(Press-News.org) [Singapore, 10:05 a.m. SGT--September 12, 2023] - A unified and concentrated lung cancer advocacy program in the United States resulted in a 25 percent increase in funding to a U.S.-based lung cancer research program, according to a presentation given today at the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer 2023 World Conference on Lung Cancer in Singapore.
Lung cancer remains a major health concern, with mortality rates posing a significant challenge both globally and in the United States. The U.S. Department of Defense Congressionally Directed Medical Research Program/Lung Cancer Research Program (LCRP) was established in 2009 with a funding level of $20 million, but had never exceeded its initial budget, and at times, funding was even reduced to as low as $10.5 million per year. In stark contrast, other cancer research programs, such as breast cancer and prostate cancer, received substantially higher annual funding.
In January 2022, the Lung Cancer Action Network (LungCAN) took action by forming a dedicated Steering Committee of passionate advocates led by Jill Morningstar, a strong advocate with Capitol Hill experience, along with her husband Al Fitzpayne, a lung cancer survivor. The committee developed a strategic plan to increase the LCRP budget, aiming to allocate funding based on the amount needed to support top-rated research proposals from the previous year.
A major obstacle faced by lung cancer advocacy organizations was the lack of a unified web-based platform for contacting members of Congress. To address this challenge, LungCAN, acting as a neutral entity, created a platform that allowed members to direct their constituents to the LungCAN "Call to Action" website without the risk of losing organizational support. Through this platform, the lung cancer advocacy community joined forces, speaking with one voice to advocate for increased lung cancer research funding.
The efforts yielded remarkable results:
The LCRP received a 25 percent increase in funding, receiving a record-breaking $25 million, the highest amount the program has ever been awarded.
The LCRP was the only CDMRP cancer program to receive an increase in funding.
Strategic social media engagement garnered a remarkable 55,000 combined impressions and 33.3 percent engagement on Twitter.
Approximately 1,847 individuals participated in the effort, reaching more than 400 legislators.
Advocates sent over 5,541 letters to legislators requesting $60 million for the LCRP through the LungCAN platform, lungcan.org/act.
Additional emails from advocates through GO2 and LUNGevity platforms exceeded 4,000.
A House “Dear Colleague” letter received more than 50 co-signers, the highest number ever.
The campaign garnered support from 80 associations and organizations, growing beyond Congress.
"This historic success highlights the power of unity and collaboration among lung cancer advocacy organizations," said Dusty Donaldson, representing Lung Cancer Action Network. "By joining forces and speaking with one voice, we were able to secure increased funding for lung cancer research, which is essential in advancing our fight against this devastating disease."
This project was a component of the LungCAN Advocacy Media Training project, funded by Lung Ambition Alliance, comprising AstraZeneca, Guardant Health, International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer, and the Global Lung Cancer Coalition.
About the IASLC:
The International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer (IASLC) is the only global organization dedicated solely to the study of lung cancer and other thoracic malignancies. Founded in 1974, the association's membership includes more than 8,000 lung cancer specialists across all disciplines in over 100 countries, forming a global network working together to conquer lung and thoracic cancers worldwide. The association also publishes the Journal of Thoracic Oncology, the primary educational and informational publication for topics relevant to the prevention, detection, diagnosis, and treatment of all thoracic malignancies. Visit http://www.iaslc.org for more information.
About the WCLC:
The WCLC is the world’s largest meeting dedicated to lung cancer and other thoracic malignancies, attracting more than 7,000 researchers, physicians, and specialists from more than 100 countries. The goal is to increase awareness, collaboration, and understanding of lung cancer, and to help participants implement the latest developments across the globe. The conference will cover a wide range of disciplines and unveil several research studies and clinical trial results. For more information, visit https://wclc2023.iaslc.org.
END
U.S. advocacy strategy nets a 25 percent increase in lung cancer research funding
2023-09-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
IASLC staging model for mesothelioma validated; study supports continued use of model
2023-09-12
[Singapore, 10:05 a.m. SGT--September 12, 2023] – A model developed by the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer in 2009 to help better stage mesothelioma cases performed well, according to an independent analysis presented today at The International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer (IASLC) 2023 Conference in Singapore.
Pleural mesothelioma is a rare but aggressive cancer primarily caused by asbestos exposure and presents complex challenges for effective staging and prognostication. The IASLC took a significant step in 2009 by establishing an international pleural mesothelioma database aimed at enhancing staging ...
Long-term outcomes of radiation techniques for locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer presented at IASLC 2023 Conference in Singapore
2023-09-12
[Singapore, 10:05 a.m. SGT--September 12, 2023] - Intensity-modulated radiation therapy, or IMRT, should be utilized for locally advanced NSCLC to reduce the risk of severe pulmonary toxicity and radiation exposure to the heart, according to research presented today at the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer 2023 World Conference on Lung Cancer in Singapore.
