Kinase-targeted therapy in subsets of colorectal cancer
2023-09-22
(Press-News.org)
“We have summarized some of our findings regarding the response of various subsets of CRC to kinase inhibitors [...].”
BUFFALO, NY- September 22, 2023 – A new editorial paper was published in Oncoscience (Volume 10) on June 27, 2023, entitled, “Kinase-targeted therapy in subsets of colorectal cancer.”
In this new editorial, researchers Patricia M. Gomez Barila and Jan Paul Medema from the University of Amsterdam and Amsterdam University Medical Centers discuss colorectal cancer (CRC) — one of the most commonly diagnosed cancers and the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. Early diagnosis and adequate treatment are crucial for improving patient prognosis, although this remains difficult due to the high molecular and clinical heterogeneity of the disease. However, recent efforts have been made to stratify CRC patients and uncover novel targeted therapies for patient groups with a poor response to available chemotherapy.
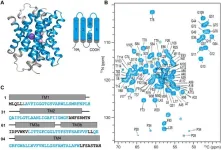
One of the CRC classification systems involves the identification of key pathways that are dysregulated due to genetic mutations or differential cellular wiring. Important known pathways in CRC include the Wnt, MAPK, PI3K and p53 pathways. Kinases are the proteins responsible for carrying out the signal transduction within the pathways, leading to particular cellular phenotypes, such as increased proliferation and migration. More specifically, higher activity and dysregulation of certain kinases has been widely shown in cancer, with the modulation of kinase activity through available chemical inhibitors leading to successful treatment options for a number of patients. Accordingly, uncovering essential kinases for tumor growth and invasion is crucial in the development of more effective targeted therapy in metastatic or later stage CRC.
“[...] further insight into the kinase dependency and the subsequent use of kinase inhibitors in a more subset specific manner will result in improved treatment for CRC patients that have a poor response to available chemotherapy.”
Read the full editorial: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/oncoscience.580
Correspondence to: Jan Paul Medema
Email: j.p.medema@amsterdamumc.nl
Keywords: colorectal cancer, kinase inhibitors, signaling pathways, drug resistance
About Oncoscience:
Oncoscience is a peer-reviewed, open-access, traditional journal covering the rapidly growing field of cancer research, especially emergent topics not currently covered by other journals. This journal has a special mission: Freeing oncology from publication cost. It is free for the readers and the authors.
To learn more about Oncoscience, visit Oncoscience.us and connect with us on social media:
X, formerly known as Twitter
Facebook
YouTube
LinkedIn
For media inquiries, please contact media@impactjournals.com.
Oncoscience Journal Office
6666 East Quaker Str., Suite 1D
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957, option 4
###
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-09-22
MIAMI, FLORIDA (Sept. 22, 2023) – Researchers at Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine found an association between “social determinants of health” and outcomes and survival in patients undergoing surgery and treatment for non-small cell lung cancer.
The findings are based on a statistical scoring system the researchers developed that consolidates and analyzes several measures of socioeconomic status and related factors.
“We believe our social determinants of health scoring system is the first to provide a composite perspective on many of the ...
2023-09-22
A research team led by Prof. WANG Junxian from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) revealed a clumped, multi-component eclipsing absorber in a study of X-ray occultation events in the active galaxy NGC 6814. The results were published in Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society on Aug. 23.
Active galactic nuclei have strong X-ray emission originating in a compact region near the supermassive black hole, the so-called corona region. When an absorbing ...
2023-09-22
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Macrophages are little cells vital to the immune system and could possibly inform cell-based therapies for a variety of medical conditions. However, realizing the full potential of macrophage therapies relies on being able to see what these cellular allies are doing inside our bodies, and a team of Penn State researchers may have developed a way to watch them do their thing.
In a study published in the journal Small, the Penn State researchers report a novel ultrasound imaging technique to view macrophages continuously in mammal tissue, with potential for human ...
2023-09-22
On August 23, 2023, a research team led by SHI Chaowei from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) published a paper titled "Fluoride permeation mechanism of the Fluc channel in liposomes revealed by solid-state NMR" in Science Advances. The team adopted the fluoride ion channel protein Fluc-Ec1 combined with deuterium substitution and 19F labeling methods, paving a new path for membrane protein nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) research.
NMR not only provides insights into molecular structures ...
2023-09-22
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — The Earth’s crust continued a slow process of reworking for billions of years, rather than rapidly slowing its growth some 3 billion years ago, according to a Penn State-led research team. The new finding contradicts existing theories that suggest the rapid formation of tectonic plates earlier in Earth’s history, researchers said.
They published the research in Geochemical Perspectives Letters.
The work may help answer a fundamental question about our planet and could hold clues as to the formation of other planets, according to lead author ...
2023-09-22
How similar are dinosaurs to modern birds? This question is at the heart of a new study that examined how proteins found in dinosaur feathers changed over millions of years and under extreme heat.
Previous studies suggest that dinosaur feathers contained proteins that made them less stiff than modern bird feathers. Now, researchers with University College Cork (UCC), the Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Light Source (SSRL) at the Department of Energy's SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory and other institutions have discovered that dinosaur feathers originally had a very similar protein composition to those of modern birds. That result ...
2023-09-22
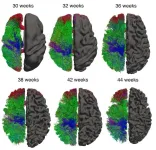
A single brain is unfathomably complex. So brain researchers, whether they’re looking at datasets built from 300,000 neurons in 81 mice or from MRIs of 1,200 young adults, are now dealing with so much information that they must also come up with new methods to comprehend it. Developing new analysis tools has become as important as using them to understand brain health and development.
A team including researchers at the University of Washington recently used new software to compare MRIs from 300 babies and discovered that myelin, a part of the brain’s so-called white matter, develops much slower after birth. The researchers published their findings Aug. ...
2023-09-22
A clinical trial has launched to test whether early intensive immune modulation for hospitalized COVID-19 patients with relatively mild illness is beneficial. The placebo-controlled study, part of the global clinical trials consortium known as Strategies and Treatments for Respiratory Infections and Viral Emergencies (STRIVE), will enroll approximately 1,500 people at research sites around the world. It is supported by the National Institutes of Health’s National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) in partnership with NIH’s National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS).
Immune ...
2023-09-22
PHILADELPHIA – A study in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) identifies five factors that Annenberg Public Policy Center (APPC) researchers say reflect public assessments of science and are associated with public support for increasing funding of science and support for federal funding of basic research. These factors are whether science and scientists are perceived to be credible and prudent, and whether their work is perceived to be untainted by bias, self-correcting, and beneficial.
Drawing on 13 questions in APPC’s 2022 nationally representative ...
2023-09-22
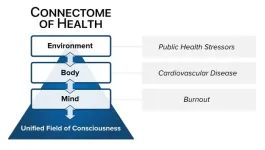
A new editorial published in the Heart and Mind journal proposes an innovative systems medicine approach to address the epidemic of clinician burnout and holistically improve clinician mental health and wellbeing (Heart and Mind: September 18, 2023. | DOI: 10.4103/hm.HM-D-23-00013, published ahead of print).
In the US and globally, clinician burnout has reached epidemic levels, with over 50% of physicians and healthcare providers reporting symptoms. Besides impairing quality of life, burnout increases risk of mental health disorders, cardiovascular disease and impaired ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Kinase-targeted therapy in subsets of colorectal cancer