(Press-News.org) Previous studies have shown that overweight and obesity are risk factors for several types of cancer. It is also known that obese women have a higher risk of cancer than their male counterparts, and that the risk level decreases with intentional weight loss. However, evidence of a link between obesity, weight loss and haematological cancer has been limited.
The current study, published in the journal Lancet Healthy Longevity, used data from the Swedish Obese Subjects (SOS) study at the University of Gothenburg and data from e.g., the Cancer Registry at the National Board of Health and Welfare.
The researchers studied 2,007 people who underwent bariatric surgery and compared them to a control group of 2,040 individuals, also obese, who did not undergo surgery. The groups were otherwise comparable in terms of e.g., gender, age, body composition, cardiovascular risk factors and psychosocial variables.
Most significant improvements in women
During the follow-up period, 34 individuals in the surgery group developed haematological cancer, in parallel with a significant weight loss. The corresponding number in the control group was 51 haematological cancers, with the group remaining at the level of severe obesity.
Most of the blood cancers were lymphomas, and when these were studied separately, there was a 55% reduction in the risk of lymphoma in the group that had undergone bariatric surgery. The corresponding risk reduction for all blood cancers was 40%.
In particular, women with high blood sugar at the start of the study seemed to benefit from bariatric surgery. This is according to Magdalena Taube, Associate Professor of Molecular and Clinical Medicine at Sahlgrenska Academy, University of Gothenburg, and corresponding author of the study.
“The benefit of the surgery is linked to baseline blood glucose levels. The reduced risk of haematological cancer was much more pronounced if the women's blood sugar levels were high at the beginning, which clearly shows that blood sugar is an important factor in cancer development,” she says.
Mechanisms with complex relationships
The researchers in the study point out that the mechanisms behind the link between obesity and blood cancers are complex and involve multiple factors, such as chronic inflammation and so-called clonal hematopoiesis, a type of genetically related risk factor for blood cancer. They suggest that the metabolic improvements that take place after bariatric surgery, including reduced inflammation, may reduce the risk of cancer.
“The results provide further support of considering obesity a risk factor for haematological cancer, and that bariatric surgery can reduce the risk of blood cancer in obese women,” says Magdalena Taube, Associate Professor of Molecular and Clinical Medicine at the Sahlgrenska Academy, University of Gothenburg and corresponding author of the study.
The journal's commentary: Obesity-associated cancer prevention, https://doi.org/10.1016/S2666-7568(23)00176-9
END
Lower risk of haematological cancer after bariatric surgery
2023-09-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
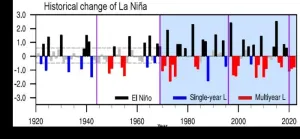
Long-lasting La Niña events more common over past century
2023-09-21
Multiyear La Niña events have become more common over the last 100 years, according to a new study led by University of Hawai‘i (UH) at Mānoa atmospheric scientist Bin Wang. Five out of six La Niña events since 1998 have lasted more than one year, including an unprecedented triple-year event. The study was published this week in Nature Climate Change.
“The clustering of multiyear La Niña events is phenomenal given that only ten such events have occurred since 1920,” said Wang, emeritus professor of atmospheric sciences in the UH Mānoa School of Ocean ...
Traumatic brain injury under-recognized as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease
2023-09-21
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a leading cause of long-term disability and premature death, especially among military personnel and those playing contact sports. Substantial research has examined acute and chronic neurological consequences of TBI; however, non-neurological conditions associated with TBI are understudied. A new review paper by investigators from Mass General Brigham presents key findings on long-term associations between TBI and cardiovascular disease, highlighting that nervous system dysfunction, neuroinflammation, changes in the brain-gut connection, and post-injury comorbidities may elevate risk of both cardiovascular ...
Doctors with long covid deserve more support
2023-09-21
Freelance journalist Adele Waters speaks to scores of doctors unable to work or play with their children, forced to sell their homes or facing financial destitution by an illness they caught while doing their jobs.
She hears of “shockingly low” access to protective equipment faced by many doctors in their workplaces, and how some have struggled for medical colleagues to take their symptoms seriously.