Dr. Stephen Chun, MD Anderson in Houston, Texas, presented a comprehensive analysis of the phase III trial NRG Oncology-RTOG 0617, comparing intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) with 3D-conformal ...
Reproductive factors associated with higher risk of lung cancer in women
2023-09-12
[Singapore, 10:05 a.m. SGT--September 12, 2023] - A study presented at the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer 2023 World Conference on Lung Cancer revealed that key reproductive factors such as early menopause, shortened reproductive span, and early age at first birth are associated with elevated risks of lung cancer in women.
Researchers from Xiangya Hospital, Changsha, Hunan, China, conducted a prospective cohort study involving 273,190 participants from the UK Biobank to delve into the links between individual reproductive ...
Dark matter halos measured around ancient quasars
2023-09-12
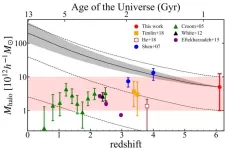
At the center of every galaxy is a supermassive black hole. Beyond a certain size, these become active, emitting huge amounts of radiation, and are then called quasars. It is thought these are activated by the presence of massive dark matter halos (DMH) surrounding the galaxy, directing matter towards the center, feeding the black hole. A team including researchers from the University of Tokyo have, for the first time, surveyed hundreds of ancient quasars and found this behavior is very consistent throughout history. This is surprising, as many large-scale processes show variation throughout the ...
Arf1 inhibitors promote the infiltration of cytotoxic T lymphocytes into tumors by affecting lipid metabolism
2023-09-12
In recent years, cancer immunotherapies, represented by immune checkpoint blockade (ICB), have been highly successful and have become an important basis for the future treatment of cancers. However, the absence of tumoral killer T cells and the complexity of tumor microenvironment can both affect the immunotherapeutic efficacy. Therefore, it is urgent to develop novel anti-tumor agents that can effectively promote effector T cell infiltration in tumors.
ADP-ribosylation factor 1 (Arf1) is a member of the Ras small GTPase family and is ...
Intensity-modulated radiation therapy provides long-term benefits to patients with locally advanced lung cancer
2023-09-12
Intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) should be the preferred choice when treating patients with locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), as it reduces radiation exposure to the heart and lungs, according to researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center.
Results from a long-term secondary analysis of the NRG Oncology-RTOG 0617 Phase III study, with a median follow-up of 5.2 years, revealed that patients receiving IMRT had a more than two-fold reduction in severe lung inflammation (pneumonitis) compared to those who received 3D-conformal radiotherapy ...
New super-fast flood model has potentially life-saving benefits
2023-09-12
Published in Nature Water, the new model has major potential benefits for emergency responses, reducing flood forecasting time from hours and days to just seconds, and enabling flood behaviour to be accurately predicted at super-fast speeds as an emergency unfolds.
University of Melbourne PHD student Niels Fraehr, alongside Professor Q J Wang, Dr Wenyan Wu and Professor Rory Nathan, from the Faculty of Engineering and Information Technology, developed the Low-Fidelity, Spatial Analysis ...
In maize, co-expression of GAT and GR79-EPSPS provides high glyphosate resistance, along with low glyphosate residues
2023-09-12
This study is led by Dr Zhihong Lang (Biotechnology Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences). To develop a new bio-breeding resource for glyphosate-resistant maize, a large transgenic maize population was generated with introducing a codon-optimized glyphosate N-acetyltransferase gene, gat, and the enolpyruvyl-shikimate-3-phosphate synthase gene, gr79-epsps, into maize and a transgenic event, designated GG2, was highly resistant to glyphosate in consecutive generations of glyphosate screening. “This result is very encouraging.” Dr Lang says.
The ...
IOP Publishing and the Japan Society of Applied Physics convert Applied Physics Express to fully gold OA
2023-09-12
IOP Publishing (IOPP) and the Japan Society of Applied Physics (JSAP) announce that Applied Physics Express (APEX) is to become fully open access (OA). From January 2024, all articles published in APEX, the journal devoted to rapid dissemination of new findings in applied physics, will be immediately and openly accessible for anyone to read. The move reflects the increasing demand for more accessible and open science, and funders’ mandates requiring authors to publish their work in OA journals.
Making APEX open access means that authors will be ...
Art, science merge in Oregon State study of 19th-century landscape paintings’ ecological integrity
2023-09-12
CORVALLIS, Ore. – An Oregon State University-led collaboration of ecologists and art historians has demonstrated that landscape paintings from more than 150 years ago can advance environmental science.
Researchers from OSU, the U.S. Forest Service, the University of Vermont and the Smithsonian American Art Museum used 19th-century depictions of preindustrial forests in the northeastern United States to show that historical artwork can reveal information about forests and other landscapes from eras that predate modern scientific investigation.
The ...