(Press-News.org)
Parkinson's disease is a complex neurodegenerative disorder that leads to the deterioration of specific types of neurons in the brain, resulting in a number of motor and non-motor symptoms. It is currently estimated that more than 10 million people in the world are living with Parkinson’s disease, the second most common neurodegenerative disorder after Alzheimer’s. That number is expected to swell up to 14 million by 2040 in what is being referred to as the Parkinson’s pandemic.
One of the key events in Parkinson's disease is the accumulation of a protein called alpha-synuclein inside neurons. That accumulation disrupts the normal functioning of the cells, giving rise to the symptoms of Parkinson’s and other disorders, and progresses into aggregates called Lewy bodies.
In a new study, researchers from two labs at EPFL have combined their expertise to explore how alpha-synuclein disrupts metabolic processes within neurons. The study is a truly interdisciplinary collaboration between the Bertarelli Platform for Gene Therapy of Bernard Schneider and the group of Anders Meibom at EPFL, with support from EPFL’s Bioelectron Microscopy Core Facility.
The researchers used cutting-edge imaging techniques, including an analytical instrument called NanoSIMS (Nanoscale Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry). NanoSIMS is an “ion microprobe” that combines high spatial resolution (50-150 nm), high-resolution mass spectrometry, and high analytical sensitivity, which allow it to produce sub-cellular maps of metabolic turnover with extreme sensitivity. Meibom’s lab at EPFL has famously used NanoSIMS for a number of ecological and geological studies.
In this study, the researchers combined NanoSIMS with stable isotope labeling, to visualize isotopic variations within tissues at high resolution, providing insights into the metabolic activity of individual cellular compartments and organelles. They combined this with Electron Microscopy to “see” more information from biological samples.
To model Parkinson's disease, the team used genetically modified rats that overexpressed human alpha-synuclein in one hemisphere of the brain, leaving the other healthy as a control. By comparing the neurons overexpressing alpha-synuclein to those in the control hemisphere, the scientists uncovered significant changes in the way carbon molecules are incorporated and processed within neurons.
One of the most remarkable findings was the effect of alpha-synuclein on the turnover of carbon within neurons. Neurons overexpressing alpha-synuclein showed a heightened overall turnover of macromolecules, suggesting that the accumulation of alpha-synuclein may lead to increased metabolic demands on these cells.
The study also found changes in the distribution of carbon between different cellular compartments, such as the nucleus and cytoplasm, which may be influenced by alpha-synuclein's interaction with DNA and histones.
The metabolic disruptions caused by alpha-synuclein also seem to affect specific organelles: Mitochondria, for example, showed abnormal carbon incorporation and turnover patterns, which agrees with previous studies showing that alpha-synuclein impairs mitochondrial function. Similarly, the Golgi apparatus – responsible for cellular trafficking and communication – exhibited metabolic defects that were likely caused by alpha-synuclein disrupting inter-organelle communication.
“This study shows the potential of the NanoSIMS technology to reveal metabolic changes in the brain, with unprecedented resolution, at the subcellular level,” says Bernard Schneider. “It hands us a tool to study early pathological changes occurring in vulnerable neurons as a consequence of alpha-synuclein accumulation, a mechanism directly linked to Parkinson’s disease.”
Other contributors
Universiteit Utrecht Department of Earth Sciences
University of Lausanne Center for Advanced Surface Analysis
Reference
Sofia Spataro, Bohumil Maco, Stéphane Escrig, Louise Jensen, Lubos Polerecky, Graham Knott, Anders Meibom, Bernard L. Schneider. Stable isotope labeling and ultra-high-resolution NanoSIMS imaging reveal alpha-synuclein-induced changes in neuronal metabolism in vivo. Acta Neuropathologica Communications 29 September 2023. DOI: 10.1186/s40478-023-01608-8
END
A new wearables study tracking over 25,000 people provides the best evidence yet that short bouts of incidental activity, the kind we do as part of daily living, could reduce risk of heart attack, stroke and even premature death – but the length of activity and intensity matters.
“From walking up the stairs to speedily mopping the floors; in recent years we’ve come to understand that it is not just structured exercise that is good for our health, but we know very little about how these short bouts of incidental activity translate to health benefits,” said the study’s senior author Professor Emmanuel Stamatakis from the University ...
