(Press-News.org) Lene Andersen, MSW, has been living with rheumatoid arthritis and disability since childhood. Her personal experience with limited mobility and the challenges faced in accessing mammography screening in Toronto, Ontario, has fueled her determination to advocate for change. Her story is featured in an upcoming themed issue of the Journal of Medical Imaging and Radiation Sciences on the topic of specialized populations, published by Elsevier.
In this personal narrative, Lene, an advocate and accessibility consultant, teamed up with Natasha Batchelor, MHSc, MRT(R), a medical imaging technologist from the York region in Ontario with expertise in creating an accessible mammography environment. Together, they have published a call to action for a national response to remove barriers in breast cancer screening. Blending personal and professional knowledge, they offer valuable insights into creating an inclusive environment and practice.
In this narrative, Lene outlines her experience as a wheelchair user with limited mobility in her arms and shoulders, which has created significant challenges in accessing mammography screenings. Despite having a lump in her breast for several decades, she was unable to undergo mammograms due to the lack of accessible equipment and procedures. She also highlights the challenges encountered as a wheelchair user with limited mobility, from contorting her body into uncomfortable positions for ultrasounds to the absence of fragrance-free gel triggering severe asthma attacks.
Reflecting on her journey, Lene emphasized, "Discovering that I was not considered or deliberately excluded from the breast cancer prevention system was a shock that still reverberates in my life. It woke me up to the many ways in which healthcare fails to meet the needs and protect the lives of disabled patients."
She further noted that “…lacking recent studies, documentation, and accessibility guides, mammography clinics are left without guidance and standards to remove barriers and make this essential screening test inclusive for people of all abilities. This results in a patchwork approach to accessibility, one that relies on the awareness of each clinic and its staff to identify a lack of equity, as well as a guesswork approach to accessibility with a resulting potential for inadequate resolution and barrier removal. It is reasonable to expect that this has a direct impact on early detection and survival rates in disabled patients.”
Natasha Batchelor, a mammography and breast imaging navigator/supervisor, has dedicated her career to improving the imaging experience for patients with disabilities. She has firsthand knowledge of the challenges faced by these individuals and has developed strategies and resources to address their unique needs. Natasha's commitment to creating an inclusive environment for patients with disabilities has led to the creation of a webinar and resource materials, providing valuable training for fellow technologists and healthcare professionals.
Together, the authors outline a three-pronged approach to tackle physical, social, and procedural barriers. The article outlines numerous common physical barriers such as standing-person only check-in counters, small mammography rooms with no room for mobility aids, or forms requiring handwriting. Essential considerations to remove physical barriers include accessibility features such as adjustable equipment, accessible changerooms, and fragrance-free policies. To address social barriers, such as bias, attitudes, and behaviors of health professionals, they stress the need for comprehensive training and resources. Procedural barriers refer to intake/admissions procedures and appointment accommodations, and the authors outline recommendations to improve these processes. By implementing the measures proposed in this call to action, healthcare systems can ensure that patients with disabilities have equal access to essential breast cancer screening services.
The authors underscore the need for meaningful consultations with disabled individuals (“nothing about us without us”) and the involvement of accessibility professionals in the analysis of existing barriers and the development of solutions. While recognizing the financial constraints faced by some areas, they urge professional associations and clinics to unite in advocating for funding to remove structural barriers. Simultaneously, they emphasize that immediate actions, such as awareness campaigns, accessibility training, and equipment adjustments, can be taken by clinics and technologists to improve accessibility and accommodate disabled patients.
Creating an inclusive environment for patients with disabilities requires collaboration among governments, healthcare systems, imaging associations, and individual clinics. The authors stress the importance of an equity-based and patient-centered approach to healthcare, urging stakeholders to prioritize the needs and experiences of disabled individuals. By addressing the identified barriers and implementing the recommended considerations, health systems can work towards eliminating inequities in breast cancer screening and ensure health equity for people with disabilities.
