(Press-News.org)
Osaka, Japan – As organizations work to reduce their energy consumption and associated carbon emissions, one area that remains to be optimized is indoor heating and cooling. In fact, HVAC – which stands for Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning – represents, on average, about 40% of a building’s total energy use. Methods that conserve electricity while still providing a comfortable indoor environment for workers could make a significant difference in the fight against climate change.
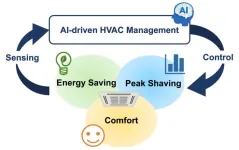
Now, researchers from Osaka University have demonstrated significant energy savings through the application of a new, AI-driven algorithm for controlling HVAC systems. This method does not require complex physics modelling, or even detailed previous knowledge about the building itself.
During cold weather, it is sometimes challenging for conventional sensor-based systems to determine when the heating should be shut off. This is due to thermal interference from lighting, equipment, or even the heat produced by the workers themselves. This can lead to the HVAC being activated when it should not be, wasting energy.
To overcome these obstacles, the researchers employed a control algorithm that worked to predict the thermodynamic response of the building based on data collected. This approach can be more effective than attempting to explicitly calculate the impact of the multitude of complex factors that might affect the temperature, such as insulation and heat generation. Thus, with enough information, ‘data driven’ approaches can often outperform even sophisticated models. Here, the HVAC control system was designed to ‘learn’ the symbolic relationships between the variables, including power consumption, based on a large dataset.
The algorithm was able to save energy while still allowing the building occupants to work in comfort. “Our autonomous system showed significant energy savings, of 30% or more for office buildings, by leveraging the predictive power of machine learning to optimize the times the HVAC should operate.” says lead author Dafang Zhao. “Importantly, the rooms were comfortably warm despite it being winter.”
The algorithm worked to minimize the total energy consumed, the difference between the actual and desired room temperature, and change in the rate of power output at peak demand. “Our system can be easily customized to prioritize energy conservation or temperature accuracy, depending on the needs of the situation,” adds senior author Ittetsu Taniguchi.
To collectively achieve the goal of a carbon-neutral economy, it is highly likely that corporations will need to be at the vanguard of innovation. The researchers note that their approach may enjoy rapid adoption during times of rising energy costs, which makes their findings good for both the environment as well as company viability.
###
The article, “Data-driven Online Energy Management Framework for HVAC Systems: an Experimental Study,” was published in Applied Energy at DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2023.121921
About Osaka University
Osaka University was founded in 1931 as one of the seven imperial universities of Japan and is now one of Japan's leading comprehensive universities with a broad disciplinary spectrum. This strength is coupled with a singular drive for innovation that extends throughout the scientific process, from fundamental research to the creation of applied technology with positive economic impacts. Its commitment to innovation has been recognized in Japan and around the world, being named Japan's most innovative university in 2015 (Reuters 2015 Top 100) and one of the most innovative institutions in the world in 2017 (Innovative Universities and the Nature Index Innovation 2017). Now, Osaka University is leveraging its role as a Designated National University Corporation selected by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to contribute to innovation for human welfare, sustainable development of society, and social transformation.
Website: https://resou.osaka-u.ac.jp/en
END
A new study conducted by researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center suggests that enhanced infection prevention and control (IPC) measures implemented to address the COVID-19 pandemic contributed to a significant decrease in many healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) and a reduction in respiratory viral infections (RVIs). The findings, published today in the American Journal of Infection Control (AJIC), provide some of the first evidence that strict pandemic-related IPC interventions reduced HAI rates among vulnerable patient populations.
“Previous, large-scale ...
New research by RMIT University and Northern Health has examined Australia’s Long COVID services, guidelines and public health information, compared with international standards.
The researchers found Australia lacking in several categories, including early investigation, accessibility and availability of trustworthy public health information, and adequate multidisciplinary Long COVID services to meet demand.
Dean of RMIT’s School of Health and Biomedical Sciences and co-author on the paper, Professor Catherine Itsiopoulos, warned that this problem will only worsen over time.
“Long ...
As Streptococcus A cases continue to be prevalent in Queensland and internationally, a new nasal vaccine could provide long-term protection from the deadly bacteria.
Associate Professor Manisha Pandey, Professor Michael Good, and their team from Griffith University’s Institute for Glycomics, are leading the development of a Strep A vaccine which is currently in Phase 1 clinical trials in Canada and quickly advancing to Phase 2 efficacy trials.
The team’s new preclinical research, recently published in Nature Communications, shows an experimental liposome-based vaccine approach incorporating a conserved M-protein epitope from Strep A and an immunostimulatory glycolipid (3D(6-acyl) ...
SAN ANTONIO, Oct. 5, 2023 – Researchers at Mays Cancer Center at The University of Texas Health Science at San Antonio (UT Health San Antonio) have identified protein markers that could signal for early development of metastatic lung cancer, providing possibilities for new treatment.
The findings already have led to a five-year, $1.6 million grant from the National Cancer Institute of the National Institutes of Health that will pave the way for a clinical trial next year for patients with advanced lung cancer. The research is detailed in a new article in Cell Reports, ...
London mayor Sadiq Khan’s efforts to expand the capital’s Ultra Low Emission Zone (ULEZ) as part of a push to reduce air pollution and improve health, is politically courageous and an example for mayors around the world, says the World Health Organization’s environment, climate change and health director, Maria Neira.
In an exclusive interview for The BMJ’s climate issue, Neira says she is tired of listening to politicians speak on climate change as if they didn't have the power to ...
Researchers have conducted trials using a software capable of detecting intricate details of emotions that remain hidden to the human eye.
The software, which uses an ‘artificial net’ to map key features of the face, can evaluate the intensities of multiple different facial expressions simultaneously.
The University of Bristol and Manchester Metropolitan University team worked with Bristol’s Children of the 90s study participants to see how well computational methods could capture authentic human emotions amidst everyday ...
The Keck School of Medicine of USC has received $2 million from the California Institute of Regenerative Medicine (CIRM) to further augment its newly launched cGMP Laboratory, a state-of-the-art facility designed to advance early-stage research into clinically viable cell and gene therapies. To expedite the translation of these therapies from the lab to the clinic, the facility needs advanced technological know-how, streamlined operations and strict protocols for developing and testing these products, all of which ...
HOUSTON (October 4, 2023) – Texas Children’s Hospital is proud to announce that its Adolescent Bariatric Surgery Program has received national accreditation from the Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery Accreditation and Quality Improvement Program (MBSAQIP).
Texas Children’s Hospital The Woodlands is the only Bariatric Surgery Center in the state of Texas that serves to an adolescent-only patient population with a multidisciplinary clinical staff who is certified to meet the surgical, medical and psychological needs of ...
Some of the thinnest materials known to mankind may provide solutions to scientists in their quest to curb the effects of global warming.
Known as MXene and MBene compounds, these substances are only a few atoms thick, making them two-dimensional. Because of their large surface area, the materials have the potential to absorb carbon dioxide molecules from the atmosphere, which could help reduce the harmful effects of climate change by safely sequestering carbon dioxide.
In a paper published Oct. 4 in the journal Chem, UC Riverside professor Mihri Ozkan and her co-authors explain the potential of MXenes and MBenes in carbon capture technologies.
“In this review, ...
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Fossil researchers have discovered a novel genus and species of tiny wasp with a mysterious, bulbous structure at the end of each antenna.
The female micro-wasp was described from 100-million-year-old Burmese amber in a study led by George Poinar Jr., who holds a courtesy appointment in the Oregon State University College of Science.
Poinar and Fernando Vega, an independent researcher based in Silver Spring, Maryland, have some ideas about the “clouds” on the ...