(Press-News.org) About The Study: Long- and short-term heat exposure during pregnancy was associated with higher risk of severe maternal morbidity in this study with 403,000 pregnancies from 2008 to 2018 in Southern California. These results might have important implications for severe maternal morbidity prevention, particularly in a changing climate.
Authors: Jun Wu, Ph.D., of the University of California, Irvine, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.32780)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.32780?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=090723
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is an online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
END
Analysis of heat exposure during pregnancy and severe maternal morbidity
JAMA Network Open
2023-09-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Calcium channel blocker use and associated glaucoma and related traits
2023-09-07
About The Study: Calcium channel blocker use was adversely associated with glaucoma prevalence in this study of 427,000 adult UK Biobank participants, suggesting that calcium channel blockers may represent an important modifiable risk factor for glaucoma, potentially through an intraocular pressure–independent mechanism.
Authors: Alan Kastner, M.D., M.Sc., of the Moorfields Eye Hospital National Health Service Foundation Trust and University College London Institute of Ophthalmology in London, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2023.3877)
Editor’s ...
Phase I clinical trial shows treatment designed to clear senescent cells in Alzheimer’s disease is safe
2023-09-07
WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. – Sept. 7, 2023 – Alzheimer’s disease is the most common cause of dementia that affects more than 6.5 million Americans, according to the Alzheimer’s Association. To find effective treatments and slow the progression of this debilitating disease, researchers have made much progress in developing new drugs that target beta-amyloid plaques, one of the hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease.
Beta-amyloid plaques are accumulations of brain protein fragments, which can impact cognition. However, these recent drugs have only yielded modest results.
Now, ...
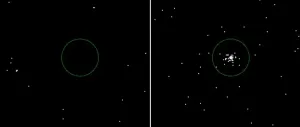
Ravenous black hole consumes three Earths’-worth of star every time it passes
2023-09-07
A star like our own Sun in a nearby galaxy is gradually being eaten away by a small but ravenous black hole, losing the equivalent mass of three Earths every time it passes close.
The discovery by University of Leicester astronomers is reported today (7 September) in Nature Astronomy and provides a ‘missing link’ in our knowledge of black holes disrupting orbiting stars. It suggests a whole menagerie of stars in the process of being consumed that still lie undiscovered.
The team was supported by the UK Space Agency and the UK Science and technology Facilities Council (STFC).
The astronomers were alerted to ...
MIT engineers design more powerful RNA vaccines
2023-09-07
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- RNA vaccines against Covid-19 have proven effective at reducing the severity of disease. However, a team of researchers at MIT is working on making them even better. By tweaking the design of the vaccines, the researchers showed that they could generate Covid-19 RNA vaccines that produce a stronger immune response, at a lower dose, in mice.
Adjuvants are molecules commonly used to increase the immune response to vaccines, but they haven’t yet been used in RNA vaccines. In this study, the MIT researchers engineered both the nanoparticles used to deliver the Covid-19 antigen, and the antigen itself, to boost the immune response, ...
Genetic tools probe microbial dark matter
2023-09-07
Patescibacteria are a group of puzzling, tiny microbes whose manner of staying alive has been difficult to fathom. Scientists can cultivate only a few types, yet these bacteria are a diverse group found in many environments.
The few types of Patescibacteria that researchers can grow in the lab reside on the cell surfaces of another, larger host microbe. Patescibacteria in general lack the genes required to make many molecules necessary for life, such as the amino acids that make up proteins, the fatty acids that form membranes, and the nucleotides in DNA. This has led researchers ...
Revolutionizing lithium production on a string
2023-09-07
A vital component of the batteries at the heart of electric vehicles and grid energy storage, lithium is key to a clean energy future. But producing the silvery-white metal comes with significant environmental costs. Among them is the vast amount of land and time needed to extract lithium from briny water, with large operations running into the dozens of square miles and often requiring over a year to begin production.
Now, researchers at Princeton have developed an extraction technique that slashes the amount of land and time needed for lithium production. The researchers say their system ...
