(Press-News.org) HOUSTON (October 4, 2023) – Texas Children’s Hospital is proud to announce that its Adolescent Bariatric Surgery Program has received national accreditation from the Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery Accreditation and Quality Improvement Program (MBSAQIP).
Texas Children’s Hospital The Woodlands is the only Bariatric Surgery Center in the state of Texas that serves to an adolescent-only patient population with a multidisciplinary clinical staff who is certified to meet the surgical, medical and psychological needs of adolescent bariatric patients.
MBSAQIP, a joint program of the American College of Surgeons (ACS) and the American Society for Metabolic Bariatric Surgery (ASMBS), is dedicated to improving the quality and safety of surgical care for patients undergoing metabolic and bariatric procedures. MBSAQIP’s prestigious accreditation signifies that Texas Children’s Bariatric Surgery Program has met rigorous criteria for staffing, training, facility infrastructure, patient care pathways and surgical outcomes.
“We are so thrilled to have received accreditation from MBSAQIP,” said Dr. Shawn J. Stafford, Chief Surgical Officer at Texas Children’s Hospital The Woodlands. “This accreditation is a testament to the hard work and expertise of our multidisciplinary team who are committed to promoting the well-being, safety and lifelong health of our patients through effective, lasting weight loss.”
MBSAQIP accredits bariatric surgery centers in the United States and Canada that have undergone an independent, voluntary and rigorous peer evaluation in accordance with nationally recognized bariatric surgical standards. This accreditation promotes both uniform standard benchmarks and continuous quality improvement.
After applying for MBSAQIP Accreditation, centers undergo an extensive site visit by an experienced bariatric surgeon who reviews the center's structure, processes and clinical outcomes data. The center also participates in a national data registry that yields semiannual reports on the quality of its surgical outcomes and identifies opportunities for quality improvement.
“This prestigious recognition is truly an honor,” said Dr. J. Ruben Rodriguez, Medical Director of Pediatric Surgery and Associate Chief Surgical Officer at Texas Children’s Hospital The Woodlands. “MBSAQIP’s accreditation is a reflection of our commitment to providing exceptional, life-changing care and ensuring the highest standards in bariatric surgery.”
As an MBSAQIP accredited center, Texas Children’s Adolescent Bariatric Surgery Program has demonstrated a commitment to:
Providing a comprehensive, patient-centered approach to care.
Maintaining a skilled team of surgeons, nurses and medical professionals specializing in metabolic and bariatric surgery.
Offering state-of-the-art facilities and equipment to support safe and effective surgical procedures.
Adhering to strict quality improvement measures to enhance patient outcomes and satisfaction.
Participating in ongoing data collection and analysis to drive continuous improvement.
Since 2004, Texas Children’s has performed more than 200 weight-loss surgeries, putting the Bariatric Surgery Program on the national map and helping patients lose more than 50% of their excess weight.
About Texas Children’s Hospital
Texas Children’s, a nonprofit health care organization, is committed to creating a healthier future for children and women throughout the global community by leading in patient care, education and research. Consistently ranked as the best children’s hospital in Texas and among the top in the nation, Texas Children’s has garnered widespread recognition for its expertise and breakthroughs in pediatric and women’s health. The system includes the Texas Children’s Duncan NRI; the Feigin Tower for pediatric research; Texas Children’s Pavilion for Women, a comprehensive obstetrics/gynecology facility focusing on high-risk births; Texas Children’s Hospital West Campus, a community hospital in suburban West Houston; and Texas Children’s Hospital The Woodlands, the first hospital devoted to children’s care for communities north of Houston. The organization also created Texas Children’s Health Plan, the nation’s first HMO for children; Texas Children’s Pediatrics, the largest pediatric primary care network in the country; Texas Children’s Urgent Care clinics that specialize in after-hours care tailored specifically for children; and a global health program that s channeling care to children and women all over the world. Texas Children’s Hospital is affiliated with Baylor College of Medicine. For more information, visit www.texaschildrens.org.
END
Texas Children’s Bariatric Surgery Program receives prestigious national accreditation
2023-10-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Two-dimensional compounds can capture carbon from the air
2023-10-05
Some of the thinnest materials known to mankind may provide solutions to scientists in their quest to curb the effects of global warming.
Known as MXene and MBene compounds, these substances are only a few atoms thick, making them two-dimensional. Because of their large surface area, the materials have the potential to absorb carbon dioxide molecules from the atmosphere, which could help reduce the harmful effects of climate change by safely sequestering carbon dioxide.
In a paper published Oct. 4 in the journal Chem, UC Riverside professor Mihri Ozkan and her co-authors explain the potential of MXenes and MBenes in carbon capture technologies.
“In this review, ...
New type of tiny wasp comes with mysterious, cloud-like structures at ends of antennae
2023-10-05
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Fossil researchers have discovered a novel genus and species of tiny wasp with a mysterious, bulbous structure at the end of each antenna.
