(Press-News.org) Community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) is a major infectious disease worldwide and contributes to high mortality and massive economic burden. Hospital mortality among the severe CAP (SCAP) remains high, ranging from 25% to more than 50%.
Early identification of patients at high risk of death is essential for improving patient outcomes. However, predicting outcomes in patients with SCAP is challenging, as the disease is complex and influenced by various factors, including the types of pathogen causing the infection, the host immune response, and underlying medical conditions.
In this study published in eBioMedicine (a Lancet publication), a team led by Dr. Jinmin Ma, BGI Genomics Infection Department Chief Science Officer and Prof. Jieming Qu, Ruijin Hospital, conducted research on SCAP patients to explore the pulmonary microbiota and host responses of different outcomes since the genetic differences could be detected more easily in the most severe patients as opposed to mildly severe patients.
Methods and Findings
BGI Genomics researchers used metagenomic and transcriptomic analysis to identify a new set of biomarkers that can predict 30-day mortality in patients with SCAP.
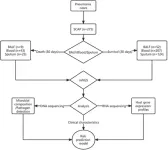
The study included 275 patients with SCAP from 18 hospitals in China.
Researchers performed DNA and RNA-based metagenomic next-generation sequencing of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF), sputum, and blood samples from 275 SCAP patients with varied characteristics and outcomes to analyze the differences in the microbes and host responses between them.
The researchers identified nine sets of biomarkers, both metagenomic and transcriptomic, that were associated with 30-day mortality.
The biomarkers were validated in an independent cohort of patients with SCAP and were able to predict 30-day mortality with an accuracy of 85%. This is significantly higher than the accuracy of existing clinical prediction models, which typically have accuracies of around 70%.
Other key findings:
The study revealed that 30-day mortality was independent of pathogen category, microbial diversity or specific microbial taxa, while significant differences in host gene expression patterns were suggested to be responsible for different outcomes.
Clinical characteristics analysis showed that male sex with age over 55 years was a risk factor for poor prognosis, and specific enrichment of genes and signaling pathways were found in omics data.
Potential of Biomarkers Utilization
The new biomarkers could have the following potential benefits for patients with SCAP
Improve the accuracy of predicting and reducing mortality, which could lead to better clinical decision-making.
Identify patients at high risk of death, who could then be targeted with more aggressive treatment.
Reduce the need for invasive procedures, such as lung biopsies, which are associated with risks.
Improve the allocation of healthcare resources by identifying patients who are most likely to benefit from intensive care.
Develop new therapeutic strategies by identifying biomarkers that are associated with poor outcomes.
About BGI Genomics:
BGI Genomics, headquartered in Shenzhen, China, is the world's leading integrated solutions provider of precision medicine. Our services cover more than 100 countries and regions, involving more than 2,300 medical institutions. In July of 2017, as a subsidiary of BGI Group, BGI Genomics (300676.SZ) was officially listed on the Shenzhen Stock Exchange.
END
Precision treatment for pneumonia care: metagenomic sequencing takes the lead
Nine sets of biomarkers, both metagenomic and transcriptomic, were identified, outperforming existing clinical prediction models
2023-09-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Curiosity about religion is viewed as morally virtuous, new research finds
2023-09-21
People from diverse religious backgrounds in the United States view curiosity about religion as morally virtuous, according to new research published in Social Psychological and Personality Science. Atheists also view this curiosity as moral, although less moral than a lack of religious curiosity.
Previous research has examined what makes people curious and how curiosity helps people learn new information, but psychologists know less about how displaying curiosity is viewed by other people. The current research finds that people ...
Scholarships awarded to high school students committed to whole body wellness
2023-09-21
DALLAS, September 21, 2023 — Supporting the next generation of health advocates, the American Heart Association awards five high school seniors with $1,000 college scholarships to energize their commitment to community health through service-learning opportunities. The grants are a part of the American Heart Challenge™, a school-based program that helps middle and high school students feel good about their health, while doing good for the community.
The American Heart Association, devoted ...
Intra-lysosomal peptide assembly for the high selectivity Index against cancer
2023-09-21
A groundbreaking anticancer treatment technology that selectively targets cancer cell lysosomes and overcomes drug resistance has been developed by Professor Ja-Hyoung Ryu and his research team in the Department of Chemistry at UNIST. This pioneering research promises a new paradigm for chemical anticancer drugs in the future.
Lysosomes are crucial organelles responsible for breaking down and recycling cellular components. Targeting lysosomes with anticancer drugs has emerged as a promising approach to combat drug resistance in cancer cells. However, ...
