(Press-News.org) PHILADELPHIA – Today, the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) released the 13th edition of its annual Cancer Progress Report, which chronicles how basic, translational, and clinical cancer research and cancer-related population sciences—primarily supported by federal investments in the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and the National Cancer Institute (NCI)—remain vitally important to improving health and saving lives.
In addition to providing the latest statistics on cancer incidence, mortality, and survivorship, the AACR Cancer Progress Report 2023 offers detailed updates and important context regarding the latest research in cancer etiology, early detection, diagnosis, treatment, prevention, and survivorship. Throughout the report, the personal stories of patients who have benefited from innovative, recently approved anticancer therapeutics highlight the real-world impact of cancer research.
This comprehensive report also features a spotlight on cancer immunotherapy and addresses persistent challenges in cancer research, including cancer disparities, slow progress against certain types of cancer, and the physical, psychosocial, and financial hardships faced by cancer patients, survivors, and their caregivers. A closing call to action outlines steps Congress and other stakeholders must take to ensure that the U.S. maintains its momentum against cancer for the benefit of all patients.
“The advances in cancer research, particularly in the last two decades, have been breathtaking,” said AACR President Philip Greenberg, MD, FAACR. “We are in an era of unparalleled opportunity to make even more breakthroughs for patients. For the cancer research community to achieve these breakthroughs, however, our representatives in Congress must continue to prioritize funding for biomedical research, from basic research to clinical trials. Through the AACR Cancer Progress Report 2023, we are sharing with the public and policy makers the progress that has been made, how that progress has been delivered to patients, how it’s changed people's lives, and the unparalleled opportunities that now exist from scientific and technologic advances, so they understand how crucial it is that we maintain this momentum through continued support of NIH and NCI.”
PROMISING TRENDS AND ADVANCES IN CANCER CARE
The medical research community—including researchers in academia and industry, physician-scientists, patient advocates, regulators, and many other stakeholders—has maintained impressive momentum against cancer in recent years. As outlined in the AACR Cancer Progress Report 2023:
From August 1, 2022, to July 31, 2023, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved 14 new anticancer therapeutics, including:
A new gene therapy-based immunotherapeutic for certain patients with bladder cancer
A first-in-class antibody drug conjugate for patients with ovarian cancer
Four new T-cell engaging bispecific antibodies for a range of hematologic malignancies
During this same time frame, the FDA approved two new imaging agents and expanded the use of 12 previously approved anticancer therapeutics to treat additional cancer types, including:
The first approval of an immune checkpoint inhibitor for pediatric and adult patients with a rare form of sarcoma
Due in large part to advances in prevention, early detection, and treatment, the age-adjusted overall cancer death rate in the U.S. fell by 33% between 1991 and 2020—an estimated 3.8 million cancer deaths averted.
This reduction is driven by declines in mortality from various cancer types, including breast, colorectal, lung, and prostate cancer, as well as melanoma. For example:
Breast cancer mortality declined by 43% between 1989 and 2020, leading to an estimated 460,000 fewer breast cancer deaths.
The decrease in lung cancer mortality has accelerated from 0.9% a year between 1995 and 2005 to nearly 5% a year between 2014 and 2020. This rapid decline is the result of a steep reduction in the U.S. smoking rate as well as the development of numerous highly effective molecularly targeted therapeutics and immunotherapeutics.
More and better treatment options have led to notable progress against many pediatric cancers as well. Among children (14 and younger) and adolescents (15-19), overall cancer death rates declined by 70% and 64%, respectively, between 1970 and 2020.
THE IMMUNOTHERAPY REVOLUTION
Immunotherapy has revolutionized cancer care. Breakthroughs in this field have contributed to much of the progress noted above, such as declines in the death rates for previously intractable cancers like advanced lung cancer and melanoma. The AACR Cancer Progress Report 2023 contains a spotlight on the history of cancer immunotherapy, the current state of this treatment modality, and the immense promise of the next generation of immunotherapeutics. Highlights include:
Since 2011, the FDA has approved 11 immune checkpoint inhibitors, which release “brakes” on the surface of certain immune cells—called T cells—so that the T cells are able to destroy cancer cells. Many of these drugs are approved for more than one type of cancer, making immune checkpoint inhibitors a treatment option for 20 cancer types and any tumor with certain specific molecular characteristics.
Since 2017, the FDA has approved six CAR T-cell therapies to treat a range of hematologic malignancies. CAR T-cell therapy is a type of adoptive cell therapy, which is designed to dramatically increase the number of cancer-killing immune cells a patient has.
The field is expanding in exciting ways, with researchers combining the power of other cells in the immune system with recent advances in gene editing to develop more personalized and effective versions of adoptive cell therapy for treatment of solid tumors; developing mRNA-based vaccines and therapeutics to treat cancer; and targeting the gut microbiome to increase the efficacy of cancer immunotherapy, among many other innovative approaches.
