(Press-News.org) Researchers at the University of Arizona Cancer Center discovered a new class of iron-targeting compounds that hamper the proliferation of cultured malignant cells in a laboratory setting. The results of the study were published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
“Cancer cells are what we call ‘addicted’ to iron, and so we are making compounds that are able to interfere with the availability of iron in cancer cells,” said Elisa Tomat, PhD, professor in the Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry at the UArizona College of Science and member of the UArizona Cancer Center.
The discovery could lead to the development of broad-spectrum, anticancer drugs that target iron metabolism.
The team has been working with Tech Launch Arizona, the university’s commercialization arm, with the goal of licensing the technology to a company that will move it into the marketplace. A patent application is pending.
Iron is the most abundant transition metal in the human body and, according to Tomat, plays a crucial role in tumor progression and metastasis. Cancer cells rely on several iron-dependent processes to sustain their rapid proliferation rates and therefore have a higher demand for this element compared with normal cells.
Tomat said the research team’s challenge was capturing iron within malignant cells yet keeping it available to the rest of the body. To do so, they targeted intracellular iron with compounds that are activated only after cellular uptake.
“As chemists, we can design and synthesize molecules that are able to bind iron only under certain conditions and not throughout the body,” Tomat said. “We've been working on various approaches toward this type of chemistry; we call these prochelator approaches because the chelator is the compound that binds the metal ion. The prochelator is the compound we designed to become activated only upon undergoing a certain reaction that occurs in cells.”
The research was inspired by a “common reagent,” a compound that is employed in laboratories worldwide to assess the ability of drug candidates to inhibit the proliferation of cultured mammalian cells.
“Because iron is such a fundamental player that is important in many cancer types, and this high demand for iron is a general characteristic of malignancy, I've been interested in this strategy for a number of years,” said Tomat, who has been exploring iron chelators and their role in tumor progression for more than 10 years.
“We're excited about this new strategy because we think this class of molecules can be further modified to optimize the properties and improve the antiproliferative activity and really become a way for us to impact the iron availability in malignant cells and halt cancer growth.”
Tomat’s co-authors include former postdoctoral associate Zoufeng Xu, PhD, and doctoral student Yu-Shien Sung.
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health under award no. R01GM127646. The UArizona Cancer Center Flow Cytometry Shared Resource is supported by the National Cancer Institute, a division of the NIH, under award no. P30CA023074.
END
UArizona Cancer Center researchers discover iron-targeting approaches to halt proliferation of cancer cells
The new molecules exploit the iron dependency of malignant cells and could lead to the development of new anticancer drugs.
2023-09-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Experimental physicist David Weld to investigate the role of feedback and measurement in quantum systems
2023-09-11
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) — Experimental physicist David Weld’s experimental research interest lies in a question that has been around for a long time, but which we’re only now approaching the ability to investigate.
“There’s a really old interest in the quantum act of measurement,” he said. “It’s something that’s at the foundations of quantum mechanics and has been puzzling people for more than a century.”
Called the “measurement problem” and famously illustrated by Erwin Schrödinger’s ...
ORNL teams receive funding through DOE BRaVE initiative to study biopreparedness
2023-09-11
The Department of Energy’s Office of Science has selected three Oak Ridge National Laboratory research teams to receive funding through DOE’s new Biopreparedness Research Virtual Environment, or BRaVE, initiative.
BRaVE, announced earlier this year, aims to build on biopreparedness research that delivered high-impact results in the fight against COVID-19. In the height of the pandemic, DOE national laboratory scientists combined fields such as biology, high-performance computing and manufacturing to bolster the national supply of personal protective equipment and improve virus testing and treatment.
“The advances made ...
Self-reported “night owls” more likely to have unhealthy lifestyle behaviors, significantly increased diabetes risk
2023-09-11
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 11 September 2023
Annals of Internal Medicine Tip Sheet
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
----------------------------
1. Self-reported “night owls” more likely to have ...
Big teeth, bigger data
2023-09-11
Virginia Tech researchers in the College of Natural Resources and Environment are assessing the efficacy of shark sanctuaries by developing a modeling system that utilizes publicly accessible fishing data to determine shark catch and mortality rates. Published in the journal Science Advances, their findings represent an important step in utilizing data science to tackle oceanic conservation challenges.
