(Press-News.org) Curtin University researchers studying diamond-rich rocks from Western Australia’s Argyle volcano have identified the missing third key ingredient needed to bring valuable pink diamonds to the Earth’s surface where they can be mined, which could greatly help in the global hunt for new deposits.
While it is known that for diamonds to form there needs to be carbon deep in the Earth, and for these diamonds to turn pink they must be subjected to forces from colliding tectonic plates, the new study has found the third ingredient needed for the presence of pink diamonds at surface level, which is continents that were ‘stretched’ during continental break-up hundreds of millions of years ago.
Lead researcher Dr Hugo Olierook, from Curtin’s John de Laeter Centre, said the ‘stretching’ of landmasses created gaps in the Earth’s crust through which diamond-carrying magma could rise to the surface.
“By using laser beams smaller than the width of a human hair on rocks supplied by Rio Tinto, we found Argyle to be 1.3 billion years old, which is 100 million years older than previously thought, meaning it would likely have formed as a result of an ancient supercontinent breaking apart,” Dr Olierook said.
“Argyle is located at the point where the Kimberley region and the rest of northern Australia smashed together many years prior, and that sort of collision creates a damaged area or ‘scar’ in the land that will never fully heal.
“While the continent that would become Australia didn’t break up, the area where Argyle is situated was stretched, including along the scar, which created gaps in the Earth’s crust for magma to shoot up through to the surface, bringing with it pink diamonds.
“As long as these three ingredients are present - deep carbon, continental collision and then stretching - then we think it will be possible to find the ‘next Argyle’, which was once the world’s largest source of natural diamonds.”
Dr Olierook said even with the knowledge of these three ingredients, finding another trove of pink diamonds will not be without its challenges.
“Most diamond deposits have been found in the middle of ancient continents because their host volcanoes tend to be exposed at the surface for explorers to find,” Dr Olierook said.
“Argyle is at the suture of two of these ancient continents, and these edges are often covered by sand and soil, leaving the possibility that similar pink diamond-bearing volcanoes still sit undiscovered, including in Australia.”
Co-author and principal geologist Murray Rayner, from Rio Tinto, said the Argyle volcano has produced more than 90 percent of the world’s pink diamonds, making it an unparalleled source of these rare and coveted gems.
“Knowing the Argyle volcano’s age, at 1.3 billion years old, and situated where some of Earth’s earliest continents fragmented, we have significant further insights into the formation of these diamonds,” Rayner said.
The authors are affiliated with the John de Laeter Centre, the Timescales of Mineral Systems Group and the Earth Dynamics Research Group, which sit within Curtin’s School of Earth and Planetary Sciences. The work was enabled by AuScope and the Australian Government via the National Collaborative Research Infrastructure Strategy.
Funded by the Geological Survey of Western Australia, the research paper published in Nature Communications is entitled ‘Emplacement of the Argyle diamond deposit into an ancient rift zone triggered by supercontinent breakup’ and is available online here.
END
Argyle study reveals crucial third clue to finding new diamond deposits
2023-09-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Assessing unintended consequences in AI-based neurosurgical training
2023-09-19
Virtual reality simulators can help learners improve their technical skills faster and with no risk to patients. In the field of neurosurgery, they allow medical students to practice complex operations before using a scalpel on a real patient. When combined with artificial intelligence, these tutoring systems can offer tailored feedback like a human instructor, identifying areas where the students need to improve and making suggestions on how to achieve expert performance.
A new study from the Neurosurgical Simulation and Artificial Intelligence Learning Centre at The Neuro (Montreal Neurological Institute-Hospital) of McGill University, ...
USPSTF recommendation on screening for hypertensive disorders of pregnancy
2023-09-19
Bottom Line: The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends screening for hypertensive disorders in pregnant persons with blood pressure measurements throughout pregnancy. Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy are among the leading causes of maternal morbidity and mortality in the U.S. The rate has been increasing from approximately 500 cases per 10,000 deliveries in 1993 to 1,021 cases per 10,000 deliveries in 2016 to 2017. The USPSTF routinely makes recommendations about the effectiveness of preventive care services and this recommendation is consistent with its 2017 recommendation statement.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website ...
