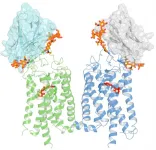
(Press-News.org) A team of scientists from the University of California, Irvine, believe they have discovered a special antibody which may lead to a treatment for Retinitis Pigmentosa, a condition that causes loss of central vision, as well as night and color vision.
The study, Structural basis for the allosteric modulation of rhodopsin by nanobody binding to its extracellular domain, was published in Nature Communications. Authors of the study were Arum Wu, PhD, David Salom, PhD, John D. Hong, Aleksander Tworak, PhD, Philip D. Kiser, PharmD, PhD, and Krzysztof Palczewski, PhD, in the Department of Ophthalmology, Gavin Herbert Eye Institute, at the University of California, Irvine. Research was conducted in collaboration with Jan Steyaert, PhD, at the Vrije Universiteit Brussel (VUB).
Retinitis Pigmentosa (RP) is a group of inherited eye diseases that affect the retina in the back of the eye. It is caused by the death of cells that detect light signals, known as photoreceptor cells. There is no known cure for RP, and the development of new treatments for this condition relies on cell and gene therapies.
UCI researchers have targeted their study on a specific molecule which they believe will provide a treatment for Rhodopsin-associated autosomal dominant RP (adRP). The molecule, Rhodopsin, is a key light-sensing molecule in the human retina. It is found in rod photoreceptor cells, and mutations in the Rhodopsin gene are a primary cause of adRP.
“More than 150 mutations in rhodopsin can cause Retinitis Pigmentosa, making it challenging to develop targeted gene therapies,” said Krzysztof Palczewski, PhD, Donald Bren Professor, UCI School of Medicine. “However due to the high prevalence of RP, there has been significant investment in research and development efforts to find novel treatments.”
Although Rhodopsin has been studied for over a century, key details of its mechanism for converting light into a cellular signal have been difficult to experimentally address.
For this study, researchers used a special type of llama-derived antibody, known as a nanobody, that can halt the process of Rhodopsin photoactivation, allowing it to be investigated at high resolution.
“Our team has developed nanobodies that work through a novel mechanism of action. These nanobodies have high specificity and can recognize the target rhodopsin extracellularly,” said David Salom , PhD, researcher and project scientist, UCI School of Medicine. “This enables us to lock this GPCR in a non-signaling state.”
Scientists discovered that these nanobodies target an unexpected site on the Rhodopsin molecule, near the location where retinaldehyde binds. They also found that the stabilizing effect of these nanobodies can also be applied to Rhodopsin mutants that are associated with retinal disease, suggesting their use as therapeutics.
“In the future, we hope to involve the in vitro evolution of these initial set of nanobodies,” said Arum Wu, PhD, researcher and project scientist, UCI School of Medicine. “We will also evaluate the safety and effectiveness of a future nanobody gene therapy for RP.”
Researchers hope to improve nanobodies’ ability to recognize Rhodopsin from other species including mice, for which several pre-clinical models of adRP are available. They also have plans to use these nanobodies to address a long-term goal in the field of structurally resolving the key intermediate states of Rhodopsin from the inactive state to the fully ligand-activated state.
About the UCI School of Medicine
Each year, the UCI School of Medicine educates more than 400 medical students and nearly 150 PhD and MS students. More than 700 residents and fellows are trained at the UCI Medical Center and affiliated institutions. Multiple MD, PhD and MS degrees are offered. Students are encouraged to pursue an expansive range of interests and options. For medical students, there are numerous concurrent dual degree programs, including an MD/MBA, MD/MPH, or an MD/MS degree through one of three mission-based programs: the Health Education to Advance Leaders in Integrative Medicine (HEAL-IM), the Program in Medical Education for Leadership Education to Advance Diversity-African, Black and Caribbean (PRIME LEAD-ABC), and the Program in Medical Education for the Latino Community (PRIME-LC). The UCI School of Medicine is accredited by the Liaison Committee on Medical Accreditation and ranks among the top 50 nationwide for research. For more information, visit https://medschool.uci.edu/
END
UC Irvine researchers discover a nanobody which may lead to treatment for Retinitis Pigmentosa
A special antibody derived from llamas —called a nanobody — can stop the misfolding and the activation of Rhodopsin, a molecule whose mutations can lead to blindness.
