(Press-News.org) Ammonia is emerging as a promising energy source to achieve carbon neutrality due to its inherent carbon-free nature. A recent study, led by Professor Hankwon Lim in the School of Energy and Chemical Engineering and the Graduate School of Carbon Neutrality at UNIST, has evaluated the feasibility of ammonia-based power generation through techno-economic and carbon footprint analyses. The research focuses on an integrated system combining ammonia decomposition and phosphoric acid fuel cells.
The study, conducted using a commercial process simulator, unveils significant findings regarding the efficiency and economic viability of utilizing ammonia in power generation systems. Results indicate an impressive energy efficiency rate of 46.7% within the designed power generation process.
Through comprehensive economic analysis, the research team identified an upper limit for ammonia pricing at 421.3 $ tNH3–1 that allows competitive pricing against industrial electricity rates—a crucial factor in determining market competitiveness.
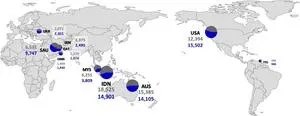
To further optimize ammonia imports into the Republic of Korea (KOR), five distinct scenarios were established based on historical data from the top ten exporting countries. Using the Monte Carlo method for ammonia production costs and carbon dioxide emissions in each nation, researchers optimized import quantities while minimizing overall emissions.
The results demonstrate that if solely reliant on carbon-based ammonia imports, carbon intensity ranges between 0.707–0.736 kgCO2-eq kWh−1—exceeding KOR’s average value over a 20-year period. However, achieving a ratio of over 78% of carbon-neutral ammonia (Scenario 4) can make both environmental and economic aspects more favorable.
According to the research team, their findings provide valuable insights into optimizing ammonia exports and reducing carbon intensity. By adopting a holistic approach that encompasses all stages of the supply chain, significant progress can be made towards sustainable energy solutions.
“Our study sheds light on the immense potential of ammonia as an energy source,” said Professor Lim. “We have analyzed costs and greenhouse gas emissions while considering different commercialized methods of producing ammonia. Although renewable energy sources were not part of this particular study, our findings offer crucial insights into enhancing ammonia exports and promoting sustainability.”
The study findings have been published ahead of their official publication in the online version of Chem. Eng. J. on May 13, 2023. This work has been supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), the Carbon Neutrality Demonstration and Research Center of UNIST, the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy and Korea (MOTIE), and Korea Evaluation Institute of Industrial Technology (KEIT). Their findings are expected to contribute to advancing the understanding and utilization of ammonia as a viable option for decentralized power generation systems.
Journal Reference
Dongjun Lim, Jong Ah Moon, Yeong Jin Koh, et al., “Expansion and optimization of ammonia import to the Republic of Korea for electricity generation,” Chem. Eng. J., (2023).
END
New study highlights feasibility and optimization of ammonia-based power generation for carbon neutrality
The study findings have been published ahead of their official publication in the online version of Chem. Eng. J. on May 13, 2023
2023-09-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
UTSA researchers explain plant’s medicinal power against COVID and glioblastoma
2023-09-08
Vibrant green leaves sprout from tall fragrant plants sitting neatly in two rows of terracotta pots in Valerie Sponsel’s UTSA biology laboratory. One floor just above her is the chemistry lab of Francis Yoshimoto, who is extracting the plant’s leaves for medicinal compounds. Soon, the researchers will meet with UTSA researcher Annie Lin, who will test the extracted compounds on cancer cells.
The plant is Artemisia annua, or Sweet Annie, and it contains medicinal compounds. UTSA researchers are studying the plant to understand the bioactive properties of one of these compounds, Arteannuin B, in cancer cells and COVID, the ...
Benchtop NMR spectroscopy can accurately analyse pyrolysis oils
2023-09-08
Benchtop NMR spectroscopy can accurately analyse pyrolysis oils
Pyrolysis bio-oils have the potential to be widely used as alternative fuels but are very complex to analyse
Cheaper, simpler, low-field, or ‘benchtop’, NMR spectrometers were able to accurately quantify key oxygen-containing components of pyrolysis bio-oils for the first time
More accessible analysis could help develop the potential of bio-oils as an alternative to fossil fuels
EMBARGOED UNTIL FRIDAY 8TH SEPTEMBER at 9am UK time 2023 | Birmingham, UK
A team of researchers at Aston University ...
