(Press-News.org) Long COVID patients have clear differences in immune and hormone function from patients without the condition, according to a new study led by the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and Yale School of Medicine.
The research, published in the September 25 issue of Nature, is the first to show specific blood biomarkers that can accurately identify patients with long COVID.
“These findings are important—they can inform more sensitive testing for long COVID patients and personalized treatments for long COVID that have, until now, not had a proven scientific rationale,” says Principal Investigator David Putrino, PhD, Professor of Rehabilitation and Human Performance and Director of the Abilities Research Center at Icahn Mount Sinai, and the Nash Family Director of the Cohen Center for Recovery From Complex Chronic Illness. “This work is so exciting because it is one of the first to show us clear, measurable differences in blood biomarkers of people with long COVID compared with people who recovered fully from an acute infection and a group of people who have never been infected with SARS-CoV-2 (the virus that causes COVID-19). This is a decisive step forward in the development of valid and reliable blood testing protocols for long COVID.”
Physicians from the Mount Sinai Health System first identified long COVID symptoms in 2020 when patients reported persisting issues after an initial, diagnosed case of COVID-19. These symptoms included cognitive impairment or “brain fog,” extreme fatigue, shortness of breath, and chronic pain. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention says one in 13 adults (or 7.5 percent) in the United States has long COVID symptoms lasting more than three months after having COVID-19. Many of these patients have no clear cause for their symptoms, and this study provides new evidence for why these may exist.
Investigators analyzed a total of 271 patients from three sites—The Mount Sinai Hospital, Mount Sinai Union Square and Yale School of Medicine—between January 2021 and June 2022. Researchers divided them into three groups: those with no prior SARS-CoV-2 infection; those who had fully recovered from a clinically confirmed case of COVID-19; those with active long COVID symptoms for at least four months or more after confirmed COVID-19 infection (median time of long-term symptoms was 12 months since the acute infection).
Each patient was asked to complete a detailed set of questionnaires about their symptoms, medical history, and health-related quality of life. The researchers took blood samples from all patients, identified biomarker differences and similarities between the groups, and then applied machine learning analyses to better understand which biomarkers were most effective in allowing the algorithm to identify patients with long COVID.
Overall, the algorithm was able to differentiate between people with and without long COVID with 96 percent accuracy and detect the condition based on distinctive features detected in the blood of participants in the long COVID group. Some of the most pronounced differences between the long COVID group and the two control groups were related to immune and hormonal dysfunction. This was characterized by biomarkers indicating abnormal T cell activity, reactivation of multiple latent viruses (including the Epstein-Barr virus and other herpesviruses) and significant reductions in cortisol levels.
“These findings show us that people with long COVID are living with a disease process that is observable using the blood testing protocols laid out in the study, but also varies from patient to patient depending on their specific medical history,” says Dr. Putrino. “This means that physicians must listen to their patients and perform a wide variety of physiological and lab tests, while adopting a highly personalized approach to the medical management of long COVID. There is no ‘silver bullet’ for treating long COVID, because it is an illness that infiltrates complex systems such as the immune and hormonal regulation. Complex illnesses require complex treatment solutions and we need more rapid research to better understand long COVID and discover new and promising therapies.”
“We are excited to see such clear differences in the immune phenotypes in people with and without long COVID. These markers need to be validated in larger studies, but provide a first step in dissecting the disease pathogenesis of long COVID,” adds co-Principal Investigator Akiko Iwasaki, PhD, Sterling Professor of Immunobiology and of Molecular, Cellular & Developmental Biology at Yale School of Medicine.
About the Mount Sinai Health System
Mount Sinai Health System is one of the largest academic medical systems in the New York metro area, with more than 43,000 employees working across eight hospitals, more than 400 outpatient practices, more than 300 labs, a school of nursing, and a leading school of medicine and graduate education. Mount Sinai advances health for all people, everywhere, by taking on the most complex health care challenges of our time—discovering and applying new scientific learning and knowledge; developing safer, more effective treatments; educating the next generation of medical leaders and innovators; and supporting local communities by delivering high-quality care to all who need it.
Through the integration of its hospitals, labs, and schools, Mount Sinai offers comprehensive health care solutions from birth through geriatrics, leveraging innovative approaches such as artificial intelligence and informatics while keeping patients’ medical and emotional needs at the center of all treatment. The Health System includes approximately 7,400 primary and specialty care physicians; 13 joint-venture outpatient surgery centers throughout the five boroughs of New York City, Westchester, Long Island, and Florida; and more than 30 affiliated community health centers. Hospitals within the System are consistently ranked by Newsweek’s® “The World’s Best Smart Hospitals” and by U.S. News & World Report's® “Best Hospitals” and “Best Children’s Hospitals.” The Mount Sinai Hospital is on the U.S. News & World Report's® “Best Hospitals” Honor Roll for 2023-2024.
###
END
People with long COVID have distinct hormonal and immune differences from those without this condition
2023-09-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New vaccine technology could protect from future viruses and variants
2023-09-25
Studies of a ‘future-proof’ vaccine candidate have shown that just one antigen can be modified to provide a broadly protective immune response in animals. The studies suggest that a single vaccine with combinations of these antigens – a substance that causes the immune system to produce antibodies against it – could protect against an even greater range of current and future coronaviruses.
