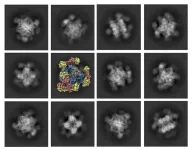
(Press-News.org) The scientists who received the 2017 Nobel Prize in chemistry were honored for their development of a technique called cryo-electron microscopy, or cryo-EM. The technology was revolutionary because it enabled scientists to see the atomic structure of biological molecules in high resolution.
But cryo-EM still had a catch: It was only effective for imaging large molecules.
Now, UCLA biochemists, working with pharmaceutical industry scientists, have developed a solution that will make it possible for cryo-EM to acquire high-quality images of smaller protein molecules, too. The scientists engineered a 20 nanometer, cube-shaped protein structure, called a scaffold, with rigid tripod-like protrusions that hold the small proteins in place.
The scaffold can be digitally removed from the picture when the imaging is being processed, leaving a composite 3D image of just the small protein scientists are analyzing.
Small and medium-sized proteins are a hot point for research on potential new drugs that might one day be used to fight some of the most intractable human illnesses. The advance, which was tested on a protein that scientists are studying for its possible use in cancer treatments, can be customized for almost any small protein. Researchers expect that expanding cryo-EM’s imaging capabilities will help them identify specific locations on proteins that they can target for therapeutic purposes.
A paper about the new research is published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
In cryo-EM, scientists use a cryo-electron microscope to send a beam of electrons through frozen samples of material, leaving behind an image of the thousands of molecules — such as proteins — in the sample. The molecules are imaged exactly as they lie in the sample, producing thousands of 2D photographs of the molecule taken from different angles. Computer processing reconciles all of those photographs to formulate a correct 3D image — separating the background, grouping images with similar orientations together and generating a high-resolution, 3D image of a single molecule.
But when it comes to imaging the smallest protein molecules, their tiny size makes it impossible to ascertain their orientations in the images, which results in relatively low-resolution images.
In previous studies, scientists attempted to solve the problem by attaching small molecules to larger scaffolds, but those experiments demonstrated that if the small molecules were attached too flexibly, they would protrude from the scaffold at different angles and orientations — which would still produce blurry images.
“The images are blurry because the computer can’t create a distinct composite image when it can’t determine the orientations accurately,” said Todd Yeates, a UCLA distinguished professor emeritus of biochemistry, interim director of the UCLA–Department of Energy Institute for Genomics and Proteomics and the paper’s corresponding author.
In the new study, the scaffold created by the scientists has tripod-shaped protrusions that capture the proteins and hold them firmly in place, which yielded the higher-resolution images they were aiming for.
“Attaching the small molecules rigidly to larger scaffolds creates particles that are large enough to be imaged, and which all have precisely the same 3D shape,” Yeates said. “And from there, the process works as usual to construct the high-resolution 3D image.”
Roger Castells-Graells, a UCLA postdoctoral researcher and the study’s lead author, said the scientists first tried another shape for the scaffold before landing on the version with tripod-shaped protrusions.
“At first we used one ‘stick’ pointing outward and that didn’t work as well,” he said. “The new scaffold has protrusions that point toward each other in triplets — like tripods — that hold the protein firmly.”
The researchers tested their scaffold by attempting to create images of a protein called KRAS. KRAS encourages cells to proliferate and is involved in about 25% of human cancers; it’s of particular interest to pharmaceutical researchers because identifying specific locations on the protein that are related to its cancer-causing abilities could help scientists design drugs that neutralize activity at those locations — which could be one path toward treating cancer.
Using cryo-EM and the scaffold they developed, the UCLA-led team was able to observe the atomic structure of KRAS attached to a drug molecule that is being studied as part of a potential treatment for lung cancer. Their work proved that the new scaffolded cryo-EM approach can illuminate how drug molecules bind with and inhibit cellular proteins like KRAS, and could help guide the development of more effective drugs.
The potential applications for the new advance don’t stop with cancer drugs, Castells-Graells said.
“Our scaffold is modular and can be assembled in any configuration to capture and hold all kinds of small protein molecules,” he said.
The research was supported by the National Institutes of Health and was a collaboration with scientists from Astra-Zeneca, whose team was led by Chris Phillips, and Gandeeva Therapeutics, whose team was led by Sriram Subramaniam.
UCLA has filed a patent on the new technology, and Yeates, Castells-Graells and colleagues have started a new company, AvimerBio, to help develop new commercial applications using the new methods, in collaboration with leading pharmaceutical companies.
END
UCLA-led team develops key improvement to Nobel Prize-winning technology
An advance in cryo-EM could be a significant boon for research on potential cancer therapies
2023-09-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
UTEP awarded $7 million to support Hispanic-serving institutions across the country
2023-09-27
EL PASO, Texas (Sept. 27, 2023) — The University of Texas at El Paso has been chosen to become a center of thought leadership for Hispanic Serving Institutions (HSIs) across the country, thanks to a new $7 million grant from the National Science Foundation (NSF).
