(Press-News.org) Sewage pollution, whether treated or untreated, was found to be the primary driver of increased nutrients, algae, and sewage fungus in rivers.
Sewage discharge also radically altered plant, animal, and microbe communities, increasing the abundance of harmful species.
Run-off from agriculture was also found to lower water quality and be particularly harmful for sensitive insect groups.
Ahead of World Rivers Day (24 September), new research by the University of Oxford reveals that sewage discharge into rivers has a greater impact on water quality, and the animals and plants that live in rivers, than surrounding land use. The findings have been published today in the journals Global Change Biology and Ecological Solutions and Evidence.
Rivers are crucial parts of the global water cycle, contain important biodiversity, and are essential for human health. However, water companies in the UK are allowed to release treated wastewater into rivers, and even untreated wastewater during heavy rainfalls (known as storm overflow). As well as the ecological consequences, this poses serious threats for human wellbeing if the water is then used for drinking, recreational, or agricultural purposes.
Researchers from the University of Oxford’s Department of Biology investigated the effects of three different pollution sources (treated sewage discharge, agriculture, and urban run-off) on different aspects of river systems. The group tested four rivers in England, both up- and downstream of sewage discharge, over three different months.
The results demonstrated that treated sewage discharge was the best predictor of high nutrient levels, bottom-dwelling algae, and sewage fungus abundance, regardless of the type of land use (agriculture or urban) in the surrounding area.
Dr Dania Albini (Department of Biology, University of Oxford), lead author of the study, said:
“Our study highlights the disproportionate impact that sewage discharge has on river quality, presenting an urgent need for a comprehensive action plan targeting the sewage discharge problem. Improvements to waste water plants should be implemented along with more regulations. These efforts are crucial in safeguarding the integrity and safety of our rivers — fundamental elements of both ecosystems and human wellbeing.”
Dr Michelle Jackson (Department of Biology, University of Oxford), senior author of the study, said:
“There is ongoing debate about the cause of the poor ecological state of many rivers in the UK because it is difficult to disentangle different pollution sources. Here, we show that even treated sewage appears to have a stronger influence on river communities than pollution from the surrounding land. This important information should be used to prioritise the management and conservation of our rivers moving forward.”
Nutrients exacerbate the decline of waterways by promoting the growth of harmful species and deteriorating others. This was seen in the rivers studied through a shift in macroinvertebrate and algae communities downstream of sewage input, with more tolerant groups such as cyanobacteria and worms becoming more abundant. This is concerning as cyanobacteria are well known for producing toxic chemicals that can kill many aquatic organisms. As a result of this, wastewater pollution has the potential to alter and degrade critical ecosystem processes via loss of critical species.
In the study, only one measurement –the abundance of the sensitive insect groups of mayflies, stoneflies, and caddisflies – was best predicted by agricultural land use. This suggests that water quality and river communities are generally more threatened by treated sewage discharge than pollution from the surrounding catchment, but agricultural pollution also needs to be kept in check.
These new findings come at a time of intense public concern over the state of the UK's waterways. A recent investigation for the Observer found that more than 90% of freshwater habitats on England’s most precious rivers have been degraded by farming pollution, raw sewage and water abstraction.
James Wallace, CEO of the UK-based charity River Action, commented on the findings: “This important research demonstrates yet again the damage from unregulated water companies and agriculture. In addition to the catastrophic impact on wildlife from nutrient pollution, the public should be aware that sewage systems do not remove dangerous bacteria such as E.coli and intestinal enterococci from treated sewage. For instance, recent citizen science on the River Thames found that Thames Water’s outflows often have four to five times the safe levels of bacteria, that has likely caused serious illness in swimmers and rowers. When will the government make water companies and farms clean up their act, especially in places where human lives and sensitive protected habitats are threatened?”
An early-detection system for spotting dangerous outbreaks
The researchers also developed a new method to allow early detection of potentially dangerous outbreaks of 'sewage fungus’. This is a complex mix of fungus, algae, and bacteria which forms large masses when there are high organic nutrient levels. They not only cause unpleasant smells, but severely reduce oxygen levels in water which can adversely affect all river species, and cause mass fish mortality.
