(Press-News.org) Remembering the order of information is central for a person when participating in conversations, planning everyday life, or undergoing an education. A new study, published in the scientific journal PLoS One, shows that this ability is probably human unique. Even the closest relatives of humans, such as bonobos, do not learn order in the same way.
“The study contributes another piece of the puzzle to the question of how the mental abilities of humans and other animals differ, and why only humans speak languages, plan space travel, and have learned to exploit the earth so efficiently that we now pose a serious threat to countless other life forms”, says Johan Lind, associate professor in ethology and deputy director at the Center for Cultural Evolution, Stockholm University. Since September also associate professor of ethology at Linköping University.
Already earlier research at Stockholm University has suggested that only humans have the ability to recognize and remember so-called sequential information, and that this ability is a fundamental building block underlying unique human cultural abilities. But previously, this sequence memory-hypothesis has not been tested in humans' closest relatives, the great apes. The new experiments now show that also bonobos, one of the great apes, struggle to learn the order of stimuli.
In the recently published book The Human Evolutionary Transition: From Animal Intelligence to Culture (Princeton University Press), ethologists Magnus Enquist and Johan Lind at Stockholm University, and Stefano Ghirlanda, researcher in psychology at Brooklyn College, New York, have launched a new theory for how humans became cultural beings. A central idea concerns the difference in how humans and other animals recognize and remember sequential information.
“We have previously analyzed a large number of studies that suggest that only humans recognize and remember sequential information faithfully. But, even though we analyzed data from a number of mammals and birds, including monkeys, there has been a lack of information from our closest relatives, the other great apes”, says Johan Lind.
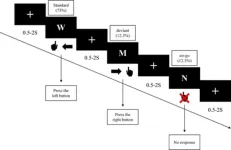
In a series of experiments, memory abilities of bonobos and humans were tested by having them press computer screens to, among other things, learn to distinguish between short sequences, including pressing right if a yellow square comes before a blue square, or by pressing to the left of the blue square appears before the yellow square.
“The study shows that bonobos forget that they have seen a blue square already five to 10 seconds after it has disappeared from the screen, and that they have great difficulty learning to distinguish the sequences blue-square-before-yellow-square from yellow-square- before-blue-square, even though they have been trained for thousands of trials”, says Vera Vinken, associated with Stockholm University, now a PhD student in Great Britain at the Biosciences Institute, Newcastle University.
In contrast, the study shows that humans learned to distinguish the short sequences nearly immediately. However, it still remains to be shown exactly how our closest relatives can remember and use sequential information.
“We now know that our closest relatives do not share the same sequential mental abilities with humans. But even if the results indicate that their working memory works in principle in the same way as in rats and pigeons, no one has yet demonstrated this in practice”, says Magnus Enquist, professor emeritus and one of the founders of the Center for Cultural Evolution.
The new results provide further support for the sequence memory-hypothesis, that during human prehistory an ability to remember and process sequences evolved, a necessary mechanism for many uniquely human phenomena such as language, planning ability and sequential thinking.
END
The sense of order distinguishes humans from other animals
2023-09-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Footballers wearing jerseys featuring small numbers are rated as more slender than those wearing big numbers, in experiments indicating how visual perception may be influenced by cognition
2023-09-06
Footballers wearing jerseys featuring small numbers are rated as more slender than those wearing big numbers, in experiments indicating how visual perception may be influenced by cognition
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0287474
Article Title: Big number, big body: Jersey numbers alter body size perception
Author Countries: USA
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
New battery holds promise for green energy
2023-09-06
Jimmy Jiang envisions a future where every house is powered by renewable energy stored in batteries.
In his chemistry lab, Jiang and his students at the University of Cincinnati have created a new battery that could have profound implications for the large-scale energy storage needed by wind and solar farms.
Innovations such as UC’s will have profound effects on green energy, Jiang said. Batteries store renewable energy for when it’s needed, not just when it’s produced. This is crucial for getting the most out of wind and solar power, he said.
“Energy ...
Amish found to be under-vaccinated for COVID-19 but not unvaccinated
2023-09-06
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — This summer, viral misinformation claimed that the Amish did not vaccinate against COVID-19 and, as a result, had a death rate 90 times lower than the rest of the United States. Now, a Penn State study is the first to provide geographically broad and population-wide evidence that while the Amish-populated counties across the nation tend to have lower vaccination rates than other populations, they are not entirely unvaccinated.
