(Press-News.org) Jeffrey Raskin, MS, MD, a neurosurgeon at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago, performed the first ever computer-guided radiofrequency ablation to decrease excessive muscle tone (called hypertonia) in a child with cerebral palsy.
In hypertonia, muscles are constantly activated, which causes severe pain and deformity in the bones and joints, and profoundly impacts the child’s quality of life. Medications are not always effective, and these patients do not have any other surgical options.
Dr. Raskin’s innovative minimally invasive surgical procedure uses a computer system to accurately place electrode needles into the nerve roots that exit the spine. Radiofrequency energy (similar to microwave heat) is then delivered to disconnect the muscle from the brain and spinal cord, which effectively decreases the ability of the nervous system to activate muscles.
While radiofrequency ablation has been used for decades for relieving pain, the procedure has not been attempted previously for decreasing tone in cerebral palsy.
Dr. Raskin reported his experience with the first patient case in the journal Operative Neurosurgery. Now eight months after the procedure, the benefits are lasting, and the child’s quality of life is greatly improved.
“We need to change the paradigm of how we care for patients with severe hypertonia,” said Dr. Raskin, Assistant Professor of Neurological Surgery at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine. “To decrease muscle tone, we need to exclude the dysfunctional nervous system, which is the main driver of pathology. Radiofrequency ablation is a safe and effective approach that is well tolerated, with patients going home the next day. Patients with severe tone despite medications are encouraged to see a neurosurgeon to see if they are candidates for this treatment.”
Research at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago is conducted through Stanley Manne Children’s Research Institute. The Manne Research Institute is focused on improving child health, transforming pediatric medicine and ensuring healthier futures through the relentless pursuit of knowledge. Lurie Children’s is a nonprofit organization committed to providing access to exceptional care for every child. It is ranked as one of the nation’s top children’s hospitals by U.S. News & World Report. Lurie Children’s is the pediatric training ground for Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine.
END
Lurie Children’s Hospital performs innovative minimally invasive surgery for severe muscle tone in cerebral palsy
Computer-guided radiofrequency ablation used for the first time to decrease muscle tone in a child with hypertonia
2023-09-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Lower risk of haematological cancer after bariatric surgery
2023-09-21
Previous studies have shown that overweight and obesity are risk factors for several types of cancer. It is also known that obese women have a higher risk of cancer than their male counterparts, and that the risk level decreases with intentional weight loss. However, evidence of a link between obesity, weight loss and haematological cancer has been limited.
The current study, published in the journal Lancet Healthy Longevity, used data from the Swedish Obese Subjects (SOS) study at the University of Gothenburg and data from e.g., the Cancer ...
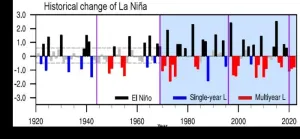
Long-lasting La Niña events more common over past century
2023-09-21
Multiyear La Niña events have become more common over the last 100 years, according to a new study led by University of Hawai‘i (UH) at Mānoa atmospheric scientist Bin Wang. Five out of six La Niña events since 1998 have lasted more than one year, including an unprecedented triple-year event. The study was published this week in Nature Climate Change.
“The clustering of multiyear La Niña events is phenomenal given that only ten such events have occurred since 1920,” said Wang, emeritus professor of atmospheric sciences in the UH Mānoa School of Ocean ...
Traumatic brain injury under-recognized as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease
2023-09-21
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a leading cause of long-term disability and premature death, especially among military personnel and those playing contact sports. Substantial research has examined acute and chronic neurological consequences of TBI; however, non-neurological conditions associated with TBI are understudied. A new review paper by investigators from Mass General Brigham presents key findings on long-term associations between TBI and cardiovascular disease, highlighting that nervous system dysfunction, neuroinflammation, changes in the brain-gut connection, and post-injury comorbidities may elevate risk of both cardiovascular ...
Doctors with long covid deserve more support
2023-09-21
Freelance journalist Adele Waters speaks to scores of doctors unable to work or play with their children, forced to sell their homes or facing financial destitution by an illness they caught while doing their jobs.
