(Press-News.org) To obtain the biggest cherry harvest, trees should be pollinated by both honey bees and mason bees. A new study led by a researcher at the University of Gothenburg shows yet another benefit of biodiversity.
Like many other fruit trees, most sweet cherry cultivars depend on cross-pollination to produce their fruit. This means that there need to be several different cultivars of sweet cherry trees in an orchard for the bees to transport pollen from one to another.
“Sweet cherry trees are usually planted in alternate rows of different cultivars. In some cases, you can put different cultivars in the same row, but this can make the harvesting logistics tricky. In other words, the bees have to fly from one row of trees to the next to ensure that the trees set fruit,” says Julia Osterman, a biologist at the University of Gothenburg and lead author of the study published in the scientific journal Ecology and Evolution.
Two bee species produce a synergy effect
Working with German researcher colleagues at Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg, Julia Osterman found that if trees were pollinated by more than one bee species, they produced more cherries. The researchers observed bees in a total of 17 cherry orchards in eastern Germany. Some growers used honey bees in hives as pollinators, while others used wild mason bees. Some orchards used both species to different extents. The researchers noticed a synergy effect in those orchards in which both species of bee were present.
“It had an impact on the sweet cherry fruit set. The orchards with honey bees and lots of mason bees could have cherries on up to 70 per cent of the blossom. In orchards with only honey bees or only mason bees as pollinators the rate could be as low as 20 per cent,” says Julia Osterman.
Many growers were already using two species of bees, often as a back-up if the weather was too cold for the honey bees when the cherry trees were in bloom, as cherries flower early. Honey bees only become active once the temperature is above 12°C, but mason bees can cope with lower temperatures. The sharp increase in fruiting occurred when both species were active. The researchers are now speculating on the reasons for this.
Bamboo sticks as nest material
“One theory is that the presence of mason bees affects the foraging behavior of honey bees,” says Julia Osterman. “This disturbs them and so they change rows more often, resulting in more cross-pollination. But all we know at the moment is that interaction between the bees produces a synergy effect.”
Of course, this is valuable data for cherry growers who can attract wild mason bees to their orchards by providing good nest material.
“Mason bees are solitary and don’t make honey in honeycombs like honey bees,” Julia Osterman explains. “They are more focused on collecting pollen to feed their offspring. They like to crawl into tube-shaped spaces where they can lay their eggs. Fruit growers can encourage mason bees to nest in their orchards by placing bamboo or wood with holes drilled in it at the site. However, it only seems to work up to a certain limit, after which you won’t attract any more mason bees, no matter how much nest material you bring in.”
Similar results have been observed in almond orchards and Julia Osterman’s next step will be to investigate whether this synergy effect applies to other fruit trees, as well as trying to determine exactly how the two bee species are affecting each other.
Facts: The study was conducted in Saxony-Anhalt and Thuringia in Germany in spring 2020 with researchers from Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg and a research institute in Erfurt and is published in Ecology and Evolution. To the study: Mason bees and honey bees synergistically enhance fruit set in sweet cherry orchards
END
Pollination by more than one bee species improves cherry harvest
2023-09-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New foresight report identifies urgent policy actions needed to put SDGs back on track
2023-09-14
Ahead of the UN’s SDG Summit (18-19 September), Earth4All, an international team of economists and scientists, and the Foundation for European Progressive Studies (FEPS), unveil groundbreaking research showing that policymakers can ensure the implementation of SDGs by 2050. The report ‘SDGs for All: Strategic scenarios’ equips policymakers with practical solutions designed to accelerate SDG implementation and to respond to the planetary emergency. It concludes that policymakers can step up the implementation of the SDGs by 2030 and beyond ...
The fourth wave of the US overdose crisis: fentanyl and stimulants
2023-09-14
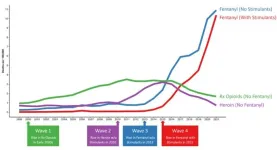
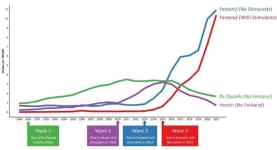
New research published in the scientific journal Addiction has found that the proportion of US overdose deaths involving both fentanyl and stimulants has increased more than 50-fold since 2010, from 0.6% (235 deaths) in 2010 to 32.3% (34,429 deaths) in 2021. By 2021, stimulants (such as cocaine and methamphetamine) had become the most common drug class found in fentanyl-involved overdoses in every US state. This rise in fentanyl/stimulant fatalities constitutes the ‘fourth wave’ in the US’s ...
