printed ‘living material’ could clean up contaminated water
2023-09-05
Researchers at the University of California San Diego have developed a new type of material that could offer a sustainable and eco-friendly solution to clean pollutants from water.
Dubbed an “engineered living material,” it is a 3D-printed structure made of a seaweed-based polymer combined with bacteria that have been genetically engineered to produce an enzyme that transforms various organic pollutants into benign molecules. The bacteria were also engineered to self-destruct in the presence ...
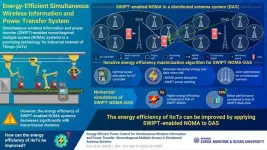
KMOU scientists develop an energy-efficient wireless power and information transfer system
2023-09-05
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoTs) refers to a technology that combines wireless sensors, controllers, and mobile communication technologies to make every aspect of industrial production processes intelligent and efficient. Since IIoTs can involve several small battery-driven devices and sensors, there is a growing need to develop a robust network for data transmission and power transfer to monitor the IIoT environment.
In this regard, wireless power transfer is a promising technology. It utilizes radio frequency signals to power small devices that consume minimal power. Recently, simultaneous wireless information ...
ERC starting grants: 400 bright minds awarded over €628 million
2023-09-05
This funding, part of the EU’s Horizon Europe programme, will be invested in scientific projects spanning all disciplines of research. For example, a geochemist in the Netherlands will study Venus’ atmosphere to better understand habitability beyond Earth; a computer scientist in Germany seeks to make virtual reality more inclusive to physically disabled people; a geneticist in the UK aims to analyse parasites that cause malaria; and a researcher in Israel is set to investigate how algorithms are used at work to supervise employees.
ERC President Professor Maria Leptin said: “It is part of our mission to give early-career talent the independence to pursue ambitious ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Advancing brain–computer interfaces for rehabilitation and assistive technologies
Detecting Alzheimer's with DNA aptamers—new tool for an easy blood test
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal study develops radiomics model to predict secondary decompressive craniectomy
New molecular switch that boosts tooth regeneration discovered
Jeonbuk National University researchers track mineral growth on bioorganic coatings in real time at nanoscale
Convergence in the Canopy: Why the Gracixalus weii treefrog sounds like a songbird
Subway systems are uncomfortably hot — and worsening
Granular activated carbon-sorbed PFAS can be used to extract lithium from brine
How AI is integrated into clinical workflow lowers medical liability perception
New biotech company to accelerate treatments for heart disease
One gene makes the difference: research team achieves breakthrough in breeding winter-hardy faba beans
Predicting brain health with a smartwatch
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
Thousands of genetic variants shape epilepsy risk, and most remain hidden
First comprehensive sex-specific atlas of GLP-1 in the mouse brain reveals why blockbuster weight-loss drugs may work differently in females and males
When rats run, their gut bacteria rewrite the chemical conversation with the brain
Movies reconstructed from mouse brain activity
Subglacial weathering may have slowed Earth's escape from snowball Earth
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
[Press-News.org] Emergency department pediatric readiness and disparities in mortality based on race and ethnicityJAMA Network Open