Global policymakers call for effective infodemic management to be a substantive article in the pandemic accord
2023-09-21
(Toronto, September 21, 2023) The United Nations General Assembly held a high-level meeting on Pandemic Prevention, Preparedness, and Response on September 20, 2023, to continue discussions on finalizing a globally enforceable Pandemic Accord or Treaty that will be presented to the World Health Organization’s (WHO) World Health Assembly in May 2024. This treaty, if agreed to and eventually ratified, will be the second international treaty instrument under WHO auspices, and represents a critical juncture in global health needed to strengthen pandemic prevention, preparedness, and response in the ...
TTUHSC researchers receive NIH grant to address preeclampsia rates
2023-09-21
According to a study recently published by the Journal of the American Medical Association, maternal morbidity and mortality rates in Texas during the last two decades have more than doubled from 1999 (10.3 deaths per 100,000 births) to 2019 (21.9 deaths per 100,000 births). This rate not only exceeds the national average (17.4 in 2018), but it also places Texas at or near the bottom of most metrics used to determine the safest states in which to have a baby.
One of the primary factors related to the lack of maternity care in the Lone Star state is the existence of maternity care deserts, which are counties where no maternity care exists. And in the Texas Panhandle, ...
SBQuantum to test quantum magnetometer in space - designed to map Earth’s magnetic field
2023-09-21
SHERBROOKE, Canada (September 21, 2023) – SBQuantum, the first company developing diamond quantum magnetometers capable of providing vector measurements of both the amplitude and the orientation of Earth's magnetic field, today announces it has been selected as a participant in the final phases of the MagQuest Challenge, along with its partner, Spire Global.
Led by the U.S. National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency, MagQuest is a multi-million dollar competition to find more accurate and efficient ways to map the earth’s electromagnetic field, also known as the World Magnetic Model (WMM). Aircraft, ...
E-cigarettes are not a gateway into smoking
2023-09-21
The most comprehensive study to date investigating whether e-cigarettes are a gateway into or out of smoking finds that, at the population level, there is no sign that e-cigarettes and other alternative nicotine delivery products promote smoking.
The study, led by Queen Mary University of London and funded by the National Institute of Health and Care Research (NIHR), also found some evidence that these products compete against cigarettes and so may be speeding up the demise of smoking, but this finding is only tentative and more data are needed to determine the size of this effect.
The study compared the time course of use and sales of electronic cigarettes with that ...
UW team’s shape-changing smart speaker lets users mute different areas of a room
2023-09-21
In virtual meetings, it’s easy to keep people from talking over each other. Someone just hits mute. But for the most part, this ability doesn’t translate easily to recording in-person gatherings. In a bustling cafe, there are no buttons to silence the table beside you.
The ability to locate and control sound — isolating one person talking from a specific location in a crowded room, for instance — has challenged researchers, especially without visual cues from cameras.
A team led by ...
Could cerebrospinal fluid leaks be a link between traumatic brain injury and dementia?
2023-09-21
TORONTO, ON – Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leaks may be one of the mechanisms that link traumatic brain injury (TBI) with dementia, according to a recently published hypothesis in Alzheimer's & Dementia: Translational Research & Clinical Interventions, a journal of the Alzheimer’s Association.
Traumatic brain injuries are strongly associated with an increased risk of dementia. Unfortunately, the exact pathways underlying this relationship are unclear. This gap in knowledge makes it difficult to create preventative strategies to support patients with TBI.
CSF leaks are associated with decreased brain buoyancy and the appearance of brain sagging on MRI. Severe ...
Cough sound analyzed to identify the severity of COVID-19 patients
2023-09-21
While most individuals impacted by COVID-19 experience milder symptoms and recover within a few weeks, the global pandemic caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus continues to pose a significant health challenge. Some of those affected may progress to develop more severe illness and pneumonia, often resulting in a more unfavorable prognosis.
Although protocols have been developed to assess patients' risk, diagnostic and prognostic tools primarily rely on expensive and less accessible imaging methods, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
Despite their contrasting reputations, bonobos and chimpanzees show similar levels of aggression in zoos
Unusual tumor cells may be overlooked factors in advanced breast cancer
Plants pause, play and fast forward growth depending on types of climate stress
University of Minnesota scientists reveal how deadly Marburg virus enters human cells, identify therapeutic vulnerability
Here's why seafarers have little confidence in autonomous ships
MYC amplification in metastatic prostate cancer associated with reduced tumor immunogenicity
The gut can drive age-associated memory loss
Enhancing gut-brain communication reversed cognitive decline, improved memory formation in aging mice
Mothers exposure to microbes protect their newborn babies against infection
How one flu virus can hamper the immune response to another
Researchers uncover distinct tumor “neighborhoods”, with each cell subtype playing a specific role, in aggressive childhood brain cancer
[Press-News.org] Precision treatment for pneumonia care: metagenomic sequencing takes the leadNine sets of biomarkers, both metagenomic and transcriptomic, were identified, outperforming existing clinical prediction models