(Press-News.org) The first use of a novel method of analyzing Mars’ gravitational force supports the idea that the planet once had an extensive northern ocean.
In doing so, the method defines the scope of what scientists refer to as the northern Martian paleo-ocean in more detail.
The work was published in July in the journal Icarus, which is affiliated with the American Astronomical Society’s Division for Planetary Sciences.
The research was led by Jaroslav Klokočník, professor emeritus at the Astronomical Institute of the Czech Academy of Sciences. Gunther Kletetschka, associate research professor at the University of Alaska Fairbanks Geophysical Institute, is among the three co-authors. Kletetschka is also affiliated with Charles University in the Czech Republic.
“A lot of people are excited about water on Mars because there may be life forms that once existed on Mars or maybe exist today in some bacterial form,” Kletetschka said. “We can use this gravity approach to look for water on Mars, because we have done it already on Earth.
“In an area of northern Africa, for example, this gravity approach found a shoreline of a long-ago lake, and its finding was consistent with the archaeological evidence indicating a shoreline of that lake,” he said.
The authors write that analyzing the gravity aspects of Mars to better understand the planet improves upon prior approaches. They note that it can “provide complete information with a better insight of the celestial body, applicable in geology, geophysics, hydrology, glaciology and other disciplines.”
The work by Kletetschka and colleagues differs from the traditional approach of mapping a surface based on gravity anomalies alone.
Gravity anomalies are areas of greater or weaker gravitational force exerted by a planetary body’s surface features. A mountain would exert a greater gravitational force because it has a higher concentration of mass than would be expected on a planet without surface features. Ocean basins and trenches would have less gravitational force.
In their Mars research, the authors used a process developed by Klokočník that analyzes gravity aspects calculated from gravity anomaly measurements. Gravity aspects are mathematical products that characterize the gravity anomalies.
They also used topographic data from the Mars Orbital Laser Altimeter instrument aboard NASA’s Mars Global Surveyor, which launched in November 1996 and mapped the planet for 4 ½ years.
Klokočník used that approach to confirm earlier research about the existence of extensive paleolakes or paleoriver systems under the Saharan sands on Earth. His 2017 research paper also suggested a part of the Grand Egyptian Sand Sea as another candidate for a paleolake.
The gravity aspects method has also been used in a comparison of Earth’s geographic features to those of the cloud-shrouded Venus. That research is described in a July 2023 paper in the journal Scientific Reports in which Kletetschka is a co-author.
CONTACTS:
• Gunther Kletetschka, University of Alaska Fairbanks Geophysical Institute, 907-474-7090, gkletetschka@alaska.edu.
• Rod Boyce, University of Alaska Fairbanks Geophysical Institute, 907-474-7185, rcboyce@alaska.edu
END
New Mars gravity analysis improves understanding of possible ancient ocean
2023-09-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Making contact: Researchers wire up individual graphene nanoribbons
2023-09-20
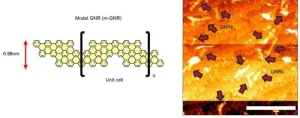
Researchers have developed a method of “wiring up” graphene nanoribbons (GNRs), a class of one-dimensional materials that are of interest in the scaling of microelectronic devices. Using a direct-write scanning tunneling microscopy (STM) based process, the nanometer-scale metal contacts were fabricated on individual GNRs and could control the electronic character of the GNRs. The researchers say that this is the first demonstration of making metal contacts to specific GNRs with certainty and that those contacts induce device functionality needed for transistor function.
The results of this research, led by electrical and computer engineering (ECE) professor Joseph Lyding, along ...
A new regulatory model which supports and encourages needed to help organizations comply with equalities legislation, study says
2023-09-20
A new type of regulation is needed to support and encourage organisations to comply with equality and human rights law because enforcement alone is ineffective, a new study says.
The introduction of the Public Sector Equality Duty and the Human Rights Act were intended to establish an equality and human rights culture within public authorities. The research highlights how this culture has failed to take hold.
An alternative is needed to the current model of regulation (the enforcement pyramid) under which penalties increasingly progress until noncompliers comply. The study says the current model cannot recognise innovation, ...