The climate crisis could reshape Italian mountain forests forever
2023-09-08
As a result of the climate crisis, future forests may become unrecognizable. Trees that currently make up European woods may no longer be seen — or they may have moved several hundred meters uphill. Scientists writing in Frontiers in Forests and Global Change have mapped the forests of five vulnerable mountain areas in Italy and modelled the future of these fragile ecosystems.
“If I imagine my daughter walking with me as an old man, in our mountain forests, I can imagine that we can see the initial stage of a profound ...
Disney princesses can be good for a child’s self-image, UC Davis researchers suggest
2023-09-08
Children have loved Disney princesses since Snow White and the Seven Dwarfs premiered in theaters in 1937. While this adoration continues to grow in terms of princess movie ratings, some parents may wonder what effects these idealized images of young women might have on how their children feel about and express themselves.
According to new research from the University of California, Davis, a favorite princess improved — but did not harm — young children’s ...
University of Miami upgrades Atmospheric Chemistry Observatory in Barbados
2023-09-08
The observatory has been used to document the transport of Saharan dust particles across the Atlantic Ocean to the Caribbean, creating the longest-running dust data set in existence. Scientists from many different disciplines use the data to understand how dust particles impact everything from coral reef health to cloud formation and tropical storms.
Through a grant from the National Science Foundation (NSF), the University of Miami Rosenstiel School of Marine, Atmospheric, and Earth Science recently completed a major upgrade to its Barbados Atmospheric Chemistry Observatory (BACO), expanding its capability ...
Beaver activity in the Arctic increases emission of methane greenhouse gas
2023-09-08
The climate-driven advance of beavers into the Arctic tundra is causing the release of more methane — a greenhouse gas — into the atmosphere.
Beavers, as everyone knows, like to make dams. Those dams cause flooding, which inundates vegetation and turns Arctic streams and creeks into a series of ponds. Those beaver ponds and surrounding inundated vegetation can be devoid of oxygen and rich with organic sediment, which releases methane as the material decays.
Methane is also released when organics-rich permafrost thaws as the result of heat carried by the spreading water.
A study linking Arctic beavers to an increase in the release of methane was ...
Labour laws need updating now remote work is here to stay
2023-09-08
Australia’s employment laws and regulations must be updated to reflect the changing nature of work, with many people continuing to work from home long after the COVID-19 pandemic.
That’s according to University of South Australia Associate Professor of Organisational Behaviour Dr Ruchi Sinha who says labour laws and protections should be updated to clarify issues related to work hours, overtime, and breaks in a remote work context, now that almost half of all employees are working from home at least once a week.
The Australian Institute of Health and Welfare ...
UArizona scientists investigate new frontiers of sound with $30M center
2023-09-08
The National Science Foundation has granted the University of Arizona $30 million over five years to establish a new NSF Science and Technology Center. The New Frontiers of Sound Science and Technology Center, which comes with an additional $30 million funding option over the following five years, will bring together researchers working in topological acoustics.
With topological acoustics, researchers exploit the properties of sound in ways that could vastly improve computing, telecommunications and sensing. Applications could include reaching quantum-like computing speeds, reducing the power usage of smartphones, and sensing changes in aging infrastructure or the natural ...
Artificial intelligence could help build pollen jigsaw of present and ancient flora
2023-09-08
An emerging system which combines rapid imaging with artificial intelligence could help scientists build a comprehensive picture of present and historic environmental change – by swiftly and accurately analysing pollen.
Pollen grains from different plant species are unique and identifiable based on their shape. Analysing which pollen grains are captured in samples such as sediment cores from lakes helps scientists understand which plants were thriving at any given point in history, potentially dating back thousands to millions of years.
Up to now, scientists have manually ...
Distance from clinic influences abortion pill access
2023-09-08
Women who live farther from a medical clinic and those who identify as multiracial are more likely to use telemedicine to get abortion pills than to visit a clinic, according to a new study by researchers at the University of Washington School of Medicine.
The findings were published Sept. 1 in JAMA Network Open.
“One of the main takeaways,” said lead author Anna Fiastro, a family medicine research scientist at UW Medicine, “is that the further patients are from a brick-and-mortar clinic, the more ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
AI expert and industry leading toxicologist Thomas Hartung hails launch of agentic AI platform a “transformative moment” in chemical safety science
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
[Press-News.org] New study highlights feasibility and optimization of ammonia-based power generation for carbon neutralityThe study findings have been published ahead of their official publication in the online version of Chem. Eng. J. on May 13, 2023