(Press-News.org) Sitting calmly in their webs, many spiders wait for prey to come to them. Arachnids along lakes and rivers eat aquatic insects, such as dragonflies. But, when these insects live in mercury-contaminated waterways, they can pass the metal along to the spiders that feed on them. Now, researchers reporting in ACS’ Environmental Science & Technology Letters have demonstrated how some shoreline spiders can move mercury contamination from riverbeds up the food chain to land animals.
Most mercury that enters waterways originates from industrial pollution and other human activities, but it can also come from natural sources. Once in the water, microbes transform the element into methylmercury, a more toxic form, which biomagnifies and increases in organisms up the food chain. Scientists increasingly recognize spiders living on lakeshores and riverbanks as a potential link between contamination in waterways and animals that mostly live on land, such as birds, bats and amphibians, which eat the insects. So, Sarah Janssen and colleagues wanted to assess if shoreline spiders’ tissues contain mercury from nearby riverbeds and establish how these animals could connect mercury pollution in water and land animals.
The researchers collected long-jawed spiders along two tributaries to Lake Superior, and they sampled sediments, dragonfly larvae and yellow perch fish from these waterways. Next, the team measured and identified the mercury sources, including direct industrial contamination, precipitation and runoff from soil. The team observed that the origin of mercury in the sediments was the same up the aquatic food chain in wetlands, reservoir shorelines and urban shorelines. For instance, when sediment contained a higher proportion of industrial mercury, so did the dragonfly larvae, spider and yellow perch tissues that were collected. Based on the data, the researchers say that long-jawed spiders could indicate how mercury pollution moves from aquatic environments to terrestrial wildlife. The implication of these findings is that spiders living next to the water provide clues to the sources of mercury contamination in the environment, informing management decisions and providing a new tool for monitoring of remediation activities, explain the researchers.
The team also collected and analyzed tissues from two other types of arachnids from some sites: fishing spiders and orb-weaver spiders. A comparison of the data showed that the mercury sources varied among the three taxa. The team attributes this result to differences in feeding strategies. Fishing spiders hunt near water but primarily on land; orb-weavers eat both aquatic and terrestrial insects; but it’s the long-jawed species that feed most heavily on adult aquatic insects. These results suggest that although long-jawed spiders can help monitor aquatic contaminants, not every species living near the shore is an accurate sentinel, the researchers say.
The authors acknowledge funding from the U.S. Geological Survey Environmental Health Program and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Great Lakes Restoration Initiative.
The paper’s abstract will be available on Sept. 13 at 8 a.m. Eastern time here: http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acs.estlett.3c00450
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS’ mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and all its people. The Society is a global leader in promoting excellence in science education and providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, eBooks and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News. ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a leader in scientific information solutions, its CAS division partners with global innovators to accelerate breakthroughs by curating, connecting and analyzing the world’s scientific knowledge. ACS’ main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact newsroom@acs.org.
Follow us: Twitter | Facebook | LinkedIn | Instagram
END
Some spiders can transfer mercury contamination to land animals, study shows
2023-09-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
National awards recognize 19 students, schools, and educators’ commitment to health
2023-09-13
DALLAS, September 13, 2023 — On Tuesday, Sept. 12, the American Heart Association, a global force for healthier lives for all, recognized 19 students, schools and educators for their commitment to end cardiovascular disease, the nation’s no. 1 killer, through the Association’s in-school programs, Kids Heart Challenge™ and American Heart Challenge™. The annual National Awards Ceremony, held virtually, was joined by program participants from coast to coast and ...
American Society for Microbiology announces ‘gain of function’ recommendations from top scientists
2023-09-13
Washington, D.C. — Sept. 13, 2023 — The American Society for Microbiology today released consensus recommendations from a workshop of leading scientists who reviewed the benefits and risks of “gain of function” research, as well as related policies and procedures, and proposed a foundation to guide discussions and improve oversight moving forward.
The recommendations – together with a call to action for the scientific community and the general public – are intended to inform assessments of “gain of function research of concern,” which makes up a small fraction of all biological research. ...
Scientists uncover COVID’s weakness
2023-09-13
New UC Riverside research has revealed COVID’s Achilles heel — its dependence on key human proteins for its replication — which can be used to prevent the virus from making people sick.
In a new paper published in the journal Viruses, the UCR research team describes an important discovery. The protein in COVID that enables the virus to make copies of itself, called N, requires the help of human cells to perform its job.