Stabilizing precipitate growth at grain boundaries in alloys
2023-09-20
Materials are often considered to be one phase, but many engineering materials contain two or more phases, improving their properties and performance. These two-phase materials have inclusions, called precipitates, embedded in the microstructure. Alloys, a combination of two or more types of metals, are used in many applications, like turbines for jet engines and light-weight alloys for automotive applications, because they have very good mechanical properties due to those embedded precipitates. The average precipitate size, however, tends to increase ...
Researchers discover biomarker for tracking depression recovery
2023-09-20
Using a novel deep brain stimulation (DBS) device capable of recording brain signals, researchers have identified a pattern of brain activity or “biomarker” related to clinical signs of recovery from treatment-resistant depression. The findings from this small study are an important step towards using brain data to understand a patient’s response to DBS treatment. The study was published in Nature and supported by the National Institutes of Health’s Brain Research Through Advancing ...
NIH awards $3.1 million to study human mitochondrial disorders
2023-09-20
The Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development awarded $3.1 million to the University of Arkansas to study a spectrum of pediatric mitochondrial disorders caused by mutations in the mitochondria. These disorders often impact different organs requiring energy and can lead to mitochondria-induced multiple organ disorder syndromes, or MIMODS.
Shilpa Iyer, an associate professor of biological sciences, will serve as the principal investigator on the five-year award. Iyer and her team conduct research on mitochondrial diseases and have received grants from Arkansas ...
Newly discovered bone stem cell causes premature skull fusion
2023-09-20
Craniosynostosis, the premature fusion of the top of the skull in infants, is caused by an abnormal excess of a previously unknown type of bone-forming stem cell, according to a preclinical study led by researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine.
Craniosynostosis arises from one of several possible gene mutations, and occurs in about one in 2,500 babies. By constricting brain growth, it can lead to abnormal brain development if not corrected surgically. In complex cases, multiple surgeries are needed.
In the study, which appears Sept. 20 in Nature, the researchers examined in detail what happens in the skull of mice with one of the most common mutations found in human ...
Disrupting a core metabolic process in T cells may improve their therapeutic efficacy
2023-09-20
SEPTEMBER 20, 2023, NEW YORK – In exploring an aspect of how killer T cells generate the raw materials required for their proliferation, a Ludwig Cancer Research study has uncovered an unexpected link between the immune cells’ metabolism, regulation of gene expression, persistence and functional efficacy that could be exploited using existing drugs to improve cancer immunotherapy.
Researchers led by Ludwig Lausanne’s Alison Jaccard and Ping-Chih Ho along with their University of Lausanne colleagues Mathias Wenes and Pedro Romero were exploring how proliferating T cells in the low-oxygen environment of tumors make citrate, a molecule essential to manufacturing membranes, which ...
Exercise and muscle regulation: implications for diabetes and obesity
2023-09-20
How do our muscles respond at the molecular level to exercise? Researchers at Helmholtz Munich and the German Institute of Human Nutrition Potsdam-Rehbrücke (DIfE) have unraveled the cellular basis and signaling pathways responsible for the positive impact of physical activity on our overall health. Regulatory T cells, a type of immune cell, play a critical role in ensuring proper muscle function. These novel insights are paving the path towards precision medicines targeting metabolic disorders like obesity and diabetes, as well as muscle-related illnesses. Their discoveries are published in Cell Metabolism.
Obesity and type ...
Study reveals structure of crucial receptor in brain development, function
2023-09-20
Scientists have revealed the molecular structure of a type of receptor that’s crucial to brain development and function.
Known as Type A GABA receptors, these receptors are already targeted by pharmaceutical anesthetics, sedatives and antidepressants because of their important role in brain function. The discovery, published today in the journal Nature, reveals the dominant assemblies and states of the GABA receptor, a finding that could enable the development of new compounds that more specifically target a range of medical disorders.
“It is the main player that balances excitation and inhibition in the ...
How to tackle the global deforestation crisis
2023-09-20
Imagine if France, Germany, and Spain were completely blanketed in forests — and then all those trees were quickly chopped down. That’s nearly the amount of deforestation that occurred globally between 2001 and 2020, with profound consequences.
Deforestation is a major contributor to climate change, producing between 6 and 17 percent of global greenhouse gas emissions, according to a 2009 study. Meanwhile, because trees also absorb carbon dioxide, removing it from the atmosphere, they help keep the Earth cooler. ...