Charities that provide financial support to doctors in need have seen a sudden rise in demand, and now there are calls for long covid to be considered an occupational disease to help doctors and other healthcare workers access support and financial ...
Study shows morning and afternoon slightly better than evening physical activity for diabetes prevention
2023-09-21
New research published in Diabetologia (the journal of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes [EASD]) shows that morning and afternoon physical activity are associated with a lower risk of developing type 2 diabetes across all population levels of education and income, but found no statistically significant association between evening physical activity and risk type 2 diabetes. The study is by Dr Caiwei Tian, Harvard University, Cambridge, MA, USA, and Dr Chirag Patel, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA. and colleagues.
Physical activity is a preventive factor for type 2 diabetes, but its timing and consistency (in contrast with overall sum of physical activity) ...
Monkeys cause a stink in response to human noise
2023-09-21
New research has found that monkeys increase their use of scent markings to compensate for human noise pollution.
Pied tamarins (Saguinus bicolor) use both vocal calls and scent markings to communicate, and the new study – published in the journal Ethology Ecology & Evolution – is the first to investigate how primates change their communication strategies in response to noise pollution.
The pied tamarin has an extremely narrow geographic range in central Brazil, much of which now lies within the city of ...
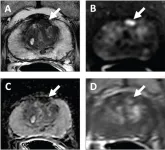
Prostate cancer upgrade, downgrade rates in PI-RADS 2.0 versus 2.1
2023-09-20
Leesburg, VA, September 20, 2023—According to an accepted manuscript published in the American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), upgrade and downgrade rates from targeted biopsy to radical prostatectomy were not significantly different between patients whose MRI examinations were clinically interpreted using PI-RADS Version v2.0 or v2.1.
“Implementation of the most recent PI-RADS update did not improve the incongruence in prostate cancer grade assessment between targeted biopsy and surgery,” wrote corresponding author Baris Turkbey, MD, from the Molecular Imaging Branch ...
New recycling method fights plastic waste
2023-09-20
Almost 80% of plastic in the waste stream ends up in landfills or accumulates in the environment. Oak Ridge National Laboratory scientists have developed a technology that converts a conventionally unrecyclable mixture of plastic waste into useful chemicals, presenting a new strategy in the toolkit to combat global plastic waste.
The technology, invented by ORNL’s Tomonori Saito and former postdoctoral researcher Md Arifuzzaman, uses an exceptionally efficient organocatalyst that allows selective deconstruction ...
Low follow-up kidney testing after hospital discharge with moderate to severe AKI
2023-09-20
A study of Canadian hospitalizations from 2007-2019 show that over 75% of patients with moderate to severe acute kidney injury (AKI) do not get appropriate follow-up kidney health testing after hospital discharge.
A study in Alberta, Canada, examined care received by over 20,000 hospitalized with AKI during hospitalization and after discharge between 2009 and 2017. The results, recently published in the American Journal of Kidney Diseases (AJKD), showed that a low proportion of patients with moderate to severe AKI were seen by a kidney specialist ...
Unzipping mRNA rallies plant cells to fight infection
2023-09-20
DURHAM, N.C. -- Living things from bacteria to plants to humans must constantly adjust the chemical soup of proteins -- the workhorse molecules of life -- inside their cells to adapt to stress or changing conditions, such as when nutrients are scarce, or when a pathogen attacks.
Now, researchers have identified a previously unknown molecular mechanism that helps explain how they do it.
Studying a spindly plant called Arabidopsis thaliana, a Duke University-led team discovered short snippets of folded RNA that, under normal conditions, keep levels of defense proteins low to avoid harming the plants themselves. But when the plants detect a pathogen, these folded RNA structures ...
New research findings: Understanding the sex life of coral gives hope of clawing it back from the path to extinction
2023-09-20
For the first time, scientists have mapped the reproductive strategies and life cycle of an endangered coral species, offering hope it can be clawed back from the path to extinction.
The purple cauliflower soft coral, Dendronephthya australis, is endemic to south-eastern Australia, with the largest populations historically found in the Port Stephens estuary in New South Wales. It is one of the 100 priority species on the Federal Government’s Threatened Species Strategy.
Not only is the future ...