The new grant, known as NODE (Network Opportunities for Developing Equitable and Effective Evaluation at HSIs), is a six-year investment that will position UTEP to provide the first full portrait of the effectiveness of all grants funded by the NSF HSI program. Anne-Marie Núñez, Ph.D., executive director of the Diana Natalicio Institute ...
JWST's first spectrum of a TRAPPIST-1 planet
2023-09-27
Image
In a solar system called TRAPPIST-1, 40 light years from the sun, seven Earth-sized planets revolve around a cold star.
Astronomers obtained new data from the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) on TRAPPIST-1 b, the planet in the TRAPPIST-1 solar system closest to its star. These new observations offer insights into how its star can affect observations of exoplanets in the habitable zone of cool stars. In the habitable zone, liquid water can still exist on the orbiting planet's surface.
The ...
Wild Asian elephants display unique puzzle solving skills
2023-09-27
New York, September 27, 2023 – Individual innovation is considered one sign of intelligence within species, and elephants are among the animals that researchers have long taken an interest in because of their sophisticated approach to problem solving. A newly published study in the journal Animal Behaviour details findings from a six-month-long study documenting the abilities of individual wild Asian elephants to access food by solving puzzles that unlocked storage boxes.
“This is the first research study to show that individual wild elephants have different willingness and abilities to problem solve in ...
Mainstay malaria drug may be beginning to fail in the Horn of Africa
2023-09-27
In eastern Africa, malaria parasites have developed resistance to artemisinins, the backbone of current treatment regimens, a development that could dramatically worsen malaria’s impact if partner drugs fail in the future.
The finding from studies in Eritrea was reported Sept. 28 in the New England Journal of Medicine by a team of researchers led by Didier Ménard, PhD, of the Université de Strasbourg/Institut Pasteur in France and including Columbia University microbiologist David Fidock, PhD, the C.S. Hamish Young Professor of Microbiology & Immunology and professor of medical sciences in the Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons.
Treatment ...
Separating molecules requires lots of energy. This new, heat-resistant membrane could change that
2023-09-27
BUFFALO, N.Y. – Industry has long relied upon energy-intensive processes, such as distillation and crystallization, to separate molecules that ultimately serve as ingredients in medicine, chemicals and other products.
In recent decades, there has been a push to supplant these processes with membranes, which are potentially a lower-cost and eco-friendly alternative. Unfortunately, most membranes are made from polymers that degrade during use, making them impractical.
To solve this problem, a University at Buffalo-led research team ...
MSU works to make drinking water safer by fighting contaminants
2023-09-27
EAST LANSING, Mich. – Providing safe drinking water was a great public health achievement in the 20th century, yet problems persist. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, about 7.15 million waterborne illnesses occur in the United States annually resulting in 601,000 emergency room visits, 6,630 deaths and $3.33 billion in direct health care costs. Michigan State University, a world leader in water research, is working to make our drinking water safer.
MSU has been awarded a $2.1 million grant from the U.S. Environmental Protection ...
Want to make better decisions? Ask for less information, not more
2023-09-27
When people have to make a tough decision, their first instinct is usually to gather as much information as possible. Just one problem: according to research published this week in Cognitive Research: Principles and Implications, most people’s decision-making actually gets worse, not better, when you give them additional facts and details.
“It’s counterintuitive, because we all like to think we use information wisely to make smart decisions,” said Farber Chair Associate Professor ...
HMS researcher to lead $104 million federal project tackling antibiotic resistance
2023-09-27
At a glance:
Johan Paulsson, HMS professor of systems biology, will lead project studying bacterial behavior and antibiotic resistance.
Efforts will focus on developing technology to improve diagnosis, speed discovery of new antibiotics, and illuminate basic mechanisms of bacterial behavior.
Harvard Medical School researcher Johan Paulsson will lead a multi-institutional $104 million effort to study bacteria and antibiotic resistance, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services announced today.
The work is funded by the newly established Advanced Research Projects Agency for Health (ARPA-H) in an ...
Study provides new look at why rare cancer often evades treatments
2023-09-27
BOSTON - Researchers at Boston Medical Center and Dana-Farber Cancer Institute conducted one of the first-ever analyses of neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) at single cell resolution, unlocking new insights into this rare and often hard-to-treat cancer. The findings represent a tremendous leap forward in understanding why these tumors are largely resistant to immunotherapy and provide key insights that could lead to future treatments.
“This study was a tour-de-force that catalyzed the efforts and innovations of researchers across Boston – including Boston Medical Center and Dana-Farber Cancer Institute - and has resulted in a better understanding ...
Opportunities to improve lung cancer care for older patients
2023-09-27
“With the majority of lung cancer patients being older than 65, it is imperative that actions are taken to encourage and facilitate clinical trials among older patients.”
BUFFALO, NY- September 27, 2023 – A new editorial paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 17, entitled, “Promising trends in lung cancer care, but are we overlooking the majority?”
In their new editorial, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] UCLA-led team develops key improvement to Nobel Prize-winning technologyAn advance in cryo-EM could be a significant boon for research on potential cancer therapies