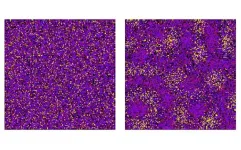
(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON – A peer-reviewed study by Environmental Working Group scientists has found unsettling details about the potential health risks of common household cleaning products.
The study, published today in Chemosphere, analyzed 30 cleaning products, including multipurpose and glass cleaners, air fresheners and more. The study revealed that these everyday products may release hundreds of hazardous volatile organic compounds, known as VOCs.
Researchers tested both conventional products and “green” cleaning products and detected a total of 530 unique VOCs in the 30 products. Of these, 193 VOCs were hazardous – identified as having the potential to cause health harms such as respiratory system damage, increased cancer risk and developmental and reproductive impacts.
VOCs in cleaning products affect the quality of air both indoors and outdoors. But they contaminate indoor air two to five times more than outdoor air, with some estimates putting it as high as 10 times more. Some products emit VOCs for days, weeks or even months.
“This study is a wake-up call for consumers, researchers and regulators to be more aware of the potential risks associated with the numerous chemicals entering our indoor air,” said Alexis Temkin, Ph.D., a senior toxicologist at EWG.
“Our findings emphasize a way to reduce exposure to hazardous VOCs – by selecting products that are ‘green,’ especially those that are ‘green’ and ‘fragrance free,’ ” she said.
The study concluded that products labeled “green” emitted fewer VOCs, compared to conventional products – about half the number, on average. The green products categorized as “fragrance free” also produced the fewest VOC emissions – nearly eight times fewer than conventional and four times fewer than green products that included fragrance on their label.
That pattern also held true for the number of VOCs considered hazardous in the products. The green products emitted just four chemicals classified as hazardous, on average, compared to about 15 in green products with fragrance and 22 for conventional products.
This suggests that choosing green, or green and fragrance free, cleaning products could be prudent for consumers concerned about indoor air quality and potential health risks.
Effect of VOC hazards
VOCs’ health harms are especially concerning because of how many Americans may be exposed to them in the workplace.
Research shows people working in the cleaning industry have a 50 percent higher risk of developing asthma and a 43 percent higher risk of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Women working in this field also face an increased risk of lung cancer.
Children’s health may also be at risk. Some studies show that higher use of certain indoor cleaners in utero and in infancy is associated with a greater risk of asthma and wheezing in childhood.
“These cleaning products may hurt our health, but they may also harm the environment,” said Samara Geller, EWG senior director of cleaning science.
The study’s results carry implications not only for human health but also for environmental health. VOCs emitted by consumer products can contribute to outdoor air pollution, adding to existing environmental concerns. A study from 2018 estimated that half of the VOCs responsible for air pollution stem from consumer products.
“Going green with your cleaning products is an easy way to reduce exposure to harmful chemicals. This may be especially important for women’s and children's health,” said Geller.
###
The Environmental Working Group (EWG) is a nonprofit, non-partisan organization that empowers people to live healthier lives in a healthier environment. Through research, advocacy and unique education tools, EWG drives consumer choice and civic action.
Note: EWG bought the products tested in the study between December 2019 and May 2022 and the test results reflect the product formulations of the products at the time of the purchase. EWG knows that some of the formulations tested might be now discontinued or reformulated.
The currently available products may not be the same formulations as the products tested and some products may have been discontinued.
A September 2023 EWG review of products tested indicates that four products are no longer available on company websites, including Febreze One, bamboo; Attitude Sensitive Skin Natural All-Purpose Cleaning with Colloidal Oatmeal; Babyganics Floor Cleaning Concentration, Fragrance-Free; and Martha Stewart Premium Wood and Floor Cleaner.
END
Professor Zorana Jovanovic Andersen, Chair of the European Respiratory Society’s Environment and Health Committee and based at the University of Copenhagen, said:
“Today’s vote by the European Parliament to strengthen the legally binding limit values for air quality is an important step in the right direction toward clean air for all, even though the full alignment with World Health Organization was moved from 2030 to 2035. As we prepare for the negotiations with the Council, this is great news for all European citizens, especially the millions who live ...