END
Making mammography inclusive for patients with disabilities
A narrative in the Journal of Medical Imaging and Radiation Sciences emphasizes the urgent need to address the existing disparities in breast cancer screening for disabled individuals
2023-09-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New imaging technique measures elasticity of multiple eye components simultaneously
2023-09-12
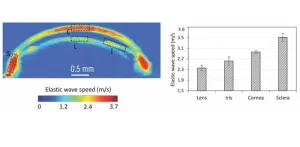
The eye is a highly complex organ, composed of intricate structures combining several types of specialized tissues. Under normal conditions, these structures work seamlessly together to provide clear images of the world around us as well as maintain intraocular pressure. However, when ocular diseases set in, the biomechanical properties of eye components change, disrupting their normal functioning. Most importantly, the alternations in biomechanical properties of the eye often lead to significant ocular diseases and vision loss. In order to study, diagnose, and monitor ocular diseases, it is, therefore, ...
Novel emerging nano-assisted anti-cancer strategies based on the STING pathway
2023-09-12
https://www.scienceopen.com/hosted-document?doi=10.15212/AMM-2023-0023
Announcing a new publication for Acta Materia Medica journal. Activation of simulator of interferon genes (STING), which induces the production of proinflammatory factors and immune effector cell activation, is considered a promising strategy for enhanced anti-cancer intervention. However, several obstacles prevent STING signaling in solid tumors, such as delivered molecules’ rapid degradation, restriction to tumor sites, insufficient intracellular concentrations, and low responsivity. ...
'Team Waponi' advances to finals of $10M XPRIZE Rainforest Competition with 'Limelight', earns $300K semi-finalist prize
2023-09-12
NJIT biology professor Eric Fortune and a team of scientists, known as “Team Waponi”, have reached the final stage of the five-year, $10M XPRIZE Rainforest Competition.
In June, Fortune and 13 other team members traveled to the rainforests of Singapore to compete in the semi-finals of the global competition, which challenged teams to develop and demonstrate new technologies for mapping the vast biodiversity of the world's tropical forests.
The team’s biodiversity sampling device, called “Limelight”, has captured exactly that so far — securing them a spot among six finalists to advance from the field of 13 teams, while earning ...
Charging ahead: New electrolyte goes extra mile for faster EV charging
2023-09-12
Oak Ridge National Laboratory researchers are taking fast charging for electric vehicles, or EVs, to new extremes.
A team of battery scientists recently developed a lithium-ion battery material that not only recharges 80% of its capacity in 10 minutes but keeps that ability for 1,500 charging cycles.
When a battery operates or recharges, ions move between electrodes through a medium called the electrolyte. ORNL’s Zhijia Du led a team who developed new formulations of lithium salts with carbonate solvents to form an electrolyte that maintains better ion flow over time and performs well when high current heats up the battery ...
Smartphone technology expected to advance assessment of neurological soft signs in schizophrenia
2023-09-12
September 12, 2023 — Since the 1980s, we have known that neurological soft signs (NSS) can distinguish people with schizophrenia from psychiatrically healthy individuals. NSS are subtle neurological impairments that principally manifest as decreased sensory integration (trouble receiving and responding to information transmitted to the brain through the senses) and difficulties with balance, rapid successive movements, and right–left orientation.
NSS doesn't always cause impairment of daily living, but identifying them could improve the diagnosis and treatment of schizophrenia and enhance understanding of the ...
Kessler Foundation receives $725,000 grant for study to accelerate functional recovery in multiple sclerosis
2023-09-12
East Hanover, NJ – September 12, 2023 – Carly Wender, PhD, associate research scientist in the Center for Neuropsychology and Neuroscience Research at Kessler Foundation received a three-year $725,499 grant from the National Multiple Sclerosis Society for her study, “A Novel Combinatory Approach to Maximize Functional Recovery of Learning and Memory in Multiple Sclerosis.”
Cognitive impairment is a common symptom in individuals with multiple sclerosis (MS) that can be particularly ...
Older adults with digestive diseases experience higher rates of loneliness, depression
2023-09-12
While life expectancy rates for older Americans are rising, nearly 40% of adults report living with a digestive disease of some kind.