Young people who are in higher education in England face a small increased risk of depression and anxiety, compared to their peers who are not attending higher education, finds a new study led by UCL researchers.
The research paper, published in The Lancet Public Health, is the first to find evidence of higher levels of depression and anxiety among higher education students compared with their peers.
The authors found that by age 25, the difference had disappeared between graduates and non-graduates.
Lead author Dr Gemma Lewis (UCL Psychiatry) said: “In recent years in the UK we have seen an increase in mental ...
September 28, 2023 – Recently popularized utility terrain vehicles (UTVs) with "side-by-side" passenger seating are associated with higher rates of severe hand injuries when compared to traditional all-terrain vehicles (ATVs), reports a study in the October issue of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery®, the official medical journal of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS). The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"Our study finds much higher rates of mutilating hand injuries and amputations associated with side-by-side UTVs, compared to ATVs," comments ASPS Member Surgeon Shaun D. Mendenhall, ...
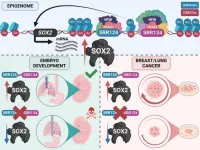
University of Toronto (U of T) researchers have found that cancer cells can enhance tumor growth by hijacking enhancer DNA normally used when tissues and organs are formed. The mechanism, called enhancer reprogramming, occurs in bladder, uterine, breast and lung cancer, and could cause these types of tumors to grow faster in patients.
Published in the journal Nucleic Acids Research, the results also pinpoint the role that specific proteins play in regulating the enhancer region which may lead to improved treatments for these cancer types.
Living cells, even cancer cells, follow instructions in the genome to turn genes on and off in different ...
The West’s electrical grid is a 136,000-mile patchwork of transmission lines connecting two Canadian provinces, 11 Western states and pieces of three others, serving 80 million people.
While it drives a vital and growing piece of the U.S. economy, this fragile network remains vulnerable to increasingly extreme weather and wildfire risks, according to Masood Parvania, an associate professor of electrical and computing engineering at the University of Utah’s John and Marcia Price College of Engineering.
“These ...
Key takeaways
Two-thirds of white Americans believe that Black Americans do not experience racism or racial inequities in health care.
UCLA psychologists exposed white study participants to the well-documented history of medical-related mistreatment of Black Americans.
Subsequently, white participants were more likely to adopt a new perspective and support policies aimed at reducing racial disparities in health care.
Being exposed to some of the many historical incidences of anti-Black racism in American health care can contribute to ...
Maximum Academic Press (MAP) is pleased to announce that 11 more journals including Circular Agricultural Systems, Food Innovation and Advances, Food Materials Research, Fruit Research, Grass Research, Medicinal Plant Biology, Ornamental Plant Research, Seed Biology, Technology in Horticulture, Tropical Plants and Vegetable Research have achieved a significant milestone by being indexed in the CABI (Centre for Agriculture and Biosciences International) database. Previously, Beverage Plant Research, Forestry Research and Studies in ...
Numerous studies have shown that leading a fulfilling and satisfying life may improve cognitive function by encouraging health-protective behaviors such as physical activity and reduced stress. Many of these studies assess this relationship from a population level, rather than among individuals.
But a closer look within the general population suggests that life satisfaction may not have a positive effect on all people, according to a new study led by Boston University School of Public Health researchers.
Published in the journal SSM – Mental Health, the ...
ANN ARBOR, Mich. – For some families, the year after childbirth may not only mean loads of diapers but stacks of unpaid medical bills as well.
Postpartum individuals are more likely to have medical debt than those who are pregnant, suggests a new Michigan Medicine led study that evaluated collections among a statewide commercially insured cohort of 14,560 pregnant people and 12,157 people in the postpartum period.
“Our findings suggest that current out-of-pocket costs before and after childbirth ...
Experimental researchers often find themselves of two minds when interacting with the public. On one side, researchers gather knowledge and test hypotheses based on participants’ responses. On the other side, they use their own knowledge and expertise to engage and educate the public about topics of public concern related to their science.
Abby Walker, associate professor of linguistics in the Department of English at Virginia Tech, and her collaborator secured a National Science Foundation ...