The very first life on earth is thought to have developed from “protocells” – liquid mixtures of many different types of molecules. Researchers from the University of Göttingen have now shown that in such mixtures, small imbalances in the number of molecules of different types can have an unexpected effect. A surprising interplay with the complex pattern of interactions strongly amplifies such imbalances – meaning that a type of molecule that is only slightly in the majority can almost entirely separate out from the others. ...
Does the human brain have an Achilles heel that ultimately leads to Autism? With a revolutionizing novel system that combines brain organoid technology and intricate genetics, researchers can now comprehensively test the effect of multiple mutations in parallel and at a single-cell level within human brain organoids. This technology, developed by researchers from the Knoblich group at the Institute of Molecular Biotechnology (IMBA) of the Austrian Academy of Sciences and the Treutlein group at ETH Zurich, ...
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- By mining data from X-ray images, researchers at MIT, Stanford University, SLAC National Accelerator, and the Toyota Research Institute have made significant new discoveries about the reactivity of lithium iron phosphate, a material used in batteries for electric cars and in other rechargeable batteries.
The new technique has revealed several phenomena that were previously impossible to see, including variations in the rate of lithium intercalation reactions in different regions of a lithium iron phosphate nanoparticle.
The paper’s most significant practical finding — that ...
About The Study: In this survey study of 2,552 survivors of cardiac arrest in Denmark, health-related quality of life up to 20 years after the event was consistently high across follow-up periods and comparable to the general Danish population. These findings support resource allocation and efforts targeted to increasing survival after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest.
Authors: Harman Yonis, M.D., of Nordsjallands Hospital in Hillerod, Denmark, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamacardio.2023.2934)
Editor’s ...
About The Study: In this economic evaluation of extended-release buprenorphine compared with transmucosal buprenorphine for the treatment of opioid use disorder, extended-release buprenorphine was not associated with efficient allocation of limited resources when transmucosal buprenorphine was available. Future initiatives should aim to improve retention rates or decrease costs associated with extended-release buprenorphine.
Authors: Juliet M. Flam-Ross, B.A., of the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine in London, and Sabrina A. Assoumou, M.D., M.P.H., of the Boston ...
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. – Glue holds the world together. Without adhesives, much of modern human civilization — including our cellphones, cars, furniture, walls and the packages arriving on our doorstep — would simply fall apart.
The trouble with all those adhesives is that they are not sustainable. A team of chemists at Purdue University led by Jonathan Wilker, professor of chemistry in the College of Science and of materials engineering, aims to change that with a new, completely sustainable adhesive system. The team’s findings were released in a paper in Nature.
Additional Information
Shellfish ...
DURHAM, N.C. -- Many of the bacteria that ravage crops and threaten our food supply use a common strategy to cause disease: they inject a cocktail of harmful proteins directly into the plant’s cells.
For 25 years, biologist Sheng-Yang He and his senior research associate Kinya Nomura have been puzzling over this set of molecules that plant pathogens use to cause diseases in hundreds of crops worldwide ranging from rice to apple trees.
Now, thanks to a team effort between three collaborating research groups, they may finally have an answer to how these molecules make plants sick -- and a way to disarm them.
The findings appear Sept. 13 in the journal Nature.
Researchers ...
Researchers at Moorfields Eye Hospital and UCL Institute of Ophthalmology have developed an artificial intelligence (AI) system that has the potential to not only identify sight-threatening eye diseases but also predict general health, including heart attacks, stroke, and Parkinson’s disease.
RETFound, one of the first AI foundation models in healthcare, and the first in ophthalmology, was developed using millions of eye scans from the NHS. The research team are making the system open-source: freely available to use by any institution worldwide, to act as a cornerstone for global efforts to detect and treat blindness using AI. ...
Key takeaways
Social determinants of at-risk neighborhoods: Higher proportions of poverty and low per-capita income were most associated with higher rates of shooting incidents.
High levels of social stressors: The study found that fatal and non-fatal firearm assaults were clustered in neighborhoods with high levels of social stressors measured with the 2018 version of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s (CDC) Social Vulnerability Index (SVI).
A potential tool for directing anti-violence initiatives: The CDC’s SVI can help policymakers target neighborhoods at ...