Prehistoric fish fills 100 million year gap in evolution of the skull
X-rays of an ancient jawless fish shows earliest-known example of internal cartilage skull, unlike that of any other known vertebrate
2023-09-20
(Press-News.org) A 455-million-year-old fossil fish provides a new perspective on how vertebrates evolved to protect their brains, a study has found.
In a paper published in Nature today (Wednesday 20th September), researchers from the University of Birmingham, Naturalis Biodiversity Centre in Leiden, Netherlands; and the Natural History Museum have pieced together the skull of Eriptychius americanus.
The research, funded by the Leverhulme Trust, suggests that the ancient jawless fish found in ancient deposits in Colorado, USA has a skull unlike that of any previously seen, and fills a gap currently spanning 100 million years in the evolutionary history of the vertebrate skull.
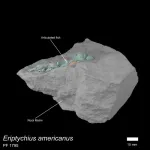
Using computed tomography, a form of x-ray technique, scientists recreated a detailed 3D representation of the skull of Eriptychius and is the first time that such a comprehensive recreation has been done on the specimen which was collected in the 1940s, originally described in the 1960s and is housed in the Field Museum of Natural History, Chicago.
This ancient fish had separated, independent cartilages encasing the brain, rather than the solid bone or cartilage structure of jawless and jawed fish that followed it.
While later species have a fully bound cage of cartilage that holds the brain, these results suggest that the early evolution of structures to separate the brain from other parts of the head may have begun with Eriptychius.
Dr Ivan Sansom, Senior Lecturer in Palaeobiology at the University of Birmingham and senior author of the paper said:
“These are tremendously exciting results that may reveal the early evolutionary history of how primitive vertebrates protected their brains. Eriptychius americanus appears to be the first evidence for a series of cartilages separating the brain from the rest of the head. This study emphasises the importance of museum collections and the application of new techniques in studying them.”
Dr Richard Dearden, Postdoctoral Research Fellow in Palaeobiology at Naturalis Biodiversity Center and lead author of the paper said:
“On the face of it Eriptychius is not the most beautiful of fossils. However, by using modern imaging techniques we were able to show that it preserves something unique: the oldest three-dimensionally preserved vertebrate head in the fossil record. This fills a major gap in our understanding of the evolution of the skull of all vertebrates, ultimately including humans.”
ENDS
For more information please contact Ellie Hail, Communications Officer, University of Birmingham at e.hail@bham.ac.uk or alternatively on +44 (0)7966 311 409. You can also contact the Press Office out of hours on +44 (0)121 414 2772 and at pressoffice.contacts@bham.ac.uk.
Images:
Video credit: Field Museum of Natural History, Richard Dearden and Ivan Samson.
Fossil images
Eriptychius_Fossil_01_Scale5mm_credit_FMNH_ISansom Credit: Field Museum of Natural History and Ivan Samson.
Eriptychius_Fossil_02_Scale5mm_credit_FMNH_ISansom Credit: Field Museum of Natural History and Ivan Samson.
3D images
Eriptychius_3D_credit_FMNH_RPDearden Credit: Field Museum of Natural History, Richard Dearden
Eriptychius_Reconstruction_credit_FMNH_RPDearden Credit: Field Museum of Natural History, Richard Dearden
Composite image
Eriptychius_Workflow-01_credit_FMNH_RPDearden_ISansom Credit: Field Museum of Natural History, Richard Dearden and Ivan Samson.
Notes to editors
The University of Birmingham is ranked amongst the world’s top 100 institutions. Its work brings people from across the world to Birmingham, including researchers, teachers and more than 8,000 international students from over 150 countries. END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-09-20
Brigham researchers reported that gentrified neighborhoods had a 62 percent higher firearm injury incidence rate than non-gentrified communities with comparable sociodemographic characteristics
Understanding the reason for this increase is vital to reducing future firearm injuries
Gentrification can have a ripple effect on communities. While it can improve certain conditions in typically low-income areas, rising housing costs can displace residents, causing social disruption and other downstream effects. Investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, conducted a study using national data to examine the relationship ...
2023-09-20
Psychoses like schizophrenia cost billions of dollars annually and derail the lives of people struggling with the disease. Now Monash University researchers have modelled how the effects of psychosis spread through the brain, allowing them to isolate areas where these changes may originate from and which could be targeted by therapies designed to reduce the disease’s progression.
The study, published today in the prestigious Journal of the American Medical Association Psychiatry, details how the scientists were able to map and model the spread of brain changes in people with different stages of psychoses such as schizophrenia,from people newly ...
