Cough sound analyzed to identify the severity of COVID-19 patients
A study led by IBEC and Hospital del Mar revealed cough characteristics in COVID-19 patients that could offer a quick, easy, and cost-effective method for identifying the severity of the disease in patients, whether at home or in any healthcare setting
2023-09-21
(Press-News.org)
While most individuals impacted by COVID-19 experience milder symptoms and recover within a few weeks, the global pandemic caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus continues to pose a significant health challenge. Some of those affected may progress to develop more severe illness and pneumonia, often resulting in a more unfavorable prognosis.
Although protocols have been developed to assess patients' risk, diagnostic and prognostic tools primarily rely on expensive and less accessible imaging methods, such as radiography, ultrasound, or computed tomography (CT). Therefore, there is a need to develop a simpler and more readily available prognostic tool that enables healthcare providers to identify patients who have developed or are at risk of developing severe disease. This would streamline patient triage and facilitate early intervention, even in home or primary care settings.
Now, a research team led by IBEC and Hospital del Mar, with collaboration from the Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (UPC), CIBER-BBN and CIBERES, has carried out a study based on the analysis and interpretation of cough sounds in the initial phases of COVID-19. This method is presented as a potential predictive, simple, and accessible tool to assess the risk of suffering severe pneumonia.
The research involved smartphone recordings of voluntary coughing sounds from 70 patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection, all recorded within the first 24 hours after their admission to the hospital. IBEC conducted an acoustic analysis of these recordings, which revealed significant differences in cough sounds depending on the severity of the respiratory condition, as previously confirmed by imaging tests and the need for supplemental oxygen. The results indicate that this analysis could be used to categorize COVID-19 patients as mild, moderate, or severe and to monitor patients with persistent COVID-19. The study was conducted using data collected between April 2020 and May 2021 at Hospital del Mar, and the findings have been published in the European Respiratory Journal Open Research.
Cough frequency: a key parameter
Raimon Jané, a professor at UPC and the principal investigator at IBEC and CIBER-BBN, leads the Biomedical Signal Processing and Interpretation (BIOSPIN) group at IBEC. This group has developed the methodology and algorithms for the acoustic analysis of cough signals collected via smartphones. Using a statistical model known as a linear mixed model, the team identified five parameters, based on sound frequencies, that exhibited significant differences in the coughs of patients with varying levels of disease severity and pneumonia progression. These differences may reflect the progressive respiratory system alterations in patients with COVID-19
While acoustic cough analysis methods have been previously proposed for diagnosing respiratory diseases, we aimed to take a step further by specifically investigating the connection between the acoustic characteristics of coughs and the varying levels of pneumonia severity in COVID-19 patients," details Jané, the senior co-author of the study.
The authors of the study explain that cough analysis can serve a dual purpose: early detection of severe COVID-19 cases and remote monitoring of their progression, including the assessment of potential complications. However, further research involving a larger patient sample will be required to validate the findings of this cross-sectional study, which could pave the way for utilizing cough analysis as a diagnostic tool for patients with COVID-19 and other respiratory diseases.
For this reason, Dr. Joaquim Gea, emeritus head of the Pneumology Service, researcher at the Hospital del Mar Research Institute, and senior co-author of the study, suggests that these findings can prove beneficial “in regions with limited medical infrastructure or during emergency situations. This approach can aid in the prompt identification and isolation of COVID-19 patients, thus facilitating proper medical care and the implementation of control measures.”
Another noteworthy aspect is that, while the study primarily centered on COVID-19, it paves the way for applying this model to other respiratory conditions.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-09-21
Sewage pollution, whether treated or untreated, was found to be the primary driver of increased nutrients, algae, and sewage fungus in rivers.
Sewage discharge also radically altered plant, animal, and microbe communities, increasing the abundance of harmful species.
Run-off from agriculture was also found to lower water quality and be particularly harmful for sensitive insect groups.
Ahead of World Rivers Day (24 September), new research by the University of Oxford reveals that sewage discharge into rivers has a greater impact on water quality, and the animals ...
2023-09-21
South Korean researchers have achieved a landmark feat by setting international standards for short-range wireless communication technology, commonly used within a 10 cm range, to enable internet communication.
ETRI(Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute) announced on the 21st July that the international standard “IETF RFC 9428(Transmission of IPv6 Packets over Near Field Communication)” was formally adopted by the Internet Engineering Task Force(IETF), a semi-private international standardization organization under the Internet Architecture Board(IAB).