Genetic study of blood glucose levels calls for stratified treatment with GLP-1R agonists in type 2 diabetes, reveals the role of the intestine, and impact on lung function
2023-09-07
New research highlights that genetic background can affect individual responses to GLP-1R agonist drugs.
Researchers reveal for the first time that high blood sugar levels in type 2 diabetes can play a causal role in lung disorders.
The study sheds light on the role of the digestive system, including the small intestine, ileum, and colon, in controlling blood sugar levels.
This is the largest-ever study into the genetic basis of random "round-the-clock" blood sugar levels.
Groundbreaking research published today in Nature Genetics describes the largest-ever study into the genetics of random "round-the-clock" ...
Bursting air bubbles may play a key role in how glacier ice melts, Oregon State research suggests
2023-09-07
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Oregon State University research has uncovered a possible clue as to why glaciers that terminate at the sea are retreating at unprecedented rates: the bursting of tiny, pressurized bubbles in underwater ice.
Published today in Nature Geoscience, the study shows that glacier ice, characterized by pockets of pressurized air, melts much more quickly than the bubble-free sea ice or manufactured ice typically used to research melt rates at the ocean-ice interface of tidewater glaciers.
Tidewater glaciers are rapidly retreating, the authors say, resulting in ice mass loss in Greenland, the Antarctic Peninsula and other glacierized regions around the globe.
“We ...
A secret passage for mutant protein to invade the brain
2023-09-07
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) show that the protein involved in Parkinson’s disease, α-synuclein, can propagate through the lymphatic system of the brain before it aggregates
Tokyo, Japan – In many neurodegenerative disorders, abnormal proteins progressively aggregate and propagate in the brain. But what comes first, aggregation or propagation? Researchers from Japan share some new insights about the mechanism involved in Parkinson’s disease.
In a study published ...
The need to hunt small prey compelled prehistoric humans to produce appropriate hunting weapons and improve their cognitive abilities
2023-09-07
A new study from the Department of Archaeology at Tel Aviv University found that the extinction of large prey, upon which human nutrition had been based, compelled prehistoric humans to develop improved weapons for hunting small prey, thereby driving evolutionary adaptations. The study reviews the evolution of hunting weapons from wooden-tipped and stone-tipped spears, all the way to the sophisticated bow and arrow of a later era, correlating it with changes in prey size and human culture and physiology.
The researchers explain: "This study was designed to examine a broader unifying hypothesis, which we proposed in a previous paper published in ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
High-fat diets cause gut bacteria to enter brain, Emory study finds
Teens and young adults with ADHD and substance use disorder face treatment gap
Instead of tracking wolves to prey, ravens remember — and revisit — common kill sites
Ravens don’t follow wolves to dinner – they remember where the food is
Mapping the lifelong behavior of killifish reveals an architecture of vertebrate aging
Designing for hard and brittle lithium needles may lead to safer batteries
Inside the brains of seals and sea lions with complex vocal behavior learning
Watching a lifetime in motion reveals the architecture of aging
Rapid evolution can ‘rescue’ species from climate change
Molecular garbage on tumors makes easy target for antibody drugs
New strategy intercepts pancreatic cancer by eliminating microscopic lesions before they become cancer
Embryogenesis in 4D: a developmental atlas for genes and cells
CNIO research links fertility with immune cells in the brain
Why do lithium-ion batteries fail? Scientists find clues in microscopic metal 'thorns'
Surface treatment of wood may keep harmful bacteria at bay
Carsten Bönnemann, MD, joins St. Jude to expand research on pediatric catastrophic neurological disorders
Women use professional and social networks to push past the glass ceiling
Trial finds vitamin D supplements don’t reduce covid severity but could reduce long COVID risk
Personalized support program improves smoking cessation for cervical cancer survivors
Adverse childhood experiences and treatment-resistant depression
[Press-News.org] Analysis of heat exposure during pregnancy and severe maternal morbidityJAMA Network Open