(Press-News.org) About The Study: This study found large increases in cannabis involvement in emergency department visits for traffic injury over time in Ontario, Canada, which may have accelerated following nonmedical cannabis commercialization. Although the frequency of visits was rare, they may reflect broader changes in cannabis-impaired driving. Greater prevention efforts, including targeted education and policy measures, in regions with legal cannabis are indicated.
Authors: Daniel T. Myran, M.D., M.P.H., of the University of Ottawa in Ottawa, Ontario, Canada, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.31551)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.31551?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=090623
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is an online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
END
Cannabis-involved traffic injury emergency department visits after cannabis legalization and commercialization
JAMA Network Open
2023-09-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Furthest ever detection of a galaxy’s magnetic field
2023-09-06
Using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), astronomers have detected the magnetic field of a galaxy so far away that its light has taken more than 11 billion years to reach us: we see it as it was when the Universe was just 2.5 billion years old. The result provides astronomers with vital clues about how the magnetic fields of galaxies like our own Milky Way came to be.
Lots of astronomical bodies in the Universe have magnetic fields, whether it be planets, stars or galaxies. “Many people ...
The first organic oscillator that makes catalysis swing
2023-09-06
Oscillating chemical systems are present at nearly every popular chemistry exhibition – especially the ones that display striking colour changes. But so far there are very few practical uses for these types of reactions beyond timekeeping. In nature, on the other hand, many important life processes such as cell division and circadian rhythms involve oscillations. Scientists at the University of Groningen have now developed an oscillating system that contains a catalyst, and exhibits periodic catalytic activity: this synthetic chemical oscillator can do more than just keep time. A description of this ...
Scripps Research chemists devise a method for C-H activation of alcohols
2023-09-06
LA JOLLA, CA—Scripps Research chemists have extended a powerful molecule-building method—called C-H activation—to the broad class of chemicals known as alcohols.
The synthetic chemistry feat, reported in Nature on September 6, 2023, follows the development of C-H activation techniques for the three other major classes of organic molecule—amines, acids and ketones—that are used to construct pharmaceuticals. It gives chemists a versatile new toolkit for making drugs and other valuable compounds now using the alcohol chemical class; moreover, its ...
Pitt researchers to study Alzheimer’s disease in marmosets
2023-09-06
PITTSBURGH – To reimagine existing preclinical trials for Alzheimer’s disease, University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine neuroscientists created the first non-human primate model of hereditary Alzheimer's in marmoset monkeys, outlining their approach in Alzheimer's & Dementia: Translational Research & Clinical Interventions.
Researchers are now working on characterizing and validating genetic, molecular, functional and cognitive features of aging and Alzheimer’s disease in marmosets that harbor mutations in the same gene that is linked to early-onset disease in humans. Scientists hope to accelerate the pace of the ...
Oral health deteriorates before and after bariatric surgery, study shows
2023-09-06
Oral health deteriorates in morbidly obese people on a diet in preparation for bariatric surgery and patients who have undergone the procedure, with increasing caries, gingivitis and periodontitis. This is the conclusion of a study conducted by researchers at the Federal University of São Paulo (UNIFESP) in Brazil. Articles on the study are published in the Journal of Oral Rehabilitation and Clinical Oral Investigations, stressing the importance of participation by a dentist in the assessment of bariatric patients.
The study was funded by FAPESP (projects 17/26400-6 and 16/10940-9), following 100 patients divided into two groups (dietary ...
Patients with AML who received vitamin C/D supplements had fewer complications, but no overall survival benefit seen
2023-09-06
Patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) who received vitamin C and D supplements while undergoing intensive chemotherapy had lower rates of complications, such as infections, bleeding, and inflammation, when compared with similar, previously treated patients who did not receive these supplements. Moreover, while the study showed no difference in survival between the two groups, a subgroup analysis showed that among patients with a genetic mutation known as NPM1 – found in about one in three patients with AML – the risk of death was nearly 50% lower among those ...
University of Colorado ophthalmologists administer novel treatment for single patient facing rare genetic condition
2023-09-06
Thirteen-year-old Grace Hoyt received potentially the best birthday gift ever this month when pediatric ophthalmologists at the University of Colorado School of Medicine and Children’s Hospital Colorado administered the first treatment designed specifically to slow her vision loss associated with posterior column ataxia with retinitis pigmentosa (PCARP), a rare genetic condition that affects vision and the nervous system.
“It’s so incredible that she has this opportunity,” Susan Hoyt says of her daughter, who received the first treatment Aug. 24. “We’ve known that Grace is going to go blind, but to have ...
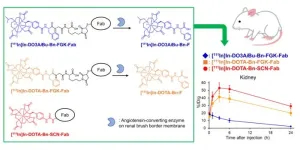
Novel molecular design for enhanced efficacy and safety in radiotheranostics
2023-09-06
Radiotheranostics embodies the convergence of diagnostic and therapeutic radiopharmaceuticals into a unified platform. In cancer treatment, radiotheranostic procedures typically involve the use of antibodies that bind to proteins abundantly found on the surface of cancerous cells. The antibodies are labeled with a suitable radioisotope, which facilitates imaging procedures used to diagnose cancer and can be used to target cancerous cells and bombard them with deadly radiation as a form of treatment.
Although radiolabeled antibodies show promise as a treatment for cancer, several hurdles impede their clinical translation. ...
Potential target for reversing drug resistance in ovarian cancer identified
2023-09-06
For the 314,000 people diagnosed with ovarian cancer each year, hope often comes in the form of platinum-based drugs such as cisplatin.
Cisplatin causes the death of quick-dividing tumour cells, so it is a potent first-line defence in the treatment of the often fatal disease.
However, over half of ovarian cancer patients develop recurrence and become resistant to cisplatin and other platinum-based chemotherapies, contributing to the five-year survival rate of 31%.
It is unclear why this resistance occurs, but a solution is urgently ...
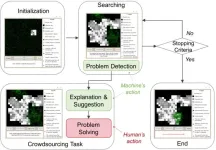
Human-AI collaboration improves source search outcomes
2023-09-06
When artificial intelligence robots that have been designed to use algorithms to complete source search tasks, such as search and rescue operations during a fire, encounter a disturbance, they are often unable to complete their task. Proposed solutions have ranged from trying to improve algorithms to introducing additional robots, but these AI-driven robots still encounter fatal problems.
Researchers have proposed a solution: a human-AI collaboration that takes advantages of the unique skills of the human brain to overcome challenges.
The paper was published in the Journal of Social ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
Major discovery sparks chain reactions in medicine, recyclable plastics - and more
[Press-News.org] Cannabis-involved traffic injury emergency department visits after cannabis legalization and commercializationJAMA Network Open