(Press-News.org) More than 10,000 Pre-Columbian archaeological sites likely rest undiscovered throughout the Amazon basin, estimates a new study. The findings, derived from remote sensing data and predictive spatial modeling, address questions about the influence of pre-Columbian societies on the Amazon region. “The massive extent of archaeological sites and widespread human-modified forests across Amazonia is critically important for establishing an accurate understanding of interactions between human societies, Amazonian forests, and Earth’s climate,” write the authors. Indigenous societies have called the Amazon basin home for more than 12,000 years, creating ancient earthwork structures and domesticated landscapes that have had long-lasting effects on modern forest composition. However, the size and scale of Amazon settlement and landscape transformation are poorly understood – sites are remote and often obscured by dense vegetation. As such, there has never been a comprehensive survey of pre-Columbian sites across the Amazon basin. Airborne LIDAR (light detection and ranging), a remote sensing technique that can map small changes in topography on the ground surface beneath the forest canopy, has been used to discover many previously unknown pre-Columbian structures and earthworks in heavily forested sites throughout Central and South America. Here, Vinicius Peripato and colleagues searched 5,315 square kilometers of LIDAR survey data and discovered 24 unreported human-made earthworks, including fortified villages, defensive and ceremonial structures, mountaintop settlements, and other geoglyphs, in regions across the Amazon basin. However, the LIDAR survey data covered only 0.08% of the total area of Amazonia. To better understand where and how many undocumented pre-Columbian sites might occur, Peripato et al. combined the data from their small basin-wide survey, as well as data on other previously identified sites with a predictive spatial distribution model. According to the model, between 10,272 and 23,648 large-scale pre-Columbian structures remain to be discovered, particularly in southwestern Amazonia. What’s more, the authors identified relationships between the predicted probability of earthworks and the occurrence and abundance of domesticated tree species and found significant association between the two, suggesting that active pre-Columbian Indigenous forest management practices have long shaped the ecology of modern forests across Amazonia. “Amazonian forests clearly merit protection not only for their ecological and environmental value but also for their high archaeological, social, and biocultural value, which can teach modern society how to sustainably manage its natural resources,” write Peripato et al.
END
More than 10,000 pre-Columbian earthworks remain hidden throughout Amazonian forests
2023-10-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New, independent ages confirm antiquity of ancient human footprints at White Sands
2023-10-05
New radiocarbon (14C) and optically simulated luminescence ages have confirmed the controversial antiquity of the ancient human footprints discovered in White Sands National Park, and reported in a study in 2021. Addressing the widespread criticism of their previous study, researchers report that the independent ages from multiple resolved sources conclusively show that the footprints were left behind between roughly 23,000 and 20,000 years ago, demonstrating that humans were present in southern North America during the Last Glacial ...
Special Issue: Ancient DNA
2023-10-05
In this Special Issue of Science, three Reviews highlight how recent advances in the field of ancient DNA have greatly advanced our understanding of the evolutionary history of many plants and animals, including our own species. “This special issue examines the changing landscape of how ancient DNA (aDNA) is studied today, including previously untapped sources, improvements in technology, and ethical challenges, and what we’ve learned about ourselves though ancient DNA,” write Corinne Simonti and Madeleine ...
What are the risks of radioactive wastewater release – the next of which is October 5th – from Fukushima Daiichi nuclear plant?
2023-10-05
Wastewater release from the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear plant in Japan is expected to have negligible effects on people and the ocean, Jim Smith and colleagues report in a Perspective. The planned releases of radioactive wastewater, 350 million gallons of which has been stored at the site since the 2011 earthquake and tsunami that triggered the Fukushima plant’s meltdown, began in August 2023 and are expected to continue for perhaps the next 30 years. The second release is scheduled to start on October 5th. While the scheduled releases have sparked international concern, Smith et al. discuss the science behind the risks and ...
Discovery made about Fischer Tropsch process could help improve fuel production
2023-10-05
A fundamental discovery about the Fischer Tropsch process, a catalytic reaction used in industry to convert coal, natural gas or biomass to liquid fuels, could someday allow for more efficient fuel production.