The female micro-wasp was described from 100-million-year-old Burmese amber in a study led by George Poinar Jr., who holds a courtesy appointment in the Oregon State University College of Science.
Poinar and Fernando Vega, an independent researcher based in Silver Spring, Maryland, have some ideas about the “clouds” on the ...
Tirzepatide is as effective at treating early-onset type 2 diabetes as diabetes diagnosed later in life
2023-10-05
Tirzepatide is as effective at treating early-onset type 2 diabetes (T2D), a more aggressive form of the condition that normally responds less well to treatment, as it is at treating T2D diagnosed later in life, new research being presented at the Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) in Hamburg, Germany (2-6 Oct) has found.
Tirzepatide belongs to a new class of drugs that mimic the effect of two hormones involved in blood sugar control and appetite suppression, ...
Commonly prescribed antibiotic, antipsychotic and prokinetic drugs are associated with a higher risk of sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) in people with type 2 diabetes, study finds
2023-10-05
New research being presented at the Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) in Hamburg, Germany (2-6 Oct) has identified a range of characteristics associated with a higher risk of sudden cardiac arrest in individuals with type 2 diabetes.
These include the some commonly prescribed antibiotic and antipsychotic drugs, prokinetics (drugs used to treat gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea and vomiting) and low fasting blood sugar.
Sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) is a leading cause of death. ...
Study reveals distinct illness trajectory in the years leading up to type 2 diabetes diagnosis
2023-10-05
New research presented at this year’s Annual Meeting of The European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD), Hamburg (2-6 Oct), reveals a marked increase in several common conditions in the years leading up to, and immediately prior to, type 2 diabetes diagnosis, suggesting considerably earlier diagnosis might be possible in some patients.
“These novel insights into the onset and natural progression of type 2 diabetes, suggest an early phase of inflammation-related disease activity long before any clinical diagnosis of type 2 diabetes is made”, says senior author Dr Adrian Heald from Manchester ...
Is lasting remission of type 2 diabetes feasible in the real-world setting?
2023-10-05
At this year’s Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) in Hamburg, Germany (2-6 Oct) experts will discuss if lasting remission from diabetes is feasible in the real-world setting.
Professor Roy Taylor of Newcastle University, Newcastle, UK, will be speaking in support of the motion
Professor Taylor will argue that through a series of studies in which people with type 2 diabetes were put on low calorie diets, he has shown that lasting remission of type 2 diabetes is indeed feasible in the real world.
He will begin ...
Second international consensus report - clinical translation of precision diabetes medicine
2023-10-05
Precision medicine is part of the logical evolution of contemporary evidence-based medicine that seeks to reduce errors and optimise outcomes when making medical decisions and health recommendations. Diabetes affects hundreds of millions of people worldwide, many of whom will develop life-threatening complications and die prematurely.
“Diabetes recommendations often focus on what works well for the average person. However, because diabetes is an incredibly heterogeneous disease, few people are Mr or Mrs “average” and one-size-fits-all ...
Wastewater surveillance research provides a 12-day lead time for RSV season: new study
2023-10-04
In a first-of-its-kind study, researchers using wastewater surveillance over conventional indicators have predicted the start of the annual respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) season 12 days early, providing more lead time for hospital preparedness and the timely initiation of RSV prevention therapy provided by the province for at risk-infants and young children.
Published in Frontiers in Public Health, the study is the first to describe the relationship between wastewater measurements and clinical data for RSV and to use near real-time wastewater measurements to accurately identify the start of the RSV season.
Working in close collaboration with CHEO Research Institute (RI) ...
Unmet health needs for HIV, hypertension and diabetes in rural South Africa
2023-10-04
The burden of non-communicable diseases like hypertension and diabetes is increasing globally, especially in low-income and middle-income countries where they occur alongside epidemics of communicable diseases like HIV. A large public health survey in South Africa led by Emily Wong, M.D., has assessed the multimorbidity health needs of individuals and communities in rural KwaZulu-Natal and established a framework to quantify met and unmet health needs for individuals living with infectious and non-communicable diseases. The study is published in The Lancet Global Health.
“Applying ...
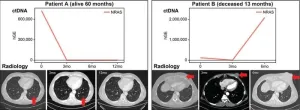
Blood-based biomarker may redefine the future treatment for advanced melanoma
2023-10-04
Circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) is emerging as a blood-based biomarker for many solid tumor types, including melanoma. A new study that assessed ctDNA in the blood of patients with BRAF wild-type (BRAF WT) stage III and IV melanoma concludes that measuring ctDNA may lead to alternative treatment options and better outcomes for these patients, report investigators in The Journal of Molecular Diagnostics, published by Elsevier.
For patients with BRAF WT stage III and IV melanoma, there is an urgent clinical need to identify prognostic biomarkers and biomarkers to predict treatment ...