Deep learning reveals valuable clues about kidney cancer in pathology slides
2023-09-19
A team of Dana-Farber researchers has identified a potential new way to assess clinically valuable features of clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC), a form of kidney cancer, using image processing with deep learning. Their AI-based assessment tool evaluates two-dimensional pictures of a tumor sample on a pathology slide and identifies previously underappreciated features, such as tumor microheterogeneity, that could help predict whether a tumor will respond to immunotherapy.
Their results suggest that ...
Poor oral health could lessen survival from head and neck cancer
2023-09-19
An international study has revealed strong associations between oral health and survival among people diagnosed with head and neck cancer. Specifically, better oral health, as evidenced by the number of natural teeth and dental visits prior to the time of diagnosis, was associated with increased survival. Importantly, those who had more frequent dental visits were more likely to have their cancer diagnosed at an earlier, and less deadly, stage of the disease than those who had few or no dental visits.
The study, by researchers at UNC Lineberger ...
Interventions for physical capacity and quality of life in adults with post–COVID-19 condition
2023-09-19
About The Study: The findings of this systematic review and meta-analysis suggest that rehabilitation interventions in adults with post–COVID-19 condition are associated with improvements in functional exercise capacity, dyspnea, and quality of life, with a high probability of improvement compared with the current standard care. The certainty of evidence was moderate for functional exercise capacity and quality of life and low for other outcomes.
Authors: Dimitra V. Pouliopoulou, M.Sc., of Western University in London, Ontario, Canada, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link ...
Premenstrual disorders, timing of menopause, and severity of vasomotor symptoms
2023-09-19
About The Study: In this study of 3,635 female participants in the U.S., premenstrual disorders (PMDs) were associated with increased risks of early menopause and moderate or severe vasomotor symptoms (VMS). PMDs may be indicative of underlying physiology linked to early menopause and VMS, suggesting a phenotype observable during the reproductive years that may allow clinicians to target women at risk of earlier menopause and subsequent health risks later in the life course.
Authors: Yihui Yang, M.P.H., and Donghao Lu, M.D., Ph.D., of the Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm, Sweden are the corresponding authors.
To ...
Study finds two antibiotics for children with sinusitis equally effective, but one had fewer side effects
2023-09-19
Brigham researchers found that patients prescribed amoxicillin-clavulanate had higher rates of gastrointestinal symptoms and yeast infections than those prescribed amoxicillin
Acute sinusitis is one of the most common causes for children to be put on antibiotic medications, with patients in the United States filing nearly 5 million antibiotic prescriptions every year to treat the condition. The drugs amoxicillin and amoxicillin-clavulanate make up most of those prescriptions, but there is a lack of consensus on which should be first-line ...
Women given new insight into blood clot risk
2023-09-19
New research from Queen Mary University of London, published in iScience, shows an increased risk of blood clots in women who have any combination of a particular gene mutation, oestrogen use, or common medical conditions – specifically: obesity, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and kidney disease.
Women with the Factor V Leiden (FVL) gene mutation who had been prescribed oestrogen had more than double the risk of blood clotting compared to women who did not have this mutation. And almost 20% of the women who carry FVL, ...
A mysterious blue molecule will help make better use of light energy
2023-09-19
Researchers at IOCB Prague are the first to describe the causes of the behavior of one of the fundamental aromatic molecules, which fascinates the scientific world not only with its blue color but also with other unusual properties – azulene. Their current undertaking will influence the foundations of organic chemistry in the years to come and in practice will help harness the maximum potential of captured light energy. The article appeared in the Journal of the American Chemical Society (JACS).
Azulene has piqued the ...
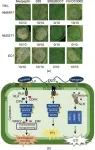
New research unveils pseudomonas cyclic lipopeptide medpeptin’s role in modulating plant immunity
2023-09-19
A groundbreaking research study conducted by Hai-Lei Wei's research team at the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences in China has revealed significant insights into the biosynthesis and modulation of plant immunity by a novel cyclic lipopeptide called medpeptin, produced by Pseudomonas mediterranea. The findings, published in Engineering, shed light on the intricate structure–function interactions of cyclic lipopeptides (CLPs) and open new avenues for the development of plant disease resistance strategies.
CLPs, multifunctional secondary metabolites produced by various bacteria, have emerged as key elicitors of plant ...