(Press-News.org) Barcelona, Spain: People who come to emergency departments with alcohol-related diseases or conditions are more likely to make return visits and to die in the following 20 years, than people who come to emergency departments for other reasons, according to new research. For many, this means they may die in their 40s or 50s.
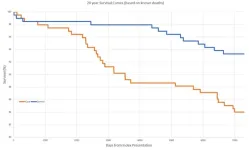
Professor Drew Richardson told the European Emergency Medicine Congress that he and his colleagues had followed 194 patients who had alcohol-related diagnoses when they arrived in the emergency department of The Canberra Hospital in 2002. They compared them with a control group of 194 patients who had diagnoses unrelated to alcohol, and they followed both groups until 2022.
“The group of patients with alcohol-related diagnoses made 44% more visits over the next decade and had a 138% higher death rate over the following 20 years, than the control group,” said Prof. Richardson, who is Professor of Emergency Medicine at Australian National University, Canberra, Australia. “The true death rate may be higher because we lost some patients during the follow-up period. After nearly 14 years, the percentage of patients lost to follow-up was similar for both groups: 40.2% for the alcohol-related cases and 39.2% for the controls.
“There was a wide variety of reasons these patients came to our emergency department, including alcohol withdrawal symptoms, trauma-related injuries, and acute alcohol intoxication.
“If these patients could be targeted by trained professionals while they are in the emergency department to educate them about the consequences of alcohol use, and to offer them assistance in moderating their alcohol consumption, it might be possible to reduce this significant health burden. Presentations related to alcohol consumption are a major burden in emergency departments.”
The study was initiated by one of Prof. Richardson’s medical students, Ms Regan Lim, who had personal family experience of the effects of alcohol and wanted to investigate further.
“Chronic and excessive consumption of alcohol has been a long-standing problem in our society. Emergency departments are the first point of contact for the many consequences of alcohol-related harm. Alcohol-related cases make up 9.5%-15.2% of presentations to emergency departments, and 8.3%-17.9% of emergency department occupancy in Australasia,” said Prof. Richardson.
The researchers analysed the number of patients who came to the emergency department between 1998-2002 (the period before the study started), 2003-2012 (the decade after) and 2013-2022 (the second decade after). The patients with alcohol-related diagnoses had made 522 presentations to the emergency department before the start of the study, compared to 389 for the patients in the control group. In 2002, the numbers were 437 compared to 399, respectively. In the first decade after, they were 1226 compared to 846 respectively. In the second decade, there was a smaller difference due to the numbers lost to follow-up: 820 compared to 673 presentations respectively.
Just over half (56%) of the patients in the alcohol group were male, the median (average) age was 28, and they were usually put into Triage Category 3, which meant they had potentially life-threatening conditions and needed treatment within 30 minutes. The majority (64%) presented in the emergency department in the late evening and over night, between 20:00 hours and 06:00 hours.
During the follow-up period, 44 patients died, of which 31 were patients with alcohol-related diagnoses who died a median of eight years after 2002, and 13 were from the control group, who died a median of 13 years after 2002.
Prof. Richardson said: “Society and policy-makers should recognise the major role that alcohol plays in illnesses and death in our community, and the need for preventative measures. Alcohol consumption is a significant part of Australasian society, but this study shows that consumption that leads to a visit to a hospital’s emergency department is extremely risky in the long term.
“We have been studying the effects of alcohol presentations in emergency departments for over a decade. The next logical step is a long-term trial of an alcohol intervention programme in the emergency department to see if this really does reduce burden of drink-related effects on patients and hard-pressed emergency staff.”
Professor Youri Yordanov from the St Antoine Hospital emergency department (APHP Paris), France, is Chair of the EUSEM 2023 abstract committee and was not involved in the research. He said: “This study shows a pattern that is familiar to many of us working in emergency departments around the world: alcohol abuse is responsible for a large proportion of patients vising emergency departments. Not only does this place significant burdens on emergency departments that are already over-stretched for a variety of reasons, including ageing populations and under-funding, but it shortens people’s lives too. Initiatives to intervene at an early stage to help prevent repeat visits to emergency departments and the problems associated with alcohol abuse would be very welcome and we look forward to seeing the results of further studies into this.”
(ends)
[1] Abstract no: OA110, “Long term outcomes after alcohol-related presentation to ED” by Drew Richardson, in the “Education, training and toxicology” oral session, Tuesday 19 September at 11.05-12.30 hrs CEST, Room 131. https://cm.eusem.org/cmPortal/Searchable/EXA/config/normal/redirectconfig/normal/redirectconference/EUSEM23#!sessiondetails/0000014290_0
END
Patients visiting emergency departments because of alcohol abuse are more likely to make return visits and to die in the following decades
2023-09-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Carnegie Mellon University College of Engineering participates in AI briefing at the UN
2023-09-18
PITTSBURGH—Today, William Sanders, dean of the College of Engineering at Carnegie Mellon University, participated in a briefing at the United Nations. He was joined by Carnegie Mellon University Africa student Choukouriyah Arinloye. The event, “Artificial Intelligence for Accelerating Progress on the Sustainable Development Goals: Addressing Society’s Greatest Challenges,” was held as part of the 78th United Nations General Assembly and was hosted by US Secretary of State Antony Blinken. The event ...