Washington State University researchers discovered previously unknown self-sustained oscillations in the Fischer Tropsch process. They found that unlike many catalytic reactions which have one steady state, this reaction periodically moves back and forth from a high to a low activity state. The discovery, reported in Science, means that these well-controlled oscillatory states might be used in the future to enhance the reaction rate and the yields of desired ...
New discovery may ‘unlock’ the future of infectious disease and cancer treatment
2023-10-05
University of Birmingham News Release
STRICTLY EMBARGOED UNTIL 14.00 Thursday 5th October ET 2023/ 19.00 Thursday 5th October UK 2023
Researchers have identified a ‘guard mechanism’ for a protein which attacks microbes in infected cells, opening the possibility of new treatments for Toxoplasma, Chlamydia, Tuberculosis and even cancer.
A study, led by the University of Birmingham and published today (5th October) in Science has discovered the lock and key mechanism that controls the attack protein GPB1. GBP1 is activated during ...
Study shows prior exposure to common virus shields against birth defects and miscarriage
2023-10-05
Researchers at Tulane University have shown for the first time that mothers are much less likely to transmit a common virus known to cause miscarriages and birth defects if they are exposed to the virus prior to becoming pregnant. The study marks a significant step toward the development of a vaccine that could protect mothers and their babies.
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) is a common herpesvirus that most women contract unknowingly before reaching child-bearing age. It's usually harmless except during pregnancy when, if passed on to the developing fetus, it is a leading cause ...
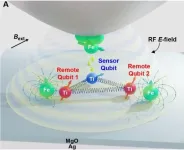
A new qubit platform is created atom by atom
2023-10-05
Seoul, Korea - Researchers at the IBS Center for Quantum Nanoscience (QNS) at Ewha Womans University have accomplished a groundbreaking step forward in quantum information science. In partnership with teams from Japan, Spain, and the US, they created a novel electron-spin qubit platform, assembled atom-by-atom on a surface. This breakthrough was published in the journal Science on 2023/10/06.
Unlike previous atomic quantum devices on surfaces where only a single qubit could be controlled, the researchers at QNS successfully demonstrated the ability to control multiple qubits simultaneously, enabling the application of single-, two-, and three-qubit gates.
Qubits, ...
Brain is ‘rewired’ during pregnancy to prepare for motherhood
2023-10-05
Francis Crick Institute press release
Under strict embargo: 19:00hrs BST Thursday 5 October 2023
Peer reviewed
Experimental study
Animals
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute have shown that pregnancy hormones ‘rewire’ the brain to prepare mice for motherhood.
Their findings, published today in Science, show that both oestrogen and progesterone act on a small population of neurons in the brain to switch on parental behaviour even before offspring arrive. These adaptations resulted in stronger and more selective responses to pups.
It is well known that while virgin female rodents do not show much interaction with pups, ...
Vulnerability to different COVID-19 mutations depends on previous infections and vaccination, study suggests
2023-10-05
A person’s immune response to variants of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, depends on their previous exposure – and differences in the focus of immune responses will help scientists understand how to optimise vaccines in the future to provide broad protection.
A new study has found that people differ in how vulnerable they are to different mutations in emerging variants of SARS-CoV-2.
This is because the variant of SARS-CoV-2 a person was first exposed to determines how well their immune system responds to different parts of the virus, and how protected they are against other variants.
It also means that the same COVID-19 ...
The end of genes: routine test reveals unique divergence in genetic code
2023-10-05
Scientists testing a new method of sequencing single cells have unexpectedly changed our understanding of the rules of genetics.
The genome of a protist has revealed a seemingly unique divergence in the DNA code signalling the end of a gene, suggesting the need for further research to better understand this group of diverse organisms.
Dr Jamie McGowan, a postdoctoral scientist at the Earlham Institute, analysed the genome sequence of a microscopic organism - a protist – isolated from a freshwater pond at Oxford University Parks.
The work was intended to test a DNA ...