DESPITE PROGRESS, CHALLENGES PERSIST
Despite the extraordinary scientific progress against cancer in recent years, this complex disease remains a significant threat to human health around the world. In the U.S., it is estimated that nearly 2 million new cases of cancer will be diagnosed and more than 609,000 people will die from the disease in 2023.
Indeed, cancer research and patient care face numerous challenges, as outlined in the AACR Cancer Progress Report 2023:
Cancer disparities are a pervasive public health problem, with racial and ethnic minorities and other medically underserved U.S. populations shouldering a disproportionally higher burden of cancer. While advances have been made in identifying, understanding, and addressing some of these disparities, more research and policy solutions are urgently needed to ensure equitable progress against cancer.
There has been uneven progress against different cancer types. Few treatment options exist for patients diagnosed with pancreatic cancer or glioblastoma, for example, and 5-year relative survival rates for these cancers are extremely low.
Incidence rates for some cancers are increasing, including for early-onset colorectal cancer, pancreatic cancer, and uterine cancer, in part due to the rising rate of obesity.
Financial toxicity is widespread, exacerbated by the rising cost of cancer care. In 2019, U.S. cancer patients paid an estimated $16.2 billion in out-of-pocket cancer care costs and lost an additional $5 billion in “time costs.”
FEDERAL FUNDING ESSENTIAL FOR CONTINUED PROGRESS
To confront these and other challenges, the AACR Cancer Progress Report 2023 calls on Congress to support robust, sustained, and predictable annual funding growth for NIH and NCI by providing increases of at least $3.465 billion and $2.6 billion, respectively, in their fiscal year 2024 base budgets. This funding is crucial to continued progress for patients. From 2010 to 2019, NIH funding contributed to the development of 354 out of 356 new drugs, including many cancer drugs, approved by the FDA.
The AACR also urges Congress to:
Provide $1.7 billion in dedicated funding for Cancer Moonshot activities in FY 2024 across NCI, FDA, and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) with the assurance that Moonshot funding will supplement rather than supplant NIH funding in FY 2024.
Appropriate at least $472.4 million in FY 2024 appropriations for the CDC Division of Cancer Prevention to support comprehensive cancer control, central cancer registries, and screening and awareness programs for specific cancers.
Allocate $50 million in funding for the Oncology Center of Excellence at FDA in FY 2024 to allow regulators with the capable staff and necessary tools to conduct expedited review of cancer-related medical products.
“We are proud to release the 13th annual AACR Cancer Progress Report,” said AACR CEO Margaret Foti, PhD, MD (hc). “It is our hope that this comprehensive resource will help to increase knowledge about the myriad diseases we call cancer as well as the innovative research that is improving and extending lives. The findings in this report, along with the personal stories of the featured patients, underscore the enormous impact that robust, sustained, and predictable funding for cancer research has had on Americans’ health, and why that support must continue.”
Resources
For a copy of the report, contact Kathleen Venango at kathleen.venango@aacr.org or 215-290-5408.
To register to attend the September 13 briefing unveiling the report in person, please fill out this form. To register to view the event livestream, please fill out this form.
The AACR has made the following graphics available for reporters’ use in stories and on social media. Download them at the links below:
Cover of the AACR Cancer Progress Report 2023 (JPG)
FDA Approvals Between August 1, 2022, and July 31, 2023 (JPG)
Reduction in Overall Cancer Death Rate (JPG) and Breast Cancer Death Rate (JPG)
5-Year Relative Survival Rate for Children and Adolescents (JPG)
Inequities in Cancer Screening (JPG)
Difficulties in Accessing Survivorship Care (JPG)
Impact of Research Funding from NIH (JPG)
Video interviews with patients featured in the report, as well as b-roll, are also available. Contact Kathleen Venango at kathleen.venango@aacr.org for clips.
Follow #CancerProgressReport on Twitter.
END
AACR Cancer Progress Report details exciting advances in cancer research and treatment
Report includes call to action outlining steps Congress must take to maintain momentum against cancer for all patients
2023-09-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Pitt surveillance system detected infection linked to eye drops months before outbreak declared
2023-09-13
An infectious diseases surveillance system created by University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine scientists and deployed at a UPMC hospital successfully flagged cases of a drug-resistant infection spread by eye drops months before national public health officials announced an outbreak.
The findings, published today in The Journal of Infectious Diseases, were obtained through a hospital-based program called Enhanced Detection System for Healthcare-Associated Transmission (EDS-HAT). They demonstrate the potential of this technology to detect and stop nationwide outbreaks sooner.
“Our study really showcases the utility of whole genome sequencing surveillance,” ...
Early ovary removal likely to accelerate aging process and health problems
2023-09-13
CLEVELAND, Ohio (Sept 13, 2023)—Increasing concerns regarding potentially harmful long-term effects of premenopausal bilateral oophorectomy (PBO) have caused a decline in the number of women choosing to proactively remove both ovaries as a precaution to protect against ovarian cancer. A new study identified specific chronic medical conditions, such as asthma and arthritis, associated with the procedure. Results of the study are published online today in Menopause, the journal of The Menopause Society.