Overdose deaths from fentanyl laced stimulants have risen 50-fold since 2010
2023-09-14
New UCLA-led research has found that the proportion of US overdose deaths involving both fentanyl and stimulants has increased more than 50-fold since 2010, from 0.6% (235 deaths) in 2010 to 32.3% (34,429 deaths) in 2021.
By 2021, stimulants such as cocaine and methamphetamine had become the most common drug class found in fentanyl-involved overdoses in every US state. This rise in fentanyl/stimulant fatalities constitutes the ‘fourth wave’ in the US’s long-running opioid overdose crisis –the death toll of which continues to rise precipitously.
“We’re now seeing ...
Most Ohio students who earn manufacturing-related credentials work in other industries
2023-09-14
Most students who complete manufacturing-related credentials in Ohio do not end up employed in manufacturing in the state, highlighting a challenge that faces policymakers as they push to create more U.S. manufacturing jobs, according to a new RAND Corporation report.
Among those who earned a manufacturing-related credential from a public postsecondary institute in Ohio from 2006 to 2019, fewer than 40% worked in manufacturing in the state within one year after completing their education.
Wages are not a likely contributor to the trend. Students who enter other fields after completing a manufacturing-related credential earn less than their peers who pursued ...
CityU achieves major breakthrough in highly efficient electrocatalyst for clean energy
2023-09-14
A research team led by City University of Hong Kong (CityU) has achieved a groundbreaking advancement in nanomaterials by successfully developing a highly efficient electrocatalyst which can enhance the generation of hydrogen significantly through electrochemical water splitting.
This major breakthrough has great application potential for the clean energy industry.
Professor Zhang Hua, Herman Hu Chair Professor of Nanomaterials at CityU, and his team have developed an electrocatalyst by using the transition-metal dichalcogenide (TMD) nanosheets with unconventional crystal phases as supports. The electrocatalyst exhibits superior activity and excellent ...
NHS still reliant on paper notes and drug charts despite electronic upgrades
2023-09-14
Three quarters of trusts in England that responded to a survey by The BMJ are still reliant on paper patient notes and drug charts, despite progress towards electronic records and prescribing.
The results came in just as an expert panel convened by a House of Commons committee concluded that the UK government had failed to meet a key target to eliminate paper prescribing in hospitals and to introduce digital or electronic prescribing across the entire NHS by 2024.
Jo Best, freelance journalist and doctor, ...
Durham University leads new £21.3M national research hub to decarbonize UK maritime sector
2023-09-14
The UK National Clean Maritime Research Hub (UK-MaRes Hub) aims to accelerate the decarbonisation and elimination of air pollution from maritime activity in ports and at sea.
As well as environmental impacts, the Hub will also focus on the potential economic and social benefits of transitioning to a clean maritime future.
The UK-MaRes Hub was announced today (Thursday 14 September) by the UK Government’s Maritime Minister, Baroness Vere of Norbiton, during London International Shipping Week. She was joined by the Director of the UK-MaRes Hub, Professor Tony Roskilly, Chair of Energy Systems in the Department of Engineering at Durham University.
The Hub will carry out ...
Study finds 1 in 5 people on Medicare travel 50 or more miles to see a neurologist
2023-09-13
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, SETEMBER 13, 2023
MINNEAPOLIS – Nearly one in five people on Medicare travel 50 or more miles one way to see a neurologist, a doctor who diagnoses and treats diseases of the brain and nervous system, according to research published in the September 13, 2023, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology (AAN). The study, funded by the American Academy of Neurology, found that people who require specialized neurologic care for diseases such as brain cancer, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and multiple sclerosis (MS) ...
Malnutrition early in life sets stage for poor growth and death
2023-09-13
In a trio of papers appearing in Nature on Sept. 13, 2023, the researchers offer the most comprehensive look yet at how malnutrition affects growth in the first two years of life, underscoring a devastating reality for millions of children in the Global South, particularly Asia.
In 2022, more than one in five children around the world – nearly 150 million – did not get enough calories to grow normally, and more than 45 million showed signs of wasting, or weighing too little for their height. More than a million children die each year as a consequence of wasting and more than 250,000 die from stunting. People who experienced ...
NIH-funded fly study to pinpoint brain’s role in navigation
2023-09-13
ITHACA, N.Y. -- Robust navigation is both critical for survival and dauntingly complex: Think of the speed and agility of an airborne fly.
A multidisciplinary team of researchers led by Itai Cohen, professor of physics in the College of Arts and Sciences, will use the fruit fly, Drosophila melanogaster, to study how the brain forms a coherent representation from multisensory information, corrects for errors from perturbations and generates robust behaviors.
The project, supported by a $6.5 million grant from the NIH Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, has potential for insight into human neurological function.
“We are gearing up to understand how ...