2023-09-20
Santa Barbara, CA and New York, NY -- The Glenn Foundation for Medical Research (GFMR) and the American Federation for Aging Research (AFAR) are pleased to announce the inaugural recipients of the
2023 Glenn Foundation Discovery Awards:
Ya-Chieh Hsu, PhD, Professor of Stem Cell and Regenerative Biology at Harvard University, and a Principal Faculty Member at the Harvard Stem Cell Institute.
Xuebing Wu, PhD, Assistant Professor of Medical Sciences (in Medicine and in Systems Biology), Columbia University.
The Glenn Foundation Discovery Award was created to support research projects with strong potential to develop pioneering discoveries ...
2023-09-20
A team of leading clinicians, engineers, and neuroscientists has made a groundbreaking discovery in the field of treatment-resistant depression. By analyzing the brain activity of patients undergoing deep brain stimulation (DBS), a promising therapy involving implanted electrodes that stimulate the brain, the researchers identified a unique pattern in brain activity that reflects the recovery process in patients with treatment-resistant depression. This pattern, known as a biomarker, serves as a measurable indicator of disease recovery and represents a significant ...
2023-09-20
A research team led by scientists from City University of Hong Kong (CityU) has achieved a significant breakthrough by inventing a new class of near-infrared-activated photo-oxidants that can effectively kill cancer cells without requiring oxygen. The photo-oxidants induce a unique form of cancer cell death that can overcome cancer cell resistance. The findings offer a new strategy, called ‘photo-oxidation therapy’, and provide a promising direction for the development of anti-cancer drugs.
Photodynamic therapy, an innovative ...
2023-09-20
WASHINGTON (September 20, 2023)—The Ann Theodore Foundation Breakthrough Sarcoidosis Initiative (ATF-BSI), in partnership with the Milken Institute, launched its latest round of funding today. Up to $3.4 million in total funding will be made available to researchers from around the world whose work aims to increase scientific understanding of sarcoidosis. The program is accepting applications for two-year research projects and intends to award four to six research grants from doctorate-level investigators at qualifying research-based institutions worldwide. Awardees may be eligible for a third year of funding.
Sarcoidosis is an inflammatory ...
2023-09-20
NEW YORK, NY (September 20, 2023)—Columbia will award the 2023 Louisa Gross Horwitz Prize to Zhijian ‘James’ Chen and Glen Barber for discovering the cGAS-STING pathway, a key component of one of the body’s first line of defenses, the innate immune system.
When pathogens infiltrate our cells, they leave behind traces of their DNA. These molecular fingerprints are detected by our cGAS-STING pathway, which sounds the alarm and mobilizes the immune system to eliminate invading threats. Research on the cGAS-STING pathway has revealed the ...
2023-09-20
The past few decades have witnessed the burgeoning development of on-orbit servicing in light of various meaningful space applications such as repair of malfunctioning satellites, debris removal, on-orbit assembly, and so on. As for the orbit-servicing targets, they are usually divided into 2 categories, i.e., cooperative and non-cooperative ones, based on whether the space targets have active cross-link communication and cooperative identifiers with the servicing spacecraft or not. Before executing the orbit-servicing task, close-range rendezvous and proximity is an inevitable process in which ...
2023-09-20
An Australian-first biobank will be established to improve and discover new treatments for children with genetic muscle diseases.
The National Muscle Disease Bio-databank, co-led by Murdoch Children’s Research Institute, Monash University and Alfred Health, will advance research into understanding why children develop genetic muscle diseases. The project forms part of a $2.5 million Medical Research Future Fund grant awarded to the team for research into congenital muscle diseases.
These diseases, spanning dystrophies and myopathies, are characterised by severe muscle weakness, usually from infancy, that can impact swallowing, ...
2023-09-20
Liver cancer is one of the most prevalent and deadly types of cancer worldwide. Most patients are diagnosed at an advanced stage, which leaves them with few treatment options. Unfortunately, the first-line drugs used in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most common type of liver cancer, are not very effective and offer only modest clinical benefits.
Over the past few years, scientists have been trying to develop new therapies for HCC by analyzing specific genetic abnormalities and the ways in which they affect the manifestation and progression of the disease. One of the most common mutations in HCC ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Prehistoric fish fills 100 million year gap in evolution of the skull
X-rays of an ancient jawless fish shows earliest-known example of internal cartilage skull, unlike that of any other known vertebrate