Genetic instructions in our cells are transcribed from DNA to messenger ...
UMass Amherst and Embr Labs develop ‘digital drug’ to predict hot flashes
2023-09-13
Researchers at the University of Massachusetts Amherst’s Institute for Applied Life Sciences (IALS) and Embr Labs have created a machine-learning algorithm to predict a hot flash before a person perceives it.
When combined with Embr Labs’ patented wearable device, Embr Wave™, immediate cooling is delivered to mitigate or fully alleviate the event. This first-of-its-kind predictive algorithm is the result of machine learning being applied to the largest data set of digital biomarkers for hot flashes ever collected, which was generated by researchers at UMass Amherst’s Center for Human ...
Socioeconomic status may be an uneven predictor of heart health
2023-09-13
Research Highlights:
The benefits of four measures of socioeconomic status (education, income, employment status and health insurance) on ideal heart health were greater for non-Hispanic white adults compared to Black, Hispanic and Asian adults in the U.S.
The new diverse representative study suggests heart disease prevention efforts should address other non-biological factors that drive cardiovascular health and not rely solely on reducing socioeconomic disparities by race or ethnic group.
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT/5 a.m. ET Wednesday, Sept. 13, 2023
DALLAS, ...
No increase in cancer risk for most patients with reflux disease
2023-09-13
Reflux disease manifests as acid regurgitation and heartburn and is a known risk factor for oesophageal cancer. However, a new study published in The BMJ by researchers at Karolinska Institutet now reports that the majority of patients do not have a higher risk of cancer. A large-scale study from three Nordic countries shows that the cancer risk is only elevated in patients whom gastroscopy reveals to have changes in the oesophageal mucosa.
“This is a gratifying result since reflux disease is a very common condition and most patients are found to have a completely normal mucus membrane on gastroscopic examination,” says the study’s ...
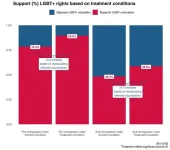
Study uncovers link between anti-immigrant prejudices and support for LGBT+ rights
2023-09-13
Cross-national research carried out by the University of Southampton and Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam (VUA) into public opinion on LGBT+ rights has shown that anti-immigrant prejudices, particularly towards Muslims, contributes to explaining some of the widespread shifts in tolerance towards the LGBT+ community. Findings of a new study show this was especially evident among socially conservative voters.
The rise of tolerance towards LGBT+ individuals in Western democracies could be seen as remarkable, according to the researchers. Whereas a majority of citizens rejected the idea of same-sex marriage a couple of decades ago, a majority of ...
Rapid acting, oral vaccines are coming soon
2023-09-13
A new paper in Biology Methods and Protocols, published by Oxford University Press, indicates that researchers studying SARS-CoV-2 may have developed new methods to administer vaccines orally, which would be both easier to administer and more effective at combatting illnesses.
The best way to neutralize viruses is before they can enter inside human cells but are only on the external surface of epithelial cells that line and produce mucus in the lungs, nose, and mouth. A specific class of antibodies known as Immunoglobulin A operate in mucus and can disable viruses. However, production of specific immunoglobulins/antibodies for a ...
Certain proteins in breast milk found to be essential for a baby’s healthy gut
2023-09-13
More than 320 million years of mammalian evolution has adapted breast milk to meet all the physiological needs of babies: it contains not only nutrients, but also hormones, antimicrobials, digestive enzymes, and growth factors. Furthermore, many of the proteins in breast milk, for example casein and milk fat globule membrane proteins, aren’t just sources of energy and molecular building blocks, but also directly stimulate immunity, at least under preclinical conditions.
Likewise, the gut microbiome, composed of bacteria, archaea, and fungi, plays a vital role in the regulation of the immune system. This raises the possibility that the immune-boosting function ...
AACR Cancer Progress Report details exciting advances in cancer research and treatment
2023-09-13
PHILADELPHIA – Today, the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) released the 13th edition of its annual Cancer Progress Report, which chronicles how basic, translational, and clinical cancer research and cancer-related population sciences—primarily supported by federal investments in the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and the National Cancer Institute (NCI)—remain vitally important to improving health and saving lives.
In addition to providing the latest statistics on cancer incidence, mortality, and survivorship, the AACR Cancer Progress Report 2023 offers detailed updates and important ...