Sylvester study shows that new protocols enable many patients to safely return home just one day after lung cancer surgery
2023-09-18
MIAMI, FLORIDA (Sept. 18, 2023) – Thoracic surgeons and researchers at Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine found that increasing numbers of patients undergoing cancer-removal lung surgery by “anatomic lung resections” – lobectomies or segmentectomies – are able to go home safely and without complications one day after the operation, thanks to growing rates of robot-assisted surgeries and improvements in patient-centered care protocols.
However, the research team found, patients of lower socioeconomic status were considerably ...
Canopy gaps help eastern hemlock outlast invasive insect
2023-09-18
A new study finds that creating physical gaps in the forest canopy give eastern hemlocks more access to resources and help those trees withstand infestation by an invasive insect. The approach adds another tool to the toolkit that foresters can use to protect these trees.
Eastern hemlocks are an ecologically important tree species found from eastern Canada to the Great Lakes states and south along the entire Appalachian mountain range. The hemlock woolly adelgid – an invasive insect that was introduced to North America 70 years ago and has spread along the East Coast – can kill a hemlock tree in as little as four years.
“An ...
Trump's anti-immigrant rhetoric, policies contributed to decline in preventive healthcare visits among children of immigrants
2023-09-18
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Monday, September 18, 2023
Contact:
Jillian McKoy, jpmckoy@bu.edu
Michael Saunders, msaunder@bu.edu
##
Trump's Anti-Immigrant Rhetoric, Policies Contributed to Decline in Preventive Healthcare Visits among Children of Immigrants
A new study shows that well-child visits for children with immigrant mothers ...
Samsung Austin Semiconductor invests $1M in UIUC to bolster semiconductor ecosystem in the US
2023-09-18
Urbana-Champaign, Illinois/Austin, Texas—[Sept. 18]—Samsung Austin Semiconductor is partnering with The Grainger College of Engineering at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign (UIUC) to continue building the talent pipeline needed to support the growing semiconductor ecosystem throughout the United States.
Samsung Austin Semiconductor is announcing a $1 million contribution per year to Grainger Engineering as part of its 5-star workforce development plan to provide support to engineering students who are interested ...
UT Dallas to lead $30 million battery initiative
2023-09-18
As announced by the Department of Defense today, The University of Texas at Dallas will receive $30 million over three years from the DOD to develop and commercialize new battery technologies and manufacturing processes, enhance the domestic availability of critical raw materials, and train high-quality workers for jobs in an expanding battery energy storage workforce.
The award, which creates a prototype Energy Storage Systems Campus, is the largest allocation from a federal agency that the University has received to date. The Energy Storage Systems Campus will leverage and stimulate over $200 million in private capital.
Dr. Kyeongjae ...
ACP issues updated Rapid, Living Practice Points on treating COVID-19 patients in outpatient settings
2023-09-18
Below please find a summary of a new article that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summary is not intended to substitute for the full article as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
----------------------------
ACP issues updated Rapid, Living Practice Points on treating COVID-19 patients in outpatient settings
Article: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M23-1636
Evidence ...
Promising gene-based approaches to repair lethal lung injury in the elderly from COVID-19, pneumonia, flu, sepsis
2023-09-18
Discovery from the lab of Youyang Zhao, PhD, from Stanley Manne Children’s Research Institute at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago offers promising treatment approaches for acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) in the elderly that can be caused by severe COVID-19, pneumonia, flu or sepsis. Currently there are no pharmacological or cell-based treatments for ARDS.
Dr. Zhao’s research established that a gene called FOXM1 is important in the repair of blood vessel through regeneration of endothelial cells, which line the vessels of the lung. He found that aging impairs this gene’s expression, ...
Lifesaving addiction medications are rarely started following opioid overdose emergencies
2023-09-18
Could future opioid overdoses, fatalities and other harms of opioid addiction be prevented if hospital emergency departments made better use of effective medications for opioid addiction?
A team of University of Michigan researchers thinks so.
Led by Thuy Nguyen of U-M's School of Public Health, the researchers analyzed national Medicaid claims data of patients ages 12 to 64 treated at U.S. emergency departments for opioid overdoses in 2018. They focused on ED visits for opioid overdose and the rate of initiation of FDA-approved medications for opioid addiction, including buprenorphine, methadone and extended release naltrexone.
The ...
Disparities in flu vaccine uptake persist in people with kidney disease
2023-09-18
Among adults with chronic kidney disease (CKD) enrolled in the Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort (CRIC), young age, Black race, and low levels of education and income were associated with lower likelihood of getting an annual flu shot.
Identifying risk factors for not receiving a flu vaccine (“non-vaccination”) in people living with kidney disease, who are at risk of flu and its complications, could inform strategies for improving vaccine uptake. In this study published in the American Journal of Kidney Diseases (AJKD), researchers led by Junichi Ishigami examined whether demographic factors, social ...