Hysterectomy is the second-most-frequently performed surgical operation for women after cesarean ...
Discovery of two potential Polar Ring galaxies suggests these stunning rare clusters might be more common than previously believed.
2023-09-13
KINGSTON, September 13, 2023 – A group of international astronomers, including researchers from Queen’s University, has identified two potential polar ring galaxies, according to results published today in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
Queen’s researchers Nathan Deg and Kristine Spekkens (Physics, Engineering Physics & Astronomy) led the analysis of data obtained using a telescope owned and operated by CSIRO, Australia’s national science agency. Looking at ...
Freshwater connectivity can transport environmental DNA through the landscape
2023-09-13
A new paper published in the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B used environmental DNA (eDNA) metabarcoding to analyze fish and zooplankton communities. The study found that the movement of water between freshwater bodies, or freshwater connectivity, can transport eDNA. This highlights the potential of eDNA to provide a comprehensive view of freshwater biodiversity.
Aquatic ecosystems are connected by waterways, which allow fish, plants, and other organisms to move from one place to another. This connectivity is important for the resilience of aquatic populations, but it can also make it difficult ...
Largest historic fire death toll belongs to aftermath of 1923 Japan Earthquake
2023-09-13
Fires that raged in the days following the 1 September 1923 magnitude 7.9 Kantō earthquake killed roughly 90% of the 105,000 people who perished in and around Tokyo, making it one of the deadliest natural disasters in history—comparable to the number of people killed in the World War II atomic bombing of Hiroshima.
The story of the conflagration, not well-known outside of Japan, holds important lessons for earthquake scientists, emergency response teams and city planners, according to a new paper published ...
Nature’s great survivors: Flowering plants survived the mass extinction that killed the dinosaurs
2023-09-13
A new study by researchers from the University of Bath (UK) and Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México (Mexico) shows that flowering plants escaped relatively unscathed from the mass extinction that killed the dinosaurs 66 million years ago. Whilst they suffered some species loss, the devastating event helped flowering plants become the dominant type of plant today.
There have been several mass extinctions in the Earth’s history, the most famous caused by an asteroid hit 66 million years ago, which has steered the course of life on Earth profoundly.
The ...
Death rates following first heart attack have gone down for those without diabetes or with type 2 diabetes, but not for type 1 diabetes
2023-09-13
*Note- this is an early release from the Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) meeting in Hamburg, October 2-6. Please credit the meeting if you use this story*
New research to be presented at this year’s Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) in Hamburg, Germany (2-6 October) shows that, following a heart attack, there have been falls in the death rates of both people without diabetes and those with type 2 diabetes, but not those with type 1 diabetes. The study is by Dr Linn ...
University of Alberta to offer pioneering AI education to all undergraduate students
2023-09-12
The University of Alberta (U of A), a globally recognized leader in Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning, along with Amii (Alberta Machine Intelligence Institute), are breaking new ground with the launch of "Artificial Intelligence Everywhere," a new online introductory course accessible to all U of A undergraduates. The course is the cornerstone for an in-development AI certification, which will be one of the first in Canada.
The course equips students across all disciplines with essential AI literacy skills. With AI permeating sectors from health care to finance, this initiative bridges the AI skills ...
Making mammography inclusive for patients with disabilities
2023-09-12
Lene Andersen, MSW, has been living with rheumatoid arthritis and disability since childhood. Her personal experience with limited mobility and the challenges faced in accessing mammography screening in Toronto, Ontario, has fueled her determination to advocate for change. Her story is featured in an upcoming themed issue of the Journal of Medical Imaging and Radiation Sciences on the topic of specialized populations, published by Elsevier.
In this personal narrative, Lene, an advocate and accessibility consultant, teamed up with Natasha Batchelor, MHSc, MRT(R), a medical imaging technologist from the York region in Ontario with expertise in creating an accessible mammography ...
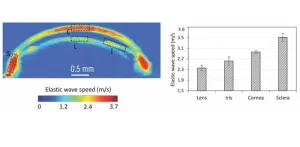
New imaging technique measures elasticity of multiple eye components simultaneously
2023-09-12
The eye is a highly complex organ, composed of intricate structures combining several types of specialized tissues. Under normal conditions, these structures work seamlessly together to provide clear images of the world around us as well as maintain intraocular pressure. However, when ocular diseases set in, the biomechanical properties of eye components change, disrupting their normal functioning. Most importantly, the alternations in biomechanical properties of the eye often lead to significant ocular diseases and vision loss. In order to study, diagnose, and monitor ocular diseases, it is, therefore, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
[Press-News.org] AACR Cancer Progress Report details exciting advances in cancer research and treatmentReport includes call to action outlining steps Congress must take to maintain momentum against cancer for all patients