“Shark sanctuaries are coastal areas designated by countries as places where the targeted ...
Article: Doctors treating patients with Parkinson’s disease must focus on stigma and emotional impacts as well as motor symptoms
2023-09-11
Even the best treatment approaches for Parkinson’s disease are inadequate if they do not address patients’ feelings of social rejection, isolation, loneliness and other psychosocial effects of stigma, according to a report from experts specializing in Parkinson’s and other movement disorders.
A new report co-authored by UCLA Health neurologist and researcher Dr. Indu Subramanian says many misconceptions and biases cause patients with Parkinson’s to be stereotyped, devalued and shunned, which, along with a progressive loss of functionality and independence, often lead to “self-stigma,” with declining self-esteem and increasing anxiety and depression. The ...
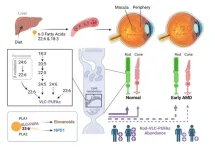
LSU Health New Orleans researchers discover a key failure in amd that may lead to progression and vision loss
2023-09-11
New Orleans, LA – Research led by Nicolas Bazan, MD, PhD, Boyd Professor, Ernest C. and Yvette C. Villere Chair for the Study of Retinal Degeneration, and Director of the Neuroscience Center of Excellence at LSU Health New Orleans School of Medicine, suggests that age-related macular degeneration (AMD) decreases an essential fatty acid, preventing the formation of a class of protective molecules and reducing repair potential. The discovery may also open new therapeutic avenues for AMD. The findings are published in Experimental Eye Research, ...
Virginia Tech has seismic role in earthquake center
2023-09-11
A Virginia Tech professor has an integral role in the establishment of a new center to study earthquakes in the Cascadia Subduction Zone off the coast of Oregon.
The project will create an earthquake center to study subduction zones — fault lines where one tectonic plate slips beneath another — to enable collaborative research and community connections for increased hazard awareness.
The Division of Earth Sciences in the Directorate for Geosciences at the National Science Foundation has awarded a $15 million grant over five years to establish the Cascadia Region ...
3D printing with coffee: Turning used grounds into caffeinated creations
2023-09-11
Coffee can do a lot of things: Wake you up, warm you up and lessen that existential dread. According to a new study, it could also help reduce the waste from 3D printing.
That’s the vision behind a new project led by Michael Rivera, an assistant professor in the ATLAS Institute and Department of Computer Science at the University of Colorado Boulder. He and his colleagues have developed a method for 3D printing a wide range of objects using a paste made entirely out of old coffee grounds, water and a few other sustainable ingredients.
The team has already experimented with using coffee grounds to craft jewelry, pots for plants and even, ...
Firms address corporate scandal with lengthy codes of ethics, study shows
2023-09-11
Corporate scandals have been on the rise for the past decade.
In 2019, Strategy& (the strategy consulting business unit of PricewaterhouseCoopers) found that for the first time in the history of its annual survey, more CEOs were dismissed for ethical concerns than for poor firm performance or internal board struggles.
There has been no shortage of highly publicized scandals, including the BP oil spill in 2010, the Target data breach in 2013 and abuses of financial incentives at Wells Fargo in 2016. A number of CEOs have resigned following alleged inappropriate relations, including Brian Krzanich at Intel, Leslie Moonves at CBS, ...
Atmospheric scientists reveal much of Houston’s ozone exceedance due to air flows from the north
2023-09-11
University of Houston atmospheric science researchers have found that while local emissions play a role in the rise of ozone levels in Houston, most of the pollutants can be carried in from other regions across the country, leading to excess ozone pollution. Their findings offer insights into strategies to mitigate future ozone pollution for the region.
The research team focused on two ozone episodes in September 2021 (Sept. 6 – 11 and Sept. 23 – 26). The month of September is the typical annual ozone peak due to high temperatures, lack of rain and air circulation patterns that transport polluted air from the north.
Their analysis revealed that roughly 63% of the excess ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Brain activity reveals how well we mentally size up others
Taiwanese and UK scientists identify FOXJ3 gene linked to drug-resistant focal epilepsy
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
[Press-News.org] UArizona Cancer Center researchers discover iron-targeting approaches to halt proliferation of cancer cellsThe new molecules exploit the iron dependency of malignant cells and could lead to the development of new anticancer drugs.