“Many people don’t realize that these conditions are very common in ambulatory care,” said Michigan Medicine gastroenterologist Shirley Ann Cohen-Mekelburg, M.D., who specializes in conditions like inflammatory bowel disease, Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
“Ultimately, this creates an excess in health care spending in the United States. Not only are these conditions debilitating for the millions of people living with them, ...
Mount Sinai receives NIH grant to develop vaccines that can protect against many different types of coronaviruses
2023-09-12
The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases has awarded the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai a five-year, $13 million grant to bring together experts from multiple disciplines across five research institutions to create better vaccines against current as well as emerging coronaviruses.
The COVID-19 pandemic, caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), has infected 280 million people and caused more than five million deaths worldwide since late 2019. While considerable progress has been made to develop interventions (i.e., monoclonal antibodies, antivirals, vaccines) to treat and prevent COVID-19, ...
Setting the gold standard in diagnosis of lupus nephritis
2023-09-12
In the ever-perilous autoimmune disease world of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE or lupus), up to 60% of adult patients and 80% of children will develop lupus nephritis (LN), and up to half of those will move on to end-stage renal disease. LN occurs when the immune system wrongly attacks the kidneys, preventing them from doing their job, i.e., cleaning blood, balancing body fluids and controlling hormones that impact blood pressure.
Unfortunately, the most precise way to diagnose LN hasn’t been ...
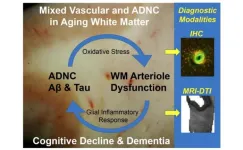
Contributions to white matter injury in Alzheimer’s disease
2023-09-12
“The molecular mechanisms that mediate enhanced dysfunction of white matter parenchymal arterioles when vascular dysfunction and ADNC coincide remain elusive.”
BUFFALO, NY- September 12, 2023 – A new editorial paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 16, entitled, “Microvascular contributions to white matter injury in Alzheimer’s disease.”
In their new editorial, researchers Zsolt Bagi, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Trapping light on thermal photodetectors shatters speed records
New review highlights the future of tubular solid oxide fuel cells for clean energy systems
Pig farm ammonia pollution may indirectly accelerate climate warming, new study finds
Modified biochar helps compost retain nitrogen and build richer soil organic matter
First gene regulation clinical trials for epilepsy show promising results
Life-changing drug identified for children with rare epilepsy
Husker researchers collaborate to explore fear of spiders
Mayo Clinic researchers discover hidden brain map that may improve epilepsy care
NYCST announces Round 2 Awards for space technology projects
How the Dobbs decision and abortion restrictions changed where medical students apply to residency programs
Microwave frying can help lower oil content for healthier French fries
In MS, wearable sensors may help identify people at risk of worsening disability
Study: Football associated with nearly one in five brain injuries in youth sports
Machine-learning immune-system analysis study may hold clues to personalized medicine
A promising potential therapeutic strategy for Rett syndrome
How time changes impact public sentiment in the U.S.
Analysis of charred food in pot reveals that prehistoric Europeans had surprisingly complex cuisines
As a whole, LGB+ workers in the NHS do not experience pay gaps compared to their heterosexual colleagues
How cocaine rewires the brain to drive relapse
Mosquito monitoring through sound - implications for AI species recognition
UCLA researchers engineer CAR-T cells to target hard-to-treat solid tumors
New study reveals asynchronous land–ocean responses to ancient ocean anoxia
Ctenophore research points to earlier origins of brain-like structures
Tibet ASγ experiment sheds new light on cosmic rays acceleration and propagation in Milky Way
AI-based liquid biopsy may detect liver fibrosis, cirrhosis and chronic disease signals
Hope for Rett syndrome: New research may unlock treatment pathway for rare disorder with no cure
How some skills become second nature
SFU study sheds light on clotting risks for female astronauts
UC Irvine chemists shed light on how age-related cataracts may begin
Machine learning reveals Raman signatures of liquid-like ion conduction in solid electrolytes
[Press-News.org] Making mammography inclusive for patients with disabilitiesA narrative in the Journal of Medical Imaging and Radiation Sciences emphasizes the urgent need to address the existing disparities in breast cancer screening for disabled individuals