2023-09-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Use of common painkillers alongside hormonal contraception linked to heightened risk of blood clots
2023-09-07
Women who use non-steroidal anti-inflammatory painkillers alongside hormonal contraception appear to be at a small increased risk of blood clots known as venous thromboembolism (VTE), finds a large Danish study published by The BMJ today.
The risk was greater in women using combined oral contraceptives containing third or fourth generation progestins, but smaller in women using progestin-only tablets, implants and coils, alongside the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) ibuprofen, diclofenac, and naproxen.
The researchers stress ...
High intake of several emulsifier E numbers linked to increased cardiovascular disease risk
2023-09-07
High intake of several emulsifiers (part of the ‘E numbers’ group of food additives), widely used in industrially processed foods to improve texture and extend shelf-life, is associated with increased risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD), suggests a study published by The BMJ today.
Given that these food additives are used ubiquitously in thousands of widely consumed ultra-processed food products, these findings have important public health implications, say the researchers.
Emulsifiers are often added to processed and packaged foods such as pastries, cakes, ice cream, ...
RIT researchers pioneer solutions for degenerative disc disease and back pain
2023-09-06
Rochester Institute of Technology researchers are improving non-invasive treatment options for degenerative disc disease, an ailment that impacts 3 million adults yearly in the U.S., according to the Mayo Clinic.
Using state-of-the-art gene editing technology in mesenchymal stem cells, the researchers will add to the growing field of regenerative medicine, the process of producing cellular therapies to alleviate pain and lack of mobility.
Karin Wuertz-Kozak and Thomas Gaborski, faculty-researchers in RIT’s Kate Gleason College of Engineering, recently received a National Institutes of Health award for “Extracellular vesicles produced by CRISPR-activated ...
Subscriptions drive views of alternative and extremist videos on YouTube
2023-09-06
As the second most popular social media platform in the world, YouTube frequently attracts criticism. In particular, critics argue that its algorithmic recommendations facilitates radicalization and extremism by sending users down "rabbit holes" of harmful content.
According to a new study published in Science Advances, however, exposure to alternative and extremist video channels on YouTube is not driven by recommendations. Instead, most consumption of these channels on the platform can be attributed to a small group of users high in gender and racial resentment who ...
Grasping entropy: Teachers and students investigate thermodynamics through a hands-on model
2023-09-06
WASHINGTON, Sept. 6, 2023 – Though a cornerstone of thermodynamics, entropy remains one of the most vexing concepts to teach budding physicists in the classroom. As a result, many people oversimplify the concept as the amount of disorder in the universe, neglecting its underlying quantitative nature.
In The Physics Teacher, co-published by AIP Publishing and the American Association of Physics Teachers, researcher T. Ryan Rogers designed a hand-held model to demonstrate the concept of entropy for students. Using everyday materials, Rogers’ approach allows students to confront ...
Immune system plays vital role in longer multiple myeloma remission
2023-09-06
MIAMI, FLORIDA (Sept. 6, 2023) – A new study from researchers with Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine and other top-tier cancer centers highlights the vital role that the immune system plays in determining the duration of patients’ remission from multiple myeloma.
Their findings, published Sept. 2 in the peer-reviewed journal Nature Communications, suggest that the health of patients’ immune systems may determine how long they will experience progression-free survival from this deadly blood cancer.
Additionally, the researchers were pleasantly surprised to discover that patients’ immune systems ...
Weill Cornell Medicine and NewYork-Presbyterian receive NIH support for project addressing postpartum maternal health in underserved communities
2023-09-06
As part of a National Institutes of Health initiative to improve maternal health and pregnancy outcomes nationwide, Weill Cornell Medicine and NewYork-Presbyterian will play a pivotal role as collaborators with Columbia University Irving Medical Center (CUIMC) as one of 10 nationwide IMPROVE (Implementing a Maternal Health and Pregnancy Outcomes Vision for Everyone) Maternal Health Research Centers of Excellence.