She hears of “shockingly low” access to protective equipment faced by many doctors in their workplaces, and how some have struggled for medical colleagues to take their symptoms seriously.
Charities that provide financial support to doctors in need have seen a sudden rise in demand, and now there are calls for long covid to be considered an occupational disease to help doctors and other healthcare workers access support and financial ...
Study shows morning and afternoon slightly better than evening physical activity for diabetes prevention
2023-09-21
New research published in Diabetologia (the journal of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes [EASD]) shows that morning and afternoon physical activity are associated with a lower risk of developing type 2 diabetes across all population levels of education and income, but found no statistically significant association between evening physical activity and risk type 2 diabetes. The study is by Dr Caiwei Tian, Harvard University, Cambridge, MA, USA, and Dr Chirag Patel, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA. and colleagues.
Physical activity is a preventive factor for type 2 diabetes, but its timing and consistency (in contrast with overall sum of physical activity) ...
Monkeys cause a stink in response to human noise
2023-09-21
New research has found that monkeys increase their use of scent markings to compensate for human noise pollution.
Pied tamarins (Saguinus bicolor) use both vocal calls and scent markings to communicate, and the new study – published in the journal Ethology Ecology & Evolution – is the first to investigate how primates change their communication strategies in response to noise pollution.
The pied tamarin has an extremely narrow geographic range in central Brazil, much of which now lies within the city of ...
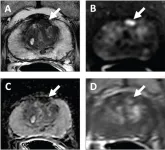
Prostate cancer upgrade, downgrade rates in PI-RADS 2.0 versus 2.1
2023-09-20
Leesburg, VA, September 20, 2023—According to an accepted manuscript published in the American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), upgrade and downgrade rates from targeted biopsy to radical prostatectomy were not significantly different between patients whose MRI examinations were clinically interpreted using PI-RADS Version v2.0 or v2.1.
“Implementation of the most recent PI-RADS update did not improve the incongruence in prostate cancer grade assessment between targeted biopsy and surgery,” wrote corresponding author Baris Turkbey, MD, from the Molecular Imaging Branch ...
New recycling method fights plastic waste
2023-09-20
Almost 80% of plastic in the waste stream ends up in landfills or accumulates in the environment. Oak Ridge National Laboratory scientists have developed a technology that converts a conventionally unrecyclable mixture of plastic waste into useful chemicals, presenting a new strategy in the toolkit to combat global plastic waste.
The technology, invented by ORNL’s Tomonori Saito and former postdoctoral researcher Md Arifuzzaman, uses an exceptionally efficient organocatalyst that allows selective deconstruction ...
Low follow-up kidney testing after hospital discharge with moderate to severe AKI
2023-09-20
A study of Canadian hospitalizations from 2007-2019 show that over 75% of patients with moderate to severe acute kidney injury (AKI) do not get appropriate follow-up kidney health testing after hospital discharge.
A study in Alberta, Canada, examined care received by over 20,000 hospitalized with AKI during hospitalization and after discharge between 2009 and 2017. The results, recently published in the American Journal of Kidney Diseases (AJKD), showed that a low proportion of patients with moderate to severe AKI were seen by a kidney specialist ...
Unzipping mRNA rallies plant cells to fight infection
2023-09-20
DURHAM, N.C. -- Living things from bacteria to plants to humans must constantly adjust the chemical soup of proteins -- the workhorse molecules of life -- inside their cells to adapt to stress or changing conditions, such as when nutrients are scarce, or when a pathogen attacks.
Now, researchers have identified a previously unknown molecular mechanism that helps explain how they do it.
Studying a spindly plant called Arabidopsis thaliana, a Duke University-led team discovered short snippets of folded RNA that, under normal conditions, keep levels of defense proteins low to avoid harming the plants themselves. But when the plants detect a pathogen, these folded RNA structures ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
[Press-News.org] Lurie Children’s Hospital performs innovative minimally invasive surgery for severe muscle tone in cerebral palsyComputer-guided radiofrequency ablation used for the first time to decrease muscle tone in a child with hypertonia