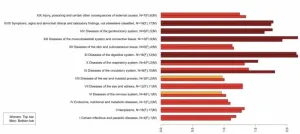
(Press-News.org) Multimorbidity describes the state of having more than one disease. Anthony Webster sought to untangle a puzzle at the heart of multimorbidity: does having had disease make a patient more likely to have another disease, independent of broad risk factors, such as age, smoking status, or weight? Webster applied a Poisson-Binomial distribution with a Weibull model to predict the incidence of 222 common diseases for approximately 500,000 individuals within the UK Biobank cohort, taking into account their age and established risk factors, but ignoring their history of previous disease or pre-existing conditions. Webster then compared the expected number of diagnoses with the actual number, which was higher by about 50%. The same likelihood was found for a large variety of diseases and across men and women, although there were some differences for groups like smokers and high-BMI individuals. For high-BMI men who smoke, the actual rate of new diseases was nearly double the rate expected by risk factors and age alone. Some disease categories, such as diseases of the digestive system and musculoskeletal diseases, also had roughly double the rate expected by risk factors and age alone. The mechanisms by which having a disease modifies future disease risk remain unclear, but the broadly similar findings across many illnesses suggest that risk models might be adapted to take into account the increased risk of developing a disease due to previous, or pre-existing diseases, according to the author.
END
Calculating disease risk in individuals with previous disease
2023-09-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
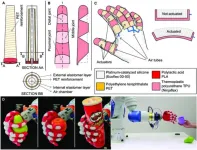
Integrated design fabrication and control of a bioinspired multimaterial soft robotic hand
2023-09-12
A research paper by scientists at the University of Coimbra proposed a soft robotic hand that composed of soft actuator cores and an exoskeleton, featuring a multimaterial design aided by finite element analysis to define the hand geometry and promote finger’s bendability. The new research paper, published on Aug. 8 in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems, presented the development, fabrication, and control of a bioinspired soft robotic hand and demonstrated finite element analysis can serve as a valuable tool to support the design and control of the hand’s fingers.
“Recent research led to impactful achievements in functional designs, modeling, ...
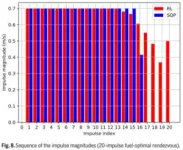
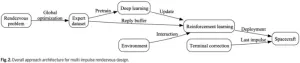
Scientists studied optimal multi-impulse linear rendezvous via reinforcement learning
2023-09-12
Multi-impulse orbital rendezvous is a classical spacecraft trajectory optimization problem, which has been widely studied for a long time. Numerical optimization methods, deeplearning (DL) methods, reinforcement learning (RL) methods have been proposed. However, for the numerical optimization methods, they need long computation time, and they are usually not valid for the many-impulse rendezvous case with the magnitude constraints. For the machine learning (ML) methods, the DL method needs large amounts of data, and the RL method has the weakness of low efficiency. Nevertheless, ML demonstrates more accurate predictions ...
SwRI engineers recognized with international AOC awards
2023-09-12
SAN ANTONIO — September 12, 2023 —The Association of Old Crows (AOC), an international organization for the electronic warfare (EW) community, has recognized three early-career Southwest Research Institute engineers for their achievements in EW research and development. Two honorees received back-to-back Electronic Warfare Professional Outstanding Young Crow Awards. AOC named one engineer a 2023 Future 5, a designation for innovative professionals building EW careers. EW technology detects and defeats enemy signals on the electromagnetic spectrum to protect U.S. and allied forces.
Recipients of the international AOC EW Professional Outstanding Young Crow Award demonstrate outstanding ...
NIH grant to fund network of data warehouses for Baton Rouge health research institutions
2023-09-12
BATON ROUGE – The National Institutes of Health has awarded the Louisiana Clinical & Translational Science Center, or LA CaTS, a grant of nearly $1.3 million to support the efforts of in-state healthcare institutions to share health data for research purposes across a common structure.
Awarded as a single grant, the funds will be primarily split between two LA CaTS member institutions: nearly $780,000 for the Pennington Biomedical Research Center and $490,000 for Tulane University School of Medicine. Together, these two projects will strengthen the LA CaTS Center’s capacity to address health care disparities, ...
New photonic neural networks promise ultrafast computing for complex tasks
2023-09-12
Photonic neural network systems, which are fast and energy efficient, are especially helpful for dealing with large amounts of data. To advance photonic brain-like computing technologies, a group of researchers at the University of Strathclyde combined a spike-based neural network with a semiconductor laser that exhibits spiking neuronal behaviors. Recently, they presented high-performance photonic spiking neural network operation with lower training requirements and introduced a novel training scheme for getting better results. This research was published Aug. 29 in Intelligent Computing, a Science Partner Journal.
Neural ...
Lee McIntyre ("Post-Truth" "How to Talk to a Science Denier") Returns with "On Disinformation"
2023-09-12
September 12th, 2023
For immediate release
Fom the bestselling author of Post-Truth and How to Talk to a Science Denier, comes On Disinformation: How to Fight for Truth and Protect Democracy
The effort to destroy facts and make America ungovernable didn't come out of nowhere. It is the culmination of seventy years of strategic denialism. In On Disinformation, Lee McIntyre shows how the war on facts began, and how ordinary citizens can fight back against the scourge of disinformation that is now threatening the very ...
More people develop sepsis than we thought — but more survive
2023-09-12
Sepsis, also colloquially referred to as blood poisoning, is a serious condition. Just over 3,000 people die with a diagnosis of sepsis in Norwegian hospitals each year.
However, sepsis is not actually poisoning at all. The condition occurs when the immune system overreacts to an infection that can be caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi or parasites. The immune system attacks the organs of the body and the patient develops organ failure.
A new study of 300,000 sepsis admissions has found that the condition is more prevalent than previously thought. However, ...
Mount Sinai researchers develop novel, automated measure of sleep studies to determine severity of obstructive sleep apnea
2023-09-12
Mount Sinai researchers have developed a novel, automated measure of analyzing sleep studies to determine the severity and risk of mortality in patients with obstructive sleep apnea, a chronic sleep disorder that affects about 30 million people in the United States. The study findings, which provide a validated tool to better manage sleep apnea and promote preventive care, were published in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine on September 12.
The Mount Sinai Sleep and Circadian Analysis (SCAN) Group developed an automated breath-by-breath measure called ventilatory burden that assesses the proportion of small breaths during a routine sleep study. This ...
Fall snow levels can predict a season's total snowpack in some western states
2023-09-12
Spring break can be a good time for ski trips — the days are longer and a little warmer. But if people are booking their spring skiing trips the fall before, it's hard to know which areas will have the best snow coverage later in the season.
Researchers who study water resources also want to know how much snow an area will get in a season. The total snowpack gives scientists a better idea of how much water will be available for hydropower, irrigation and drinking later in the year.
A team led by researchers at the University of ...
Ten superintendents drive national initiative to champion health in schools
2023-09-12
With the start of the new school year, ten school system superintendents from coast to coast are working with the American Heart Association, a global force for healthier lives for all, to improve the health and well-being of students, families and educators nationwide. These top volunteer leaders, who are members of the association’s 2023-2024 national Superintendent Council will focus on providing guidance on how schools across the country can combat challenges that affect physical and mental well-being – contemporary issues like ...