Near ...
2023-09-21
Injecting drugs into the bloodstream can often harm healthy tissues as well. Drug delivery systems (DDSs) are an innovative solution designed to target specific cells and minimize such side effects. One strategy for drug delivery that has steadily gained traction involves a combination of microbubbles and ultrasound. Microbubbles are small gas-filled bubbles that can be loaded with drugs or other therapeutic agents on their surface. When exposed to ultrasound waves, these microbubbles begin to oscillate, with the ensuing ...
2023-09-21
MIAMI, FLORIDA (Sept. 20, 2023) – A researcher with Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine has been selected to receive a prestigious honor from Columbia University.
Glen N. Barber, PhD, Sylvester’s internationally known cell biologist who chairs UM’s Department of Cell Biology, has been awarded the 2023 Louisa Gross Horwitz Prize from Columbia for outstanding contributions to basic research in biology and biochemistry.
Barber is the first UM faculty member to receive this award, and more than 50% of previous honorees have gone on to win the Nobel Prize. The award, which carries a $10,000 ...
2023-09-21
Prior studies of uromodulin, the most abundant protein in urine, and kidney disease have focused primarily on urinary uromodulin levels. The current study evaluated associations of serum uromodulin levels with risk of end-stage kidney disease and mortality in a cohort of African American adults with hypertension and chronic kidney disease. The research, recently published in the American Journal of Kidney Diseases (AJKD), found that participants with lower levels of uromodulin at baseline were more likely to develop end-stage kidney disease, even after accounting for baseline kidney ...
2023-09-21
Jeffrey Raskin, MS, MD, a neurosurgeon at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago, performed the first ever computer-guided radiofrequency ablation to decrease excessive muscle tone (called hypertonia) in a child with cerebral palsy.
In hypertonia, muscles are constantly activated, which causes severe pain and deformity in the bones and joints, and profoundly impacts the child’s quality of life. Medications are not always effective, and these patients do not have any other surgical options.
Dr. ...
2023-09-21
Previous studies have shown that overweight and obesity are risk factors for several types of cancer. It is also known that obese women have a higher risk of cancer than their male counterparts, and that the risk level decreases with intentional weight loss. However, evidence of a link between obesity, weight loss and haematological cancer has been limited.
The current study, published in the journal Lancet Healthy Longevity, used data from the Swedish Obese Subjects (SOS) study at the University of Gothenburg and data from e.g., the Cancer ...
2023-09-21
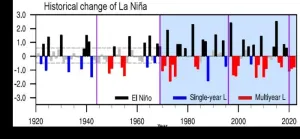
Multiyear La Niña events have become more common over the last 100 years, according to a new study led by University of Hawai‘i (UH) at Mānoa atmospheric scientist Bin Wang. Five out of six La Niña events since 1998 have lasted more than one year, including an unprecedented triple-year event. The study was published this week in Nature Climate Change.
“The clustering of multiyear La Niña events is phenomenal given that only ten such events have occurred since 1920,” said Wang, emeritus professor of atmospheric sciences in the UH Mānoa School of Ocean ...
2023-09-21
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a leading cause of long-term disability and premature death, especially among military personnel and those playing contact sports. Substantial research has examined acute and chronic neurological consequences of TBI; however, non-neurological conditions associated with TBI are understudied. A new review paper by investigators from Mass General Brigham presents key findings on long-term associations between TBI and cardiovascular disease, highlighting that nervous system dysfunction, neuroinflammation, changes in the brain-gut connection, and post-injury comorbidities may elevate risk of both cardiovascular ...
2023-09-21
Freelance journalist Adele Waters speaks to scores of doctors unable to work or play with their children, forced to sell their homes or facing financial destitution by an illness they caught while doing their jobs.
She hears of “shockingly low” access to protective equipment faced by many doctors in their workplaces, and how some have struggled for medical colleagues to take their symptoms seriously.
Charities that provide financial support to doctors in need have seen a sudden rise in demand, and now there are calls for long covid to be considered an occupational disease to help doctors and other healthcare workers access support and financial ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Cough sound analyzed to identify the severity of COVID-19 patients
A study led by IBEC and Hospital del Mar revealed cough characteristics in COVID-19 patients that could offer a quick, easy, and cost-effective method for identifying the severity of the disease in patients, whether at home or in any healthcare setting