The research was published recently in the journal Population Research and Policy Review.
The Amish are a distinctive Christian subculture that traces its roots to the 16th century Protestant ...
Groundbreaking study reveals new insights into behavioral inhibitory control through functional neuroimaging
2023-09-06
A recent article published in Volume 3 of the journal Psychoradiology, researchers from Sichuan Normal University introduced an innovative Three-Choice BIC paradigm that merges the GNG and two-choice oddball (TCO) tasks. This study engaged 48 college students who responded to varied stimuli using designated keys and restrained responses to no-go stimuli. Employing functional neuroimaging coupled with conjunction and ROI analyses, the researchers sought to unveil unique neural pathways linked to BIC ...
Stress test abnormalities reveal more than just cardiovascular risks, Mayo Clinic study finds
2023-09-06
ROCHESTER, Minn. — The treadmill exercise test with electrocardiogram (ECG), also known as an exercise stress test, is one of the most familiar tests in medicine. While exercise testing typically is focused on diagnosing coronary artery disease, a recent study from Mayo Clinic finds that exercise test abnormalities, such as low functional aerobic capacity, predicted non-cardiovascular causes of death such as cancer in addition to cardiovascular-related deaths. These new findings are published in Mayo Clinic Proceedings.
The exercise stress test is noninvasive, easily available and provides important diagnostic information. In addition to the ECG itself, ...
Canine health data to guide new cancer study
2023-09-06
DENVER/Sept. 6, 2023 — A newly funded study will evaluate both the frequency and major risk factors for cancer in golden retrievers, a breed commonly affected by the disease.
The study will use data from Morris Animal Foundation’s Golden Retriever Lifetime Study, which is one of the largest and most comprehensive canine health studies in the world. The study will also incorporate data from Veterinary Companion Animal Surveillance System (VetCompass), a not-for-profit research project based at the Royal Veterinary College ...
Insomnia drug helps prevent oxycodone relapse, Scripps Research study shows
2023-09-06
LA JOLLA, CA—A good night’s sleep has many proven health benefits, and a new Scripps Research study suggests one more: preventing opioid relapse.
In the new study, published online in Neuropharmacology on August 12, 2023, scientists gave an experimental insomnia treatment to rats experiencing oxycodone withdrawal. The researchers found that the animals were far less likely to seek out drugs again in the future—even after ending the treatment. These findings could eventually lead to therapies to help prevent opioid addiction or relapse in humans.
“These results are very encouraging,” says Rémi Martin-Fardon, PhD, associate professor of molecular medicine ...
Disease affects blackbirds more than previously thought
2023-09-06
The researchers studied birds given a simulated bacterial infection in order to stimulate their immune system. The birds were then compared with birds whose immune system was not stimulated – and their activity was measured for several weeks using miniature data loggers.
“We found that the birds whose immune system was stimulated had reduced activity for three weeks, which is much longer than we expected. We could also see that the "sick" blackbirds stopped their activities ...
The António Champalimaud Vision Award 2023 distinguishes St John of Jerusalem Eye Hospital for their fight against blindness in Palestine
2023-09-06
The 2023 edition of the António Champalimaud Vision Award recognizes the St John of Jerusalem Eye Hospital Group (SJEHG) for its work supporting hundreds of thousands of people living in the Gaza Strip, West Bank and East Jerusalem, helping in the fight against blindness while providing access to essential health services in a region marked by conflict and instability.
The SJEHG has been developing its activity at the centre of three major world religions. The ongoing conflict in the region has had a severe impact on health care access and delivery. Without the intervention of the SJEHG, the rate of blindness would be rampant, increasing ...
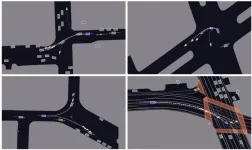
CityU’s novel AI system enhances the predictive accuracy of autonomous driving
2023-09-06
Precisive real-time prediction of the movement of nearby vehicles or the future trajectory of pedestrians is essential for safe autonomous driving. A research team led by City University of Hong Kong (CityU) recently developed a novel AI system that improves predictive accuracy amid dense traffic and increases computational efficiency by over 85%, offering great potential for enhancing the safety of autonomous vehicles.
Professor Wang Jianping, in the Department of Computer Science (CS) at CityU, who led the study, explained the critical importance ...