(Press-News.org)
Cells are capable of translating mechanical changes into biological responses. This process is known as mechanotransduction and plays a fundamental role in the progression of solid tumors, such as breast cancer.
It is well-established that a common mechanical alteration in cancer progression involves tissue hardening. This stiffness is precisely what is detected during self-examinations or breast palpations for potential tumor detection. The stiffness of breast tissue triggers a chain reaction, inducing tension within cells and distorting their nuclei. Ultimately, this nuclear deformation activates genes responsible for controlling cell proliferation, which are closely associated with tumor growth.
A study published today in the journal Nature Materials demonstrates a cellular mechanism that could be pivotal in slowing the progression of breast tumors. The results of the study, led by Pere Roca-Cusachs, the principal investigator at the Institute of Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) and the University of Barcelona, indicate that laminin, a protein that provides structure and support to healthy breast tissues, hinders the mechanotransduction process in cells, thereby protecting the nucleus from deformation.
“Our findings demonstrate that the presence of laminin mitigates the effects of stiffness, effectively shielding cells from tumor growth. We have showcased this mechanism in vitro, but we believe it holds potential for in vivo application, considering what we have observed in samples from breast cancer patients.” Explains Zanetta Kechagia, postdoctoral researcher at IBEC and first author of the study.
"Through this mechanism, which we have shown can prevent the invasion of tumor cells, there is potential for the development of more sensitive diagnostic tools or even new therapies for breast cancer. However, further research will be needed to explore these possibilities, Pere Roca-Cusachs, IBEC researcher, Serra-Hunter associate professor at the University of Barcelona (UB) and leader of the study, explains.
It has already been demonstrated that an increase in tissue stiffness triggers mechanical responses within cells. The most common responses are associated with alterations in the cell's cytoskeleton, affecting its interaction with the surrounding tissue and facilitating migration. Additionally, this stiffness leads to the activation of the YAP protein, which enters the nucleus and initiates the expression of genes linked to cell proliferation.
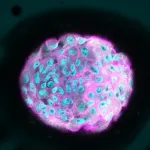
To study the mechanotransduction process, the research team cultured breast tissue cells on gels with varying stiffness to mimic both healthy (soft) and malignant (stiff) tissues. They compared the behavior of the cells on gels coated with laminin to those on gels coated with collagen or fibronectin, which are other cell-supporting proteins that are overproduced in carcinogenic processes.
Thus, the researchers observed that the cells seeded on the laminin-rich gel had a very mild mechanical response to the stiffness of the substrate, compared to those seeded on the gels rich in collagen and fibronectin.
As a result, the researchers observed that the cells seeded on the laminin-rich gel exhibited a significantly less pronounced mechanical response to the substrate's stiffness when compared to those seeded on gels abundant in collagen and fibronectin.
This work is part of the European project MECHANO· CONTROL, receiving funding exceeding 7 million euros within the framework of the European FET (Future and Emerging Technologies) projects.
"These results represent the culmination of over 6 years of work, during which we received support from the European Commission and collaborated with a team of international institutions, led by IBEC, to better understand how mechanical forces impact breast cancer," said Daniel Caudepón, IBEC project manager overseeing MECHANO·CONTROL.
This research also includes significant contributions from other institutions participating in MECHANO-CONTROL, such as Pablo Sáez and Marino Arroyo from Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya, and Thijs Koorman and Patrick Derksen from University Medical Center Utrecht, The Netherlands.
END
September 14, 2023 — More than 90% of the active members of the National Association of Neonatal Nurses (NANN) believe the organization should pursue racial equity work, and many have specific suggestions for a strategic plan. This feedback comes from the survey results the association released this month in its journal, Advances in Neonatal Care. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"Neonatal care has advanced significantly in recent years, yet ...
The rate at which the universe is expanding, known as the Hubble constant, is one of the fundamental parameters for understanding the evolution and ultimate fate of the cosmos. However, a persistent difference called the “Hubble Tension” is seen between the value of the constant measured with a wide range of independent distance indicators and its value predicted from the big bang afterglow.
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope provides new capabilities to scrutinize and refine some of the strongest observational evidence for this tension. Nobel Laureate Adam Riess from the Johns Hopkins University and ...
PHILADELPHIA – CAR T cell therapy pioneer Carl June, MD, the Richard W. Vague Professor in Immunotherapy in the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania and director of the Center for Cellular Immunotherapies (CCI) at Penn Medicine’s Abramson Cancer Center, has been named a winner of the 2024 Breakthrough Prize in Life Sciences for the development of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell immunotherapy, a revolutionary cancer treatment approach in which each patient’s T cells are modified to target and kill their cancer cells. The invention sparked a new path in cancer care, harnessing the power of patients’ own immune systems, a once-elusive ...
One quarter of food consumed in the EU-27 originates from outside the region, highlighting the vulnerability of the EU’s food system.
New research coordinated by Global Footprint Network’s sustainability scientists in collaboration with food system experts published the article “EU-27 Ecological Footprint was primarily driven by food consumption and exceeded regional biocapacity from 2004 to 2014” today in Nature Food. The way food is provided to and consumed by Europeans represents ...
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Rivers are warming and losing oxygen faster than oceans, according to a Penn State-led study published today (Sept. 14) in the journal Nature Climate Change. The study shows that of nearly 800 rivers, warming occurred in 87% and oxygen loss occurred in 70%.
The study also projects that within the next 70 years, river systems, especially in the American South, are likely to experience periods with such low levels of oxygen that the rivers could “induce acute death” for certain species of fish and threaten aquatic diversity at large.
“This is a wake-up call,” ...
A model to map energy demand down to street level shows cooling demand in the capital grew by 5% per year between 1980 and 2022 as summers heat up.
The Demand.ninja model, created by researchers at Imperial College London and TU Delft, was designed to show how the weather influences hourly energy consumption in buildings. It can also account for changes in demand as the climate changes, including the increase in cooling demand in the summer as heatwaves become more common and more intense.
Countries ...
Researchers have discovered a new way to target and kill cancer cells in hard-to-treat brain tumours using electrically charged molecules to trigger self-destruction, that could be developed into a spray treatment used during surgery.
A multidisciplinary team of researchers from the University of Nottingham, led by the School of Pharmacy found a new way to harness the extraordinary capabilities of bio-nanoantennae—gold nanoparticles intricately coated with specialised redox active molecules to induce programmed cell death, or apoptosis, in cancer cells on electrical stimulation. The research ...
About The Study: The findings of this study of 805,000 patients ages 18 or older suggest that receipt of physical therapy (PT) after presentation for dizziness was associated with a reduction in fall risk during the subsequent 12 months; thus, timely PT referral for dizziness may be beneficial for these patients. Future research, ideally with a clinical trial design, is needed to explore the independent impact of PT on subsequent falls for adults with dizziness.
Authors: Meredith E. Adams, M.D., M.S., of ...
About The Study: The results of this study of 2,176 counties suggest that breast cancer mortality in the U.S. can be affected by where individuals live, and that more comprehensive and geographically targeted interventions may lead to healthier communities.
Authors: Taylor Anderson, Ph.D., of George Mason University in Fairfax, Virginia, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.33618)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions ...
Combination immunotherapy with the anti-PD-L1 monoclonal antibody durvalumab and other novel agents outperforms durvalumab alone in the neoadjuvant (pre-surgical) setting for early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC), according to researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center.
The findings, published today in Cancer Discovery, were first presented at the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting 2022.
The multicenter, randomized Phase II NeoCOAST clinical trial evaluated neoadjuvant durvalumab alone ...