(Press-News.org) Using zebrafish as a model, investigators have determined a suitable combination of chemical compounds in which to store hearts, and potentially other organs, when frozen for extended periods of time before transplantation.
The work, which is published in The FASEB Journal, involved a variety of methods, including assays at multiple developmental stages, techniques for loading and unloading agents, and the use of viability scores to quantify organ function.
These methods allowed scientists to perform the largest and most comprehensive screen of cryoprotectant agents to determine their toxicity and efficiency at preserving complex organ systems during storage at -10°C. As a result, adult zebrafish hearts’ cardiac function was successfully preserved after 5 days of storage.
“Zebrafish are a powerful model system that have never been used in the context of solid organ preservation for transplantation, despite several advantages,” said corresponding author Shannon N. Tessier, PhD, of the Center for Engineering in Medicine and Surgery, Harvard Medical School. “We hope this research will encourage other in transplantation sciences to leverage this important model organism.”
URL: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1096/fj.202300076R
Additional Information
NOTE: The information contained in this release is protected by copyright. Please include journal attribution in all coverage. For more information or to obtain a PDF of any study, please contact: Sara Henning-Stout, newsroom@wiley.com.
About the Journal
The FASEB Journal publishes high quality and impactful multidisciplinary research covering biology and biomedical sciences at every level of organization: atomic, molecular, cell, tissue, organ, organismic, and population. The journal’s scope includes the spectrum of biological and biomedical sciences as well as interdisciplinary research cutting across multiple fields and extending in related areas.
About Wiley
Wiley is a knowledge company and a global leader in research, publishing, and knowledge solutions. Dedicated to the creation and application of knowledge, Wiley serves the world’s researchers, learners, innovators, and leaders, helping them achieve their goals and solve the world's most important challenges. For more than two centuries, Wiley has been delivering on its timeless mission to unlock human potential. Visit us at Wiley.com. Follow us on Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn and Instagram.
END
Researchers develop mixture of compounds to help preserve organs before transplantation
2023-10-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
A surprising way to disrupt sleep
2023-10-02
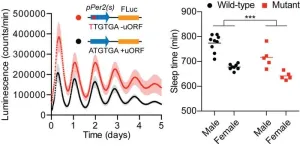
Osaka, Japan - Circadian rhythms, the internal biological clocks that regulate our daily activities, are essential for maintaining health and well-being. While the role of transcription in these rhythms is well-established, a new study sheds light on the critical importance of post-transcriptional processes. The research, titled “Circadian ribosome profiling reveals a role for the Period2 upstream open reading frame in sleep,” to be published in PNAS, redefines our understanding of how translation and post-transcriptional processes influence the body’s internal clock and its impact on sleep patterns.
Timing Is Everything: ...
To Eat or Not to Eat: Targeting autophagy to enhance memory immune responses
2023-10-02
Osaka, Japan – Memory B cells depend on autophagy for their survival, but the protein Rubicon is thought to hinder this process. Researchers from Osaka University have discovered a shorter isoform of Rubicon called RUBCN100, which enhances autophagy in B cells. Mice that lacked the longer isoform, RUBCN130, produced more memory B cells in a way that relied on autophagy. These findings provide further insight into the role of Rubicon in autophagy.
Autophagy is a mechanism that degrades and ...
Researchers find a cause of Parkinson’s disease
2023-10-02
Until recently, our understanding of Parkinson's disease has been quite limited, which has been apparent in the limited treatment options and management of this debilitating condition.
Our recent understanding has primarily revolved around the genetic factors responsible for familial cases, while the causative factors in the vast majority of patients remained unknown.
However, in a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen have unveiled new insights into the workings of the brain in Parkinson's patients. Leading the groundbreaking discovery is Professor Shohreh Issazadeh-Navikas.
“For the first time, we can show that mitochondria, ...
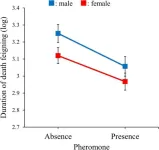
Pheromones influence death feigning behavior in beetles
2023-10-02
Predation is a driving force in the evolution of anti-predator strategies, and death feigning, characterized by immobility in response to threats, is a common defensive mechanism across various animal species. While this behavior can enhance an individual's survival prospects by reducing a predator's interest, it also carries costs, such as limited opportunities for feeding and reproduction. Recently, researchers from Okayama University, Japan, investigated how pheromones, important chemical signals that affect foraging and reproduction, might influence death-feigning behavior in the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum.
“Male beetles release an aggregation pheromone called ...
Genetics of attraction: mate choice in fruit flies
2023-10-02
Genetic quality or genetic compatibility? What do female fruit flies prioritize when mating? Researchers at the University of Zurich show that both factors are important at different stages of the reproductive process and that females use targeted strategies to optimize the fitness of their offspring.
Breeding female fruit flies face a difficult decision: do they mate with the male that has the best genes, or with the one whose genes best match their own? Evolutionary biologists from the University of Zurich and Concordia University have now investigated ...
FAU Engineering study employs deep learning to explain extreme events
2023-10-02
Identifying the underlying cause of extreme events such as floods, heavy downpours or tornados is immensely difficult and can take a concerted effort by scientists over several decades to arrive at feasible physical explanations.
Extreme events cause significant deviation from expected behavior and can dictate the overall outcome for a number of scientific problems and practical situations. For example, practical scenarios where a fundamental understanding of extreme events can be of vital importance include rogue waves in the ocean that could endanger ships and offshore structures or increasingly ...
New study uncovers potential treatment for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
2023-10-02
A breakthrough study, jointly led by Professor Jang Hyun Choi and Professor Sung Ho Park from the Department of Biological Sciences at UNIST has identified an important factor involved in the development of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) caused by obesity. The research team discovered that Thrap3, a protein associated with thyroid hormone receptors, plays a significant role in exacerbating NAFLD by inhibiting the activity of adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK), a key regulator of fat metabolism in the liver.
NAFLD encompasses various metabolic diseases such as fatty hepatitis and cirrhosis resulting from excessive fat accumulation. ...
Susan G. Komen® analysis shows many breast cancer patients struggle to afford basic needs: Housing, transportation, utilities
2023-10-02
Lower income breast cancer patients often struggle to afford life’s necessities such as housing, transportation and utilities due to direct and incidental costs related to their treatment, according to a new analysis by Susan G. Komen®, the world’s leading breast cancer organization. These top needs were identified by Susan G. Komen’s Patient Care Center, which provided nearly $9.1 million in grants to more than 16,000 breast cancer patients from April 1, 2022 to March 31, 2023, as part of Komen’s direct-to-patient ...
Dense measurement network revealed high level of PM2.5 in Punjab due to crop residue burning and its transport to Haryana and Delhi NCR
2023-10-02
A group of international collaborators led by the Research Institute for Humanity and Nature (RIHN) team performed the first quantitative study of air pollution in the north-western India region using 29 low-cost and reliable instruments, demonstrating the advantages of source region observations to link crop residue burning (CRB) and air pollution at local to regional scales.
Exposure to particulate matter less than 2.5 µm in diameter (popularly known as PM2.5) causes health hazards in cities and major emission regions of the world. Although the major sources ...
Next-generation printing: precise and direct, using optical vortices
2023-10-02
Osaka, Japan – Will printed photographs ever match the precision of a mirror's reflection? Even though the answer may still be no for a while, Osaka Metropolitan University scientists have made significant strides in precision printing with their innovative optical vortex laser-based technique that allows for the precise placement of minuscule droplets with micrometer-scale accuracy.
Inkjet technology is a well-known printing technique that emits microdroplets from a nozzle directly onto a surface. However, when the ink droplets are viscous, with high density, ...