The vaccine antigen technology, developed by the University of Cambridge and spin-out DIOSynVax in early 2020, provided protection against all known variants of SARS-CoV-2 – the virus that causes COVID-19 – as well as other ...
Racial disparities in emergency department physical restraint use
2023-09-25
About The Study: In this systematic review and meta-analysis of 10 studies, physical restraint was uncommon, occurring in less than 1% of encounters, but adult Black patients experienced a significantly higher risk of physical restraint in emergency department settings compared with other racial groups. Emergency departments should carefully consider, and take steps to address, how racism may affect disparate use of restraints among adult patients.
Authors: Vidya Eswaran, M.D., of the Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit ...
Access to marijuana by minors via online dispensaries
2023-09-25
About The Study: This analysis of 80 online marijuana dispensaries based in 32 states found that most lacked adequate age verification features and most accepted nontraceable payment methods, enabling youth to hide their transactions. Almost 1 in 5 online dispensaries required no formal age verification at any stage of the purchasing process.
Authors: Ruth L. Milanaik, D.O., of Steven and Alexandra Cohen Children’s Medical Center of New York in Lake Success, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2023.3656)
Editor’s ...
Racial, ethnic, and sex diversity in academic medical leadership
2023-09-25
About The Study: The results of this study suggest that select specialties in academic medicine have bridged diversity gaps in academic medical leadership whereas others continue to lag behind.
Authors: Charles S. Day, M.D., M.B.A., of Henry Ford Health in Detroit, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.35529)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and ...
Distinct immune, hormone responses shed light on mysteries of long COVID
2023-09-25
New Haven, Conn. — People who have experienced brain fog, confusion, pain, and extreme fatigue for months or longer after being infected with the COVID-19 virus exhibit different immune and hormonal responses to the virus than those not diagnosed with long COVID, according to a new study by researchers at Yale School of Medicine and Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai.
The discovery of these distinct responses can help scientists for the first time identify the causes — and potentially ...
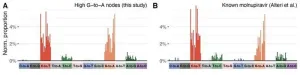
Antiviral drug linked to SARS-CoV-2 mutations
2023-09-25
Francis Crick Institute press release
Under strict embargo: 16:00hrs BST 25 September 2023
Peer reviewed
Observational study
People
Antiviral drug linked to SARS-CoV-2 mutations
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute, the University of Cambridge, Imperial College London, the University of Liverpool, the University of Cape Town and UKHSA have uncovered a link between an antiviral drug for COVID-19 infections called molnupiravir and a pattern of mutations in the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
Molnupiravir works by inducing mutations in the virus’s ...
Pioneering research links the increase of misinformation shared by Republican US politicians to a changing public perception of honesty
2023-09-25
The international study, published in Nature Human Behaviour, analysed millions of tweets by members of Congress over the last decade. Its findings showed both Republican and Democratic politicians were increasingly sharing their beliefs and opinions as well as evidence-based information. But among Republicans, their expression of honestly-held beliefs and opinions was strongly linked to less trustworthy information sources.
Lead author Jana Lasser, a postdoctoral research fellow in computational social science at Graz University of Technology (TU Graz), said: “We wanted to find out what reasons and social changes contribute to people sharing ...
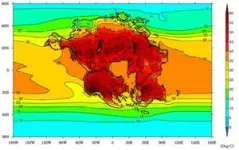
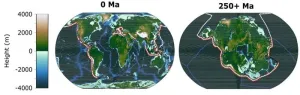
New research reveals extreme heat likely to wipe out humans and mammals in the distant future
2023-09-25
A new study shows unprecedented heat is likely to lead to the next mass extinction since the dinosaurs died out, eliminating nearly all mammals in some 250 million years time.
The research, published today in Nature Geoscience and led by the University of Bristol, presents the first-ever supercomputer climate models of the distant future and demonstrates how climate extremes will dramatically intensify when the world’s continents eventually merge to form one hot, dry and largely uninhabitable supercontinent.
The ...
Theories about the natural world may need to change to reflect human impact
2023-09-25
New research, reported in Nature Ecology & Evolution, (25 September 2023) has for the first time validated at scale, one of the theories that has underpinned ecology for over half a century. In doing so, the findings raise further questions about whether models should be revised to capture human impacts on natural systems.
Scientists working in the 50’s and 60’s developed theories to predict the ecological distribution of species. These theories could be applied across a broad range of environments and variables such as food supply or temperature and when tested on a small scale they were found to be accurate. Amongst the earliest examples of these ...
Ocean acidification research is robust despite ebbs and flows
2023-09-25
A new objective examination of almost a quarter-of-a-century of ocean acidification research shows that, despite challenges, experts in the field can have confidence in their research.
The University of Adelaide’s Professor Sean Connell from the Ecology and Evolutionary Biology unit led the study.
“In our field, the marine science community was galvanised by the demonstration of how ocean acidification impairs shell-building life, which has profound implications for life on the planet,” ...