The research center, called the NY Community-Hospital-Academic Maternal Health Equity Partnerships, or NY-CHAMP, ...
ACM publishes new journal of Proceedings of the ACM On Networking
2023-09-06
ACM, the Association for Computing Machinery, has announced the publication of the first issue of Proceedings of the ACM on Networking (PACMNET), a new peer-reviewed journal. Issued quarterly, PACMNET publishes original research papers on new technologies, novel experimentation, creative use of networking technologies, and new insights into network management. The journal features articles on system design and performance evaluations of computer networks, experience learned from deployments, traffic engineering, and network programmability from academic experts as well as practitioners working in ...
NASA’s Webb wins Howard Hughes Memorial Award
2023-09-06
The Aero Club of Southern California has awarded the Howard Hughes Memorial Award to NASA's James Webb Space Telescope. The award will be accepted at a ceremony Wednesday, Sept. 6, at the California Club in Los Angeles.
The Howard Hughes Memorial Award honors exceptional leaders who have advanced the fields of aviation or aerospace technology. Hughes’ first cousin, William R. Lummis, established the award in 1978, and the Aero Club of Southern California presents the award annually.
Accepting the award will be Mike Menzel, the NASA mission systems engineer for Webb at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland.
“On behalf of the entire ...
$1.92M NIH award fuels research to uncover how key protein transport mechanism goes awry in cancer
2023-09-06
MIAMI, FLORIDA (Sept. 6, 2023) – The National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS) has awarded Justin Taylor, M.D., a researcher at Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, a five-year grant totaling $1.92 million for his work to better define the role of XPO1 (Exportin-1) in cancer. XPO1 is a nuclear export protein shown to play a role in many cancer types, including solid tumors and blood cancers.
NIGMS is the arm of the National Institutes of Health that supports basic research aimed at increasing the understanding of biological processes and laying the foundation for advances ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Exposure to life-limiting heat has soared around the planet
New AI agent could transform how scientists study weather and climate
New study sheds light on protein landscape crucial for plant life
New study finds deep ocean microbes already prepared to tackle climate change
ARLIS partners with industry leaders to improve safety of quantum computers
Modernization can increase differences between cultures
Cannabis intoxication disrupts many types of memory
Heat does not reduce prosociality
Advancing brain–computer interfaces for rehabilitation and assistive technologies
Detecting Alzheimer's with DNA aptamers—new tool for an easy blood test
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal study develops radiomics model to predict secondary decompressive craniectomy
New molecular switch that boosts tooth regeneration discovered
Jeonbuk National University researchers track mineral growth on bioorganic coatings in real time at nanoscale
Convergence in the Canopy: Why the Gracixalus weii treefrog sounds like a songbird
Subway systems are uncomfortably hot — and worsening
Granular activated carbon-sorbed PFAS can be used to extract lithium from brine
How AI is integrated into clinical workflow lowers medical liability perception
New biotech company to accelerate treatments for heart disease
One gene makes the difference: research team achieves breakthrough in breeding winter-hardy faba beans
Predicting brain health with a smartwatch
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
Thousands of genetic variants shape epilepsy risk, and most remain hidden
First comprehensive sex-specific atlas of GLP-1 in the mouse brain reveals why blockbuster weight-loss drugs may work differently in females and males
When rats run, their gut bacteria rewrite the chemical conversation with the brain
Movies reconstructed from mouse brain activity
Subglacial weathering may have slowed Earth's escape from snowball Earth
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
[Press-News.org] UC Irvine researchers discover a nanobody which may lead to treatment for Retinitis PigmentosaA special antibody derived from llamas —called a nanobody — can stop the misfolding and the activation of Rhodopsin, a molecule whose mutations can lead to blindness.