Currently, sewage fungus is only assessed visually, so it is only found once it has become large enough to already be having negative effects. The researchers developed a new method to allow early detection, an essential step to enable swift intervention to avoid extensive outbreaks. Their method uses imaging techniques and machine learning to rapidly identify sewage particles and sewage fungus in water samples.
The technique could be used as a ‘canary in the coal mine’ by both water companies and monitoring organisations such as the Environment Agency, and could prove to be a valuable tool in limiting pollution build-up and halting species decline.
Dr Michelle Jackson said: "Rapid identification of sewage fungus pollution events will allow early intervention which would help prevent any potential negative consequences for local wildlife.”
Notes to editors
Interviews with Dania Albini are available on request. Media contact: twitter: @DaniaAlbini, email: dania.albini@gmail.com
The paper ‘The combined effects of treated sewage discharge and land use on rivers’ will be published in Global Change Biology at 08:01 AM BST, Thursday 21 September. It will be available online at https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/gcb.16934
The paper ‘Early detection and environmental drivers of sewage fungus outbreaks in rivers’ will be published in Ecological Solutions and Evidence at 05:01 AM BST, Thursday 21 September. It will be available online at https://besjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/2688-8319.12277
The links will go live when the embargo lifts. To view a copy of the manuscripts under embargo contact Dr Caroline Wood: caroline.wood@admin.ox.ac.uk
About the University of Oxford
Oxford University has been placed number 1 in the Times Higher Education World University Rankings for the seventh year running, and number 3 in the QS World Rankings 2024. At the heart of this success are the twin-pillars of our ground-breaking research and innovation and our distinctive educational offer.
Oxford is world-famous for research and teaching excellence and home to some of the most talented people from across the globe. Our work helps the lives of millions, solving real-world problems through a huge network of partnerships and collaborations. The breadth and interdisciplinary nature of our research alongside our personalised approach to teaching sparks imaginative and inventive insights and solutions.
Through its research commercialisation arm, Oxford University Innovation, Oxford is the highest university patent filer in the UK and is ranked first in the UK for university spinouts, having created more than 300 new companies since 1988. Over a third of these companies have been created in the past five years. The university is a catalyst for prosperity in Oxfordshire and the United Kingdom, contributing £15.7 billion to the UK economy in 2018/19, and supports more than 28,000 full time jobs.
The Department of Biology is a University of Oxford department within the Maths, Physical and Life Sciences Division. It utilises academic strength in a broad range of bioscience disciplines to tackle global challenges such as food security, biodiversity loss, climate change and global pandemics. It also helps to train and equip the biologists of the future through holistic undergraduate and graduate courses. For more information visit www.biology.ox.ac.uk.
END
New study finds that sewage release is worse for rivers than agriculture
2023-09-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
ETRI sets global standard for NFC-based internet communication
2023-09-21
South Korean researchers have achieved a landmark feat by setting international standards for short-range wireless communication technology, commonly used within a 10 cm range, to enable internet communication.
ETRI(Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute) announced on the 21st July that the international standard “IETF RFC 9428(Transmission of IPv6 Packets over Near Field Communication)” was formally adopted by the Internet Engineering Task Force(IETF), a semi-private international standardization organization under the Internet Architecture Board(IAB).
Near ...
Unveiling the science of ultrasound-driven microbubble desorption
2023-09-21
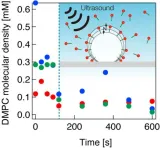
Injecting drugs into the bloodstream can often harm healthy tissues as well. Drug delivery systems (DDSs) are an innovative solution designed to target specific cells and minimize such side effects. One strategy for drug delivery that has steadily gained traction involves a combination of microbubbles and ultrasound. Microbubbles are small gas-filled bubbles that can be loaded with drugs or other therapeutic agents on their surface. When exposed to ultrasound waves, these microbubbles begin to oscillate, with the ensuing ...
Sylvester researcher earns prestigious Columbia University award
2023-09-21
MIAMI, FLORIDA (Sept. 20, 2023) – A researcher with Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine has been selected to receive a prestigious honor from Columbia University.
Glen N. Barber, PhD, Sylvester’s internationally known cell biologist who chairs UM’s Department of Cell Biology, has been awarded the 2023 Louisa Gross Horwitz Prize from Columbia for outstanding contributions to basic research in biology and biochemistry.
Barber is the first UM faculty member to receive this award, and more than 50% of previous honorees have gone on to win the Nobel Prize. The award, which carries a $10,000 ...
Uromodulin levels may indicate risk for kidney failure
2023-09-21
Prior studies of uromodulin, the most abundant protein in urine, and kidney disease have focused primarily on urinary uromodulin levels. The current study evaluated associations of serum uromodulin levels with risk of end-stage kidney disease and mortality in a cohort of African American adults with hypertension and chronic kidney disease. The research, recently published in the American Journal of Kidney Diseases (AJKD), found that participants with lower levels of uromodulin at baseline were more likely to develop end-stage kidney disease, even after accounting for baseline kidney ...
Lurie Children’s Hospital performs innovative minimally invasive surgery for severe muscle tone in cerebral palsy
2023-09-21
Jeffrey Raskin, MS, MD, a neurosurgeon at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago, performed the first ever computer-guided radiofrequency ablation to decrease excessive muscle tone (called hypertonia) in a child with cerebral palsy.
In hypertonia, muscles are constantly activated, which causes severe pain and deformity in the bones and joints, and profoundly impacts the child’s quality of life. Medications are not always effective, and these patients do not have any other surgical options.
Dr. ...
Lower risk of haematological cancer after bariatric surgery
2023-09-21
Previous studies have shown that overweight and obesity are risk factors for several types of cancer. It is also known that obese women have a higher risk of cancer than their male counterparts, and that the risk level decreases with intentional weight loss. However, evidence of a link between obesity, weight loss and haematological cancer has been limited.
The current study, published in the journal Lancet Healthy Longevity, used data from the Swedish Obese Subjects (SOS) study at the University of Gothenburg and data from e.g., the Cancer ...
Long-lasting La Niña events more common over past century
2023-09-21
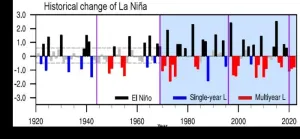
Multiyear La Niña events have become more common over the last 100 years, according to a new study led by University of Hawai‘i (UH) at Mānoa atmospheric scientist Bin Wang. Five out of six La Niña events since 1998 have lasted more than one year, including an unprecedented triple-year event. The study was published this week in Nature Climate Change.
“The clustering of multiyear La Niña events is phenomenal given that only ten such events have occurred since 1920,” said Wang, emeritus professor of atmospheric sciences in the UH Mānoa School of Ocean ...
Traumatic brain injury under-recognized as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease
2023-09-21
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a leading cause of long-term disability and premature death, especially among military personnel and those playing contact sports. Substantial research has examined acute and chronic neurological consequences of TBI; however, non-neurological conditions associated with TBI are understudied. A new review paper by investigators from Mass General Brigham presents key findings on long-term associations between TBI and cardiovascular disease, highlighting that nervous system dysfunction, neuroinflammation, changes in the brain-gut connection, and post-injury comorbidities may elevate risk of both cardiovascular ...
Doctors with long covid deserve more support
2023-09-21
Freelance journalist Adele Waters speaks to scores of doctors unable to work or play with their children, forced to sell their homes or facing financial destitution by an illness they caught while doing their jobs.
She hears of “shockingly low” access to protective equipment faced by many doctors in their workplaces, and how some have struggled for medical colleagues to take their symptoms seriously.
Charities that provide financial support to doctors in need have seen a sudden rise in demand, and now there are calls for long covid to be considered an occupational disease to help doctors and other healthcare workers access support and financial ...
Study shows morning and afternoon slightly better than evening physical activity for diabetes prevention
2023-09-21
New research published in Diabetologia (the journal of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes [EASD]) shows that morning and afternoon physical activity are associated with a lower risk of developing type 2 diabetes across all population levels of education and income, but found no statistically significant association between evening physical activity and risk type 2 diabetes. The study is by Dr Caiwei Tian, Harvard University, Cambridge, MA, USA, and Dr Chirag Patel, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA. and colleagues.
Physical activity is a preventive factor for type 2 diabetes, but its timing and consistency